HHS/ACF/OPRE Head Start Classroom-based Approaches and Resources for Emotion and Social skill promotion (CARES) project: Impact and Implementation Studies- Follow-up Lead Teacher Self-Report Survey
HHS/ACF/OPRE Head Start Classroom-based Approaches and Resources for Emotion and Social skill promotion (CARES) project: Impact and Implementation Studies
OMB CARES 2nd Package_Appendix A.2_Follow-up Lead Teacher Self-Report Survey
HHS/ACF/OPRE Head Start Classroom-based Approaches and Resources for Emotion and Social skill promotion (CARES) project: Impact and Implementation Studies- Follow-up Lead Teacher Self-Report Survey
OMB: 0970-0364
Appendix A.2: Head Start CARES Follow-up Lead Teacher Self-Report Survey
 Updated:
January 27, 2009
Updated:
January 27, 2009
FOLLOW-UP TEACHER SELF-REPORT SURVEY FOR
HEAD START CARES
TABLE OF CONTENTS
IMPACT MEASURES:
4 Section A – Demographic Characteristics
Questions are for matching purposes only
5 Section B – Structural Characteristics of the Classroom
6 Section C – Emotion-Related Parenting Styles Self-Test
Hakim-Larson, Parker, Lee, Goodwin, & Voelker (2006)
Shortened Dismissing/Disapproving and Emotion-Coaching subscales (5 items each) based on a recent factor analysis by Hakim-Larson.
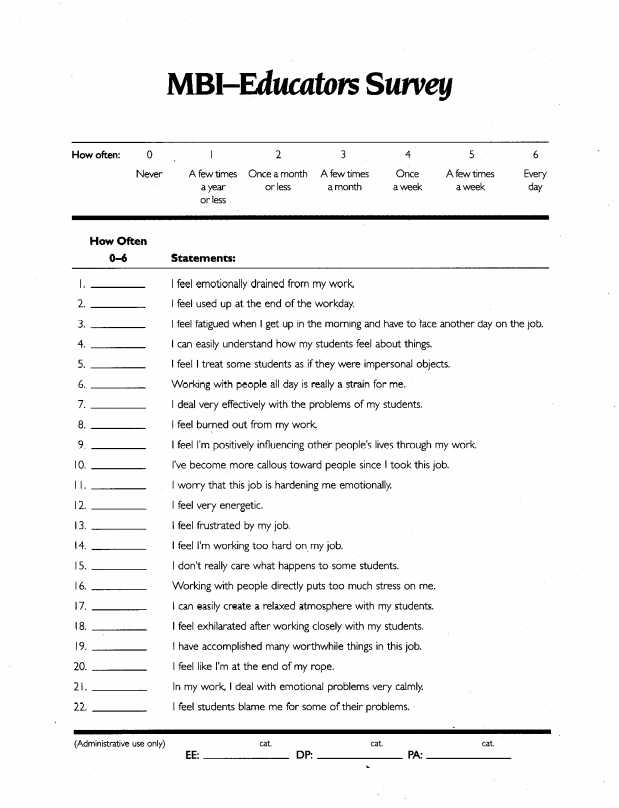
7 Section D – Maslach Burnout Inventory – Educators Survey
Maslach, Jackson, & Leiter (1986)
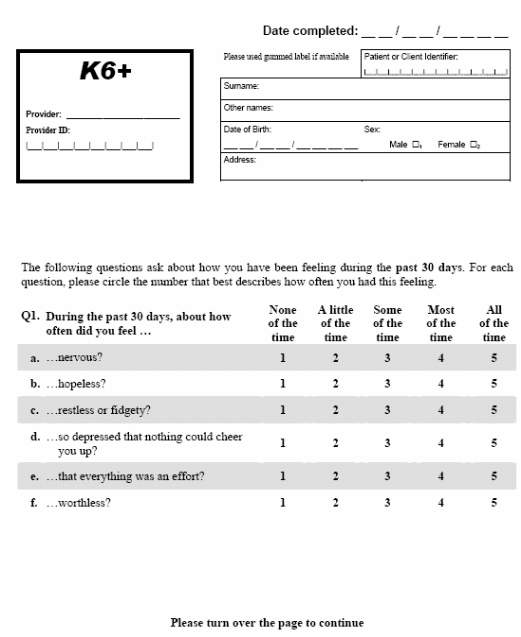
8 Section E – K-6 Kessler Psychological Distress Scale
Kessler, Andrews & Colpe (2002)
IMPLEMENTATION MEASURES:
Questions in sections G through J were developed based on implementation research (e.g., Durlak & DuPre, 2008; Han & Weiss, 2005; Ialongo et al., 1999; Lochman et al., in press)
9 Section F – Views on social-emotional development – ALL teachers
10 Section G – Social-emotional-related classroom practices – ALL teachers
11 Section H – Working with your coach – Program model teachers only
Some items are from PATHS to PAX
13 Section I – Perceptions of program model – Program model teachers only
14 Section J – Organizational Climate: Cohesion – ALL teachers
From TCU Organizational Readiness for Change measure (Lehman, Greener, & Simpson, 2002)
15 Section K – Questions about past training and professional development – ALL teachers
Questions developed by Lewin
17 Section L – Wehby Teacher-Consultant Alliance Scale – ALL teachers
Adapted from PATHS measure of teacher-coach relationship
Adapted for teacher-teaching assistant
This measure is currently proposed to capture facets of the teacher-teaching assistant relationship.
18 Section M – Supervisor monitoring and support – Program teachers only
Questions developed by Lewin
Section A – Demographic Characteristics
To be completed by the Lead Teacher
Date: __ __ /__ __ / 2009
School/Center Name: _______________________________________
Teacher Name: ______________ _____________________________________
First Last
What is your date of birth? ______ / ______ / 19_____
Section B – Structural Characteristics of the Classroom
Today’s date: _____ / _____ / __________
Teacher name: ________________________________________
Head Start Center: ___________________________________
Class: _______________
Room: _______________
Average number of children absent on any given day: _______________
Average number of children late on any given day: _______________
Number of students today: __________
Names of other teachers/teaching assistants in the classroom on any given day (and circle one):
________________________________________ Teacher / Teaching Assistant / Other
________________________________________ Teacher / Teaching Assistant / Other
________________________________________ Teacher / Teaching Assistant / Other
________________________________________ Teacher / Teaching Assistant / Other
Section C – Emotion-Related Parenting Styles Self-Test
When my child is acting sad, he turns into a real brat.
Children often act sad to get their way.
I don’t mind dealing with a child’s sadness, so long as it doesn’t last too long.
When my child is sad, I try to help the child explore what is making him sad.
When my child is sad, we sit down to talk over the sadness.
When my child is sad, I try to help him figure out why the feeling is there.
When she gets sad, I warn her about not developing a bad character.
When my child is angry, it’s time to solve a problem.
When my child gets angry, my goal is to get him to stop.
It’s important to help the child find out what caused the child’s anger.
Factor 1: Dismissing/Disapproving: Items 1,2,3,7,9
Factor 2: Emotion Coaching: Items 4,5,6,8,10
The Likert scale ranges from 1 (always false) to 5 (always true).
Section D – Maslach Burnout Inventory – Educators Survey
Section E – K-6 Kessler Psychological Distress Scale
Section F – Views on social-emotional development – ALL teachers
Before entering kindergarten, there are academic and social-emotional milestones that children should be able to master.
Examples of academic skills include: can recite ABCs, knows all the letters in his/her first name, can recognize basic shapes and colors, and can count to 10.
Examples of social-emotional skills include: plays nicely with other same-aged children, follows simple directions given by an adult, stays in seat when appropriate, and can wait his/her turn and share.
Please indicate which of the following options best represents your opinion by filling in the appropriate circle.
Would you say:
О I value children’s academic readiness for school a lot more than I value children’s social-emotional readiness for school.
О I value children’s academic readiness for school a little more than I value children’s social-emotional readiness for school.
О I value children’s academic readiness for school as much as I value children’s social-emotional readiness for school.
О I value children’s academic readiness for school a little less than I value children’s social-emotional readiness for school.
О I value children’s academic readiness for school a lot less than I value children’s social-emotional readiness for school.
Section G – Social-emotional-related classroom practices – ALL teachers
How often do you implement the following social-emotional practices?
|
Very rarely or never |
A few times a month |
Once a week |
A few times per week |
Once a day |
Several times a day |
Establish clear expectations of classroom behavior |
□ |
□ |
□ |
□ |
□ |
□ |
Reiterates rules and routines |
□ |
□ |
□ |
□ |
□ |
□ |
Use clear commands and consistently set limits |
□ |
□ |
□ |
□ |
□ |
□ |
Support children’s positive behavior (e.g., support prosocial interaction such as cooperation play) |
□ |
□ |
□ |
□ |
□ |
□ |
Emotion coaching children (i.e., helping children recognize, label, and deal with their feelings) |
□ |
□ |
□ |
□ |
□ |
□ |
Help children with their social problem-solving skills (e.g., helping children with their ability to communicate or “dialogue” their problems to peers) |
□ |
□ |
□ |
□ |
□ |
□ |
Help children with their self-regulation skills (e.g., self-control, thinking before acting) |
□ |
□ |
□ |
□ |
□ |
□ |
Offer reward structures |
□ |
□ |
□ |
□ |
□ |
□ |
Scaffold children’s learning |
□ |
□ |
□ |
□ |
□ |
□ |
Assist children in understanding various social roles (through make-believe play) |
□ |
□ |
□ |
□ |
□ |
□ |
Foster child planning/organizing skills (e.g., encourage planful, self-directed learning) |
□ |
□ |
□ |
□ |
□ |
□ |
Other (please describe: ) |
□ |
□ |
□ |
□ |
□ |
□ |
Section H – Working with your coach – Program teachers only
Overall, how easy was the coach to work with?
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
Very Difficult |
Somewhat Difficult |
Somewhat Easy |
Very Easy |
Please indicate how frequently your coach displays the following behaviors.
|
Never |
Seldom |
Sometimes |
Often |
Always |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Please indicate how often you feel this way about your coach.
|
Never |
Seldom |
Sometimes |
Often |
Always |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Please indicate how often you feel this way about the coaching sessions.
|
Never |
Seldom |
Sometimes |
Often |
Always |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
How much does the quality of your relationship with your coach affect how you implement <program model> in your classroom?
-
1
2
3
4
A lot
Somewhat
Very little
Not at all
Section I – Perceptions of Program Model – Program teachers only
For each item, check the box that best represents your views.
|
Very well |
Pretty well |
Somewhat |
Not at all well |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Overall, would you say it has been easy or difficult to implement <program model>?
1 |
2 |
4 |
5 |
Very difficult |
Somewhat difficult |
Somewhat easy |
Very easy |
How confident are you in your ability to implement <program model>?
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
Not at all confident |
Somewhat confident |
Pretty confident |
Very confident |
Overall, how effective do you think <program model> has been?
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
Not at all effective |
Somewhat effective |
Pretty effective |
Very effective |
Section J – Organizational Climate: Cohesion – ALL teachers
![]()
How strongly do you agree or disagree
with each of the following statements?
Staff here all get along very well. …………….… ○ ○ ○ ○ ○
There is too much friction among staff members. ○ ○ ○ ○ ○
The staff here work together effectively as a team. ○ ○ ○ ○ ○
Staff here are always quick to help one another
when needed. …………………………………… ○ ○ ○ ○ ○
Mutual trust and cooperation among staff here
are strong………………………………………….. ○ ○ ○ ○ ○
Some staff members do not do their fair
share of work…………………………………….. ○ ○ ○ ○ ○
Section K – Questions about past training and professional development – ALL teachers
(ALL teachers): Within the last year, how many professional development days did you use? _____
(Program model teachers): How many of these days were used for <program model>? ____
(Control teachers): Within the last year, have you had training in:
(Program model teachers): Not including the training you received in <program model>, in the last year, have you had training in:
|
No |
Yes |
If yes, when? |
If yes, number of hours? |
a. how to foster social behavior and emotional skills in preschoolers? |
|
|
|
|
b. classroom management?
|
|
|
|
|
c. children’s attention or self-regulation skills? |
|
|
|
|
d. children’s early literacy |
|
|
|
|
e. child health |
|
|
|
|
f. other (_________________________) |
|
|
|
|
(ALL teachers): In the last year, have you had training in the following curricula:
|
No |
Yes |
If yes, when? |
If yes, number of hours? |
Al’s Pals |
|
|
|
|
As I am Program |
|
|
|
|
Behavior Modeling Curriculum |
|
|
|
|
Chicago School Readiness Project |
|
|
|
|
COMPASS |
|
|
|
|
Conscious Discipline |
|
|
|
|
CSEFEL (The Center on the Social and Emotional Foundations for Early Learning) |
|
|
|
|
Denham’s Teacher Training Intervention |
|
|
|
|
Emotions Course |
|
|
|
|
FACET |
|
|
|
|
Foundations of Learning |
|
|
|
|
Functional Assessment |
|
|
|
|
Gillespie Modeling Program |
|
|
|
|
Guralnick’s Intervention |
|
|
|
|
Head Start REDI |
|
|
|
|
Incredible Years Dinosaur School |
|
|
|
|
Incredible Years Parenting Program |
|
|
|
|
Incredible Years Teacher Training Program (Remove for program teachers) |
|
|
|
|
Positive Behavior Support |
|
|
|
|
Preschool PATHS (Remove for program teachers) |
|
|
|
|
Project STAR |
|
|
|
|
Resilient Peer Treatment |
|
|
|
|
Second Step |
|
|
|
|
Tools of the Mind (Remove for program teachers) |
|
|
|
|
Other (please specify: ) |
|
|
|
|
Section L – Wehby Teacher-Consultant Alliance Scale (adapted) – ALL teachers
For each question, please fill in the circle that best represents your experience with the teacher or teaching assistant with whom you have been working.
|
|
Never |
Seldom |
Sometimes |
Often |
Always |
1. |
The teaching assistant and I agree on what the most important goals for the program are. |
О |
О |
О |
О |
О |
2. |
I feel confident of the teaching assistant’s ability to help implement the program. |
О |
О |
О |
О |
О |
3. |
The teaching assistant and I trust one another. |
О |
О |
О |
О |
О |
4. |
The teaching assistant and I are working together collaboratively to improve the effectiveness of the program in the classroom. |
О |
О |
О |
О |
О |
5. |
The teaching assistant followed through with commitments and responsibilities. |
О |
О |
О |
О |
О |
6. |
Overall, the teaching assistant has shown a sincere desire to understand and improve the implementation of the program model. |
О |
О |
О |
О |
О |
Section M – Supervisor monitoring and support - Program teachers only
Relative to the other requirements of your Head Start program, what priority does your supervisor place on using <program model>?
-
1
2
3
4
Very low priority
Somewhat low priority
Somewhat high priority
Very high priority
For each of the following, please fill in the circle that best represents your experience with your supervisor.
-
Never
Seldom
Sometimes
Often
Always
a.
My supervisor has clear expectations regarding my implementation of <program model>.
О
О
О
О
О
b.
My supervisor asks me what help/resources I need to implement <program model>.
О
О
О
О
О
c.
My supervisor monitors how much time I spend implementing <program model>.
О
О
О
О
О
d.
My supervisor rewards me for using <program model> in my classroom.
О
О
О
О
О
| File Type | application/msword |
| Author | Matthew Kim |
| Last Modified By | Ximena Portilla |
| File Modified | 2009-02-02 |
| File Created | 2008-12-23 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy