0702-0127_ssa_11.25.2024
0702-0127_SSA_11.25.2024.docx
Automated Biometric Identification System (ABIS)
OMB: 0702-0127
SUPPORTING STATEMENT - PART A
Automated Biometric Identification System (ABIS)
OMB Control Number: 0702-0127
Summary of Changes from Previously Approved Collection
|
Need for the Information Collection
In a 13 January 2012 DoD Memorandum [OSD 14940-11], the Deputy Secretary of Defense (DSD) authorized all Combatant Commanders and Military Components to employ DoD biometric capabilities across the full range of military operations unless otherwise prohibited by law or agreement. The Department of Defense Automated Biometric Identification System (DoD ABIS)) is an authoritative biometrics data repository that processes, matches, and stores biometric identity information data, collected by global U.S. forces during the course of military operations. Biometric data may also be collected for use in field identification and recovery of persons, or their physical remains, who have been captured, detained, missing, prisoners of war (POW), or personnel recovered from hostile control. The biometric data collected in accordance with these policies, stored as approved by the Records Retention Schedule, supports military operations including, but not limited to, counterterrorism and installation base access.
Additional authorities to operate and maintain DoD ABIS are derived from:
Section 112 of Public Law (Pub. L.) 106-246, Emergency Supplemental Act of 2000
Title 5, United States Code (U.S.C.), section 552a (Privacy Act of 1974), as amended
National Security Presidential Directive (NSPD)-59/HSPD-24, Biometrics for Identification and Screening to Enhance National Security
National Security Presidential Memorandum (NSPM) 7, Integration, Sharing, and Use of National Security Threat Actor Information to Protect Americans
DoD Directive (DoDD) 5200.27 (Acquisition of Information Concerning Persons and Organizations not Affiliated with the Department of Defense), 7 January 1980
DoDD 8521.01E (DoD Biometrics), incorporating change 2, 15 October 2018
DoD Instruction (DoDI) 5400.11 (DoD Privacy and Civil Liberties Program), incorporating change 1, 8 December 2020
DoDD 5205.15E (DoD Forensics Enterprise (DFE)), incorporating change 2, 15 October 2018
DoDI 8320.02 (Sharing Data, Information, and Information Technology (IT) Services in the Department of Defense), incorporating change 1, effective 24 June 2020
Army Regulation (AR) 10–90 (Department of Defense Executive Agent Responsibilities of the Secretary of the Army), 9 February 2018
Use of the Information
The information processed by DoD ABIS is collected by DoD military personnel worldwide across the full range of military operations for DoD warfighting, intelligence, law enforcement, security, force protection, base access, homeland defense, counterterrorism, business enterprise purposes, and in information environment mission areas. Records collected by DoD military personnel using hand-held biometric collection devices include biometric information, such as images, photos, and templates of biological (anatomical and physiological) and/or behavioral characteristics that can be used for automated recognition, including, fingerprints, palm prints, facial images, iris images, DNA, and voice samples. Biographic information (such as name, date of birth, place of birth, height, weight, eye color, hair color, race, etc.) and contextual information (i.e. organization, telephone number, office symbol, security clearance, etc.) is also collected by the DoD military personnel during the enrollment process. This information can be collected through questioning by DoD military personnel or by viewing the information from a document bearing the identifying information (such as an ID card). DoD ABIS also includes identity-related information and data (biometric, biographic, behavioral, and contextual data) from individuals collected and shared from interagency and foreign partners’ data repositories.
The information collected and processed by DoD ABIS is shared, accessed, and leveraged by DoD partners, U.S. Government inter-agencies and departmental stakeholders (such as the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), Department of Homeland Security (DHS), and Office of the Director of National Intelligence (ODNI)), and approved multi-national partners for intelligence, counterterrorism, military force protection, national security, and law enforcement purposes. DoD provides collected and processed information to the FBI/Terrorist Screening Center (TSC) to place individuals on National Watchlists. Required biometric fields for every record include name, ten (10) fingerprints, and two (2) iris scans. All other data fields in DoD ABIS, such as Social Security Number (SSN), are optional and vary based on each record and situation.
For possible biometric data fields collected from respondent(s), reference the mandated version of the “DoD Electronic Biometric Transmission Specification (EBTS)” (Version 4.1, April 2019) in the DoD IT Standards Registry (DISR). In most cases, numerous biometric data fields are not completed due to limited information at the time and/or the expediency of operational collection activity. Different types of data enrollments result in various data field entries. In sum, record types, modalities, and other contextual and biographical information are binned and divided into specific record type categories and are defined in more detail in accordance with American National Standards Institute/National Institute of Standards and Technology Information Technology Laboratory (ANSI/NIST-ITL) standards.
Use of Information Technology
DoD ABIS is an authoritative biometrics data repository that uses software applications to: process, match, and store biometrics modalities (i.e., fingerprints, palm prints, iris scans, and facial recognition data) from collection assets across the globe; update the biometric database repository with new biometrics data; produce biometrics match results (against stored data); share responses among approved DOD, interagency, and multi-national partners, in accordance with applicable law and policy; and provide tools to monitor the health and status of the system.
DoD ABIS biometric data submissions and responses are nearly 100% (>99%) electronic and automated. There are a small number of exceptions for respondents who cannot provide electronic records or records that require manual input. Manual processes are constantly reviewed to determine if they can be automated. For biometric data submissions that are unable to produce a match using automated processes, biometric examiners (i.e., subject matter experts) use DoD ABIS workstations with specialized software to attempt to manually match the respective submissions.
Non-Duplication
The information obtained through this collection is unique and is not already available for use or adaptation from another cleared source. As a biometric search system, one of the primary functions of DoD ABIS is to de-duplicate records. All biometric submissions are searched and queried against previous biometric submissions with any positive matches, consolidated into one record, with appropriate markers denoting each record in the set.
Burden on Small Business
This information collection does not impose a significant economic impact on a substantial number of small businesses or entities.
Less Frequent Collection
Without this collection, matching, and sharing of biometric and associated contextual data there would be significant implications to national security and the force protection of our military forces deployed abroad.
Paperwork Reduction Act and Other Guidelines
This collection of information does not require collection to be conducted in a manner inconsistent with the guidelines delineated in 5 CFR 1320.5(d)(2).
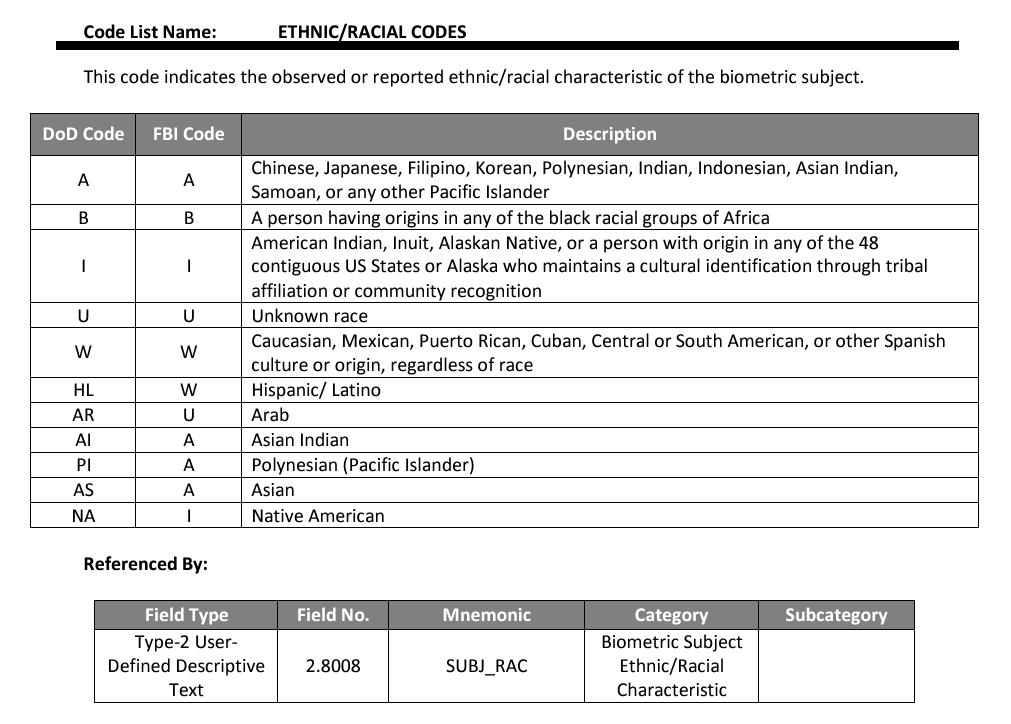
Race and ethnicity data exists in over 13 million files within DoD ABIS and is still collected as part of non-sensitive personally identifiable information to align with federal standards. Race/Ethnicity is potential field that may be collected at the point of an encounter with an individual (for example: an encounter on the battlefield or an individual requesting access at a US base point of entry). These fields can either be answered directly from the individual or, if no answer is given, may be determined by the US military member by observation. Frequently, this field is answered as “U” (unknown race). Race and ethnicity information in DoD ABIS has historically been a single character field under the EBTS 2.025 standards. With the update to EBTS 4.1 in 2019, the 2.025 standard was reclassified as a legacy data field, and a new data field with new options was created (see below). DoD EBTS modified the existing ethnic/racial data enumerations to better recognize and differentiate the different ethnic/racial groups. This arose from the community determining that the current ethnic racial classifications as flawed. Ethnic/racial data will continue to be scrutinized for improvements and will be the subject of future DoD EBTS updates, particularly in light of the new guidelines in OMB's revised Statistical Policy Directive No. 15.
Consultation and Public Comments
Part A: PUBLIC NOTICE
A 60-Day Federal Register Notice (FRN) for the collection published on Monday, July 15, 2024. The 60-Day FRN citation is 89 FR 57395.
4 comments were received at Regulations.gov. However, none of the comments were determined to be relevant to the information collection.
A 30-Day Federal Register Notice for the collection published on Friday, November 22, 2024. The 30-Day FRN citation is 89 FR 92665.
Part B: CONSULTATION
No additional consultation apart from soliciting public comments through the Federal Register was conducted for this submission.
Gifts or Payment
No payments or gifts are being offered to respondents as an incentive to participate in the collection.
Confidentiality
Pursuant with The Privacy Act, data will be protected, and respondents will be notified to the extent permitted by law, regulation, policies, directives, and all other applicable DoD authorities. A Privacy Act Statement is included in the ICR package for OMB’s review. Respondents that have voluntarily given biometrics are notified of the Privacy Act Statement at that time.
The applicable SORN (A0025-2 PMG (DFBA), Defense Biometric Identification Records System) can be accessed at: https://dpcld.defense.gov/Privacy/SORNsIndex/DOD-wide-SORN-Article-View/Article/581425/a0025-2-pmg-dfba-dod/
Per OMB Memo M-03-22, a Privacy Impact Assessment (PIA) is not required because DoD ABIS is a national security system as defined at 40 U.S.C. 11103 and exempt from the definition of information technology (see section 202(i) of the E-Government Act).
In accordance with the Federal Records Act, the Records Retention Schedule: DoD ABIS has received approval for its disposition schedule: destroy one hundred and ten (110) year(s) after the cutoff or when no longer needed for military operations or DoD business functions occurs, whichever is later.
Sensitive Questions
Social Security Number (SSN) is a potential data field in DoD ABIS but is optional and varied based on each record and situation. Pursuant to DoDI 1000.30, The Social Security Number Justification Memo is currently being updated with Army and DoD Privacy offices and the draft document is included in the package.
Respondent Burden and its Labor Costs
Part A: ESTIMATION OF RESPONDENT BURDEN
Collection Instrument(s)
DoD ABIS
Number of Responses Per Respondent: 1
Number of Total Annual Responses: 1,430,000
Response Time: 7 minutes (.117 hours)
Respondent Burden Hours: 166,833.33 hours
Total Submission Burden
Total Number of Respondents: 1,430,000
Total Number of Annual Responses: 1,430,000
Total Respondent Burden Hours: 166,833 hours
Part B: LABOR COST OF RESPONDENT BURDEN
Collection Instrument(s)
DoD ABIS
Number of Total Annual Responses: 1,430,000
Response Time: 7 minutes
Respondent Hourly Wage: $7.25
Labor Burden per Response: $0.85
Total Labor Burden: $1,209,541.67
Overall Labor Burden
Total Number of Annual Responses: 1,430,000
Total Labor Burden: $1,209,542
All information was derived using the Federal minimum wage of $7.25 as the estimated hourly wage.
Respondent Costs Other Than Burden Hour Costs
There are no annualized costs to respondents other than the labor burden costs addressed in Section 12 of this document to complete this collection.
Cost to the Federal Government
Part A: LABOR COST OF THE FEDERAL GOVERNMENT
Collection Instrument
DoD ABIS
Number of Total Annual Responses: 1,430,000
Processing Time per Response: 7 minutes
Hourly Wage of Worker(s) Processing Responses: $31.20
Cost to Process Each Response: $3.64
Total Cost to Process Responses: $5,205,200
Overall Labor Burden to the Federal Government
The Respondent hourly wage was derived from the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) for the mean hourly rates for a Forensic Science Technician ($31.20).
Part B: OPERATIONAL AND MAINTENANCE COSTS
Cost Categories:
Equipment: $1,988,375
Printing: $0
Postage: $0
Software Purchases: $0
Licensing Costs: $3,745,257
Other: $11,361,344
Total Operational and Maintenance Cost: $17,094,976
Section 14 Part B (O&M) figures were provided by Product Manager Biometric Enabling Capability (PM Bio), Program Executive Officer (PEO) for Intelligence, Electronic Warfare and Sensors (IEW&S) and was re-verified by DFBA for accuracy purposes.
Part C: TOTAL COST TO THE FEDERAL GOVERNMENT
Total Labor Cost to the Federal Government: $5,205,200
Total Operational and Maintenance Costs: $17,094,976
Total Cost to the Federal Government: $22,300,176
Reason for Change in Burden
The small increase in respondent burden is the result of revised response estimates since the 2021 submittal.
Publication of Results
The results of this information collection will not be published.
Non-Display of OMB Expiration Date
We are not seeking approval to omit the display of the expiration date of the OMB approval on the collection instrument.
Exceptions to “Certification for Paperwork Reduction Submissions”
We are not requesting any exemptions to the provisions stated in 5 CFR 1320.9.
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| Author | Zavada, Alexa M CTR HQDA PMG |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 2024-11-26 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy