Download:
docx |
pdf

State
Library Administrative Agency Survey, FY 2024
Web-Based
Data Collection Tool User’s Guide and Instructions
Institute
of Museum and Library Services
The
Institute of Museum and Library Services is authorized under 20
U.S.C. Chapter 72 to fulfill the congressional mandate to carry out
analyses of the impact of library services.
OMB
Control Number: 3137-0072 (Expires 9/30/2025)
Table
of Contents
Introduction
The State Library
Administrative Agency (SLAA) Survey provides descriptive information
about state library agencies from 50 states and the District of
Columbia. The survey collects information on state library agency
information, governance, public service hours, service outlets,
collections, library service transactions, library development
transactions, services to other libraries in the state, allied
operations, staff, income, expenditures, and electronic services and
other related information.
The data are collected as a
resource for Chief Officers of State Library Agencies (COSLA),
policymakers in the executive and legislative branches of federal and
state governments, government and library administrators at the
federal, state, and local levels, the American Library Association
and its members or customers, library and public policy researchers,
the public, journalists, and others.
This document provides
information
needed to
complete
the
FY 2024
SLAA Survey. It includes 1) information about how to navigate the
web-based data collection tool, 2) high-level information about the
content of the submission, 3) a glossary of terms in Appendix
A,
4) a detailed list of content-related instructions for the data
elements in the submission in Appendix B, and 5) a list of data
elements that are automatically summed by the data collection
platform in appendix C.
Web-Based Data
Collection Tool
Overview
There are
six steps you
must
complete
to submit your data: access the survey, enter data, review and
resolve any issues, submit the data, acquire the State Libraries
certification, and follow-up (if needed).
Changes from the prior
survey include updates to the data collection platform based on
keyholder feedback and modifications to a select number of items to
improve data quality. Data collection for FY 2024 opens on January 9,
2025, and ends on March 31, 2025. If you encounter any problems with
the system, please contact the survey administrators at the American
Institutes for Research (AIR) at
SLAA@air.org
or
202.403.5634.
The Help Desk is open from 9 a.m. to 5 p.m. (ET) Monday through
Friday. Respondents who require assistance outside of these hours may
schedule an appointment with the Help Desk.
Data from previous SLAA
surveys are available for download on the IMLS
website in several different formats (CSV, SPSS, SAS and PDF).
Each state will also receive a copy of the completed FY 2022 survey
and a blank copy of the FY 2024 survey to assist in preparing for the
current survey.
Survey Access
Key holders are responsible for their state’s
data submission. The key holder will receive an email message with a
link to the survey login page on the day the survey opens. The key
holder will receive a second email message containing a password.
From the survey login page, the key holder will enter their email
address and the assigned password and then access the survey.
The survey opens with a list
of all the sections. Use this list to track progress through the
survey, starting with Part A. As the key holder progresses through
the survey by navigating to the next section, answers are stored as
responses in progress. Answers are saved automatically, and there is
no need for key holders to click a “Save” button.
Navigation
Each screen for the survey
has a list of survey sections with links to each part of the survey
(Part A through Part M) and a link to Validations. Some sections rely
on data collected in previous sections to compute and populate fields
in subsequent sections. It is a best practice to start with Part A
and work your way through the survey sections sequentially. The list
of survey sections will allow you to return to previous sections if
you need to review or alter responses.
Figure
1. Each screen in the SLAA
Survey has a list of sections to use in navigating the questions.
If
possible, select a response for each survey question before advancing
to the next part. Survey questions that are not answered will trigger
an error message when you try to advance. The only way to resolve the
error message is to provide or adjust an answer. When you have
successfully completed a part, use the arrow at the bottom of the
screen to advance to the next section.
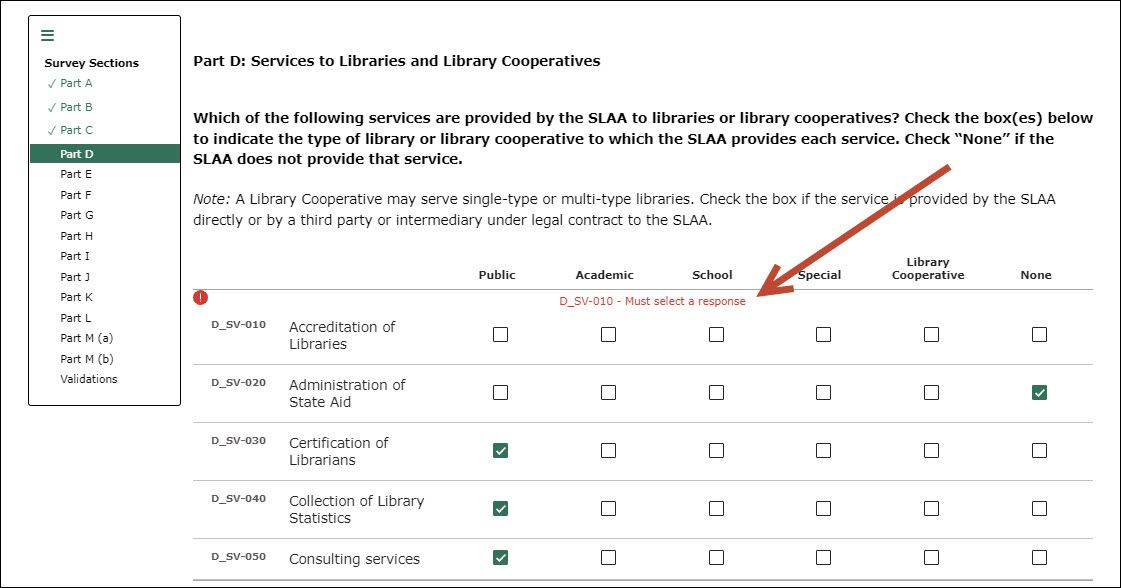
Figure
2. A skipped response will
result in an error message: “Must select a response.”
A
checkmark in the list of survey sections does not mean that the
section is complete. The validations section will show all the items
that must be corrected before responses can be submitted.
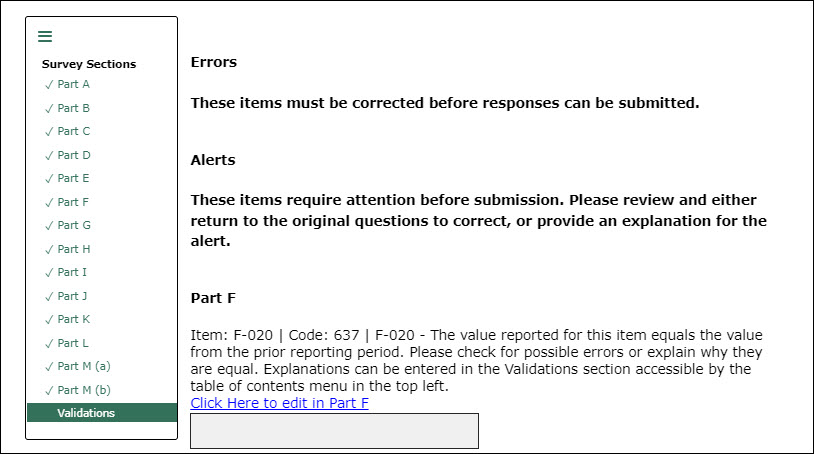
Figure
3. The Validations section
lists items that need to have a value entered before the survey can
conclude.
When you have corrected your
responses and reach the final screen, you can review a summary of
responses and download a printable PDF.
Auto-Calculation on Total Fields
The web system automatically calculates the
totals for survey items that are a sum of other items, and the
calculated total will be displayed on screen. The input box will be
disabled for entry, i.e., e.g., you will not be able to type values
into this box. If you have JavaScript disabled on your browser, this
functionality will not be available. See Appendix C
to view which line items are affected.
Data Submission
After all edit messages have
been resolved on the Validations screen, and the survey is complete,
submit your data.
After submitting your data,
you will be able to review a summary of your responses and download a
copy by using the Download PDF
link in the upper right corner.
At
this point, you will
not
be
able
to
make
any
changes
to
the
data
unless
a
request
is
submitted
to
the
SLAA
Help
Desk.
This
action
should
not
be
a
substitute
for entering
the
correct
data
initially.
If
you
discover a data error
after
submitting your survey, contact
the SLAA
Help
Desk at
@air.org
or 202.403.5634.
The
Help
Desk
will
assist
in
correcting
any
errors
and
resubmitting
the
data.
The
survey administrators
will
notify
the
State Librarian
that previously
locked
data have been
“unlocked,” and
certification
will
be
required after
the data
are resubmitted.
The Certification Process
After the key holder submits
the survey data, the system will automatically generate and send an
e-mail message to inform the State Librarian that the certification
process can begin. The e-mail will include a web link for the
certification, and instructions concerning the process; and a second
email with a password to login.
The key holder will be
notified by e-mail when the State Librarian has certified the
accuracy of the data submission.
Post-Edit Survey Follow-up
After data submission, AIR
analysts will review the data and contact the key holder by email if
there are questions about the data.
Changes from the Prior Survey
Updated User Interface
The
SLAA user interface has been improved in response to stakeholder
feedback. For example, login procedures have changed due to
challenges reported with the FY 2022 collection which provided key
holders with direct links to complete the survey which sometimes
expired and required help desk intervention and delays from key
holders being able to access the survey. Other changes include
revising the language in the edit check messages to be more
instructive and user friendly, as well as reducing the number of
conditions that trigger checks, and restructuring the validations
summary page.
Additional Changes
Item-level changes include
the following:
Updated age categories
for questions about the target populations for statewide reading
programs to align with categories in the Public Library Survey (see
D_PA-060.1-3 items in Appendix B);
Increased character
limit to allow states to more fully report SLAA partnerships (see
D_PA-010.1 in Appendix B);
Streamlined the
information collected about the total hours that the main or central
SLAA outlet is open (see E-020 in Appendix B);
Added options to the
list of items about recent or emerging technologies and adding
definitions to clarify this section of questions (see M-081 through
M-085 in Appendix B);
Deleted item M-084
because
SLAAs
do not fund or facilitate access to digital materials
through the Digital Public Library of America (DPLA).
Updated and moved
questions about statewide expenditures for research databases and
online learning platforms from Part M to Part K (see K-M160 in
Appendix B) and added a “TOTAL” field; and
Deleted two remaining
items about COVID.
General Survey Instructions
Respond to each item in this
survey. Before responding to any items in a question, read the note
(if any) following the question in the survey instructions.
Refer to the Glossary
(Appendix A) and the Specific Instructions for Data Elements
(Appendix B) for additional definitions and/or instructions for each
item, as needed.
All data in this survey, INCLUDING federal
fiscal data, are to be reported on the basis of State fiscal year
(FY) 2024, as specified in items A-230 and A-240. EXCEPTION: Data in
Part B and Part I are requested as of October 1, 2024.
In responding to items,
include data
for
all outlets
of
the
SLAA,
unless
otherwise directed. EXCLUDE
data
for
a
local public
or academic library
serving as a State resource
center or State reference/information service center under contract
with the SLAA.
For
data items requiring numerical answers, provide a value greater than
0 if appropriate or 0 if the answer is zero or none. If exact data do
not exist, a good estimate is acceptable. Some information in the FY
2024 survey is pre-filled based on responses from the previous SLAA
survey and may be edited, if needed (e.g., physical location address,
mailing address, survey respondent).
For some questions, your
SLAA’s responses from the previous survey are available as a
reference. These numbers cannot be edited.
All items will display an
item code, which starts with the letter of the section in which the
item appears. These identifiers are unique across time so that data
from different years of this survey can be linked. Sometimes these
identifiers do not appear in a sequential order because of changes to
the instrument over time.
Appendix A: Glossary
The following list provides
definitions for terms used in the FY 2024
SLAA Survey.
CO
(Chief Officer): Certifies the data
entered by the Key holder (KH). Also referred to as State Librarian
or Director of the Library.
Consulting
services: Individual or small-group
contacts to help libraries to attain goals and objectives and to deal
with specific needs and problems.
Continuing
education: Learning activities to
increase skills and knowledge of the library workforce.
Digital
literacy: Programs that promote the
ability to effectively find, evaluate, and create information using
digital technology.
E-rate:
Universal Service Program for Schools and Libraries. This
program makes discounts available to eligible schools and libraries
for telecommunications services, Internet access and internal
connections so that schools and libraries may have access to
affordable telecommunications and information services.
Electronic
materials: E-journals, E-books, full
text databases for access to scholarly information, and digital
documents and materials such as MP3 audio and streaming video
downloads.
Financial
literacy: Programs that promote the
ability to understand personal financial matters.
Fiscal
year: A fiscal year is a 12-month
period that an organization uses to report its finances. All data in
the SLAA, including federal fiscal data, are to be reported on the
basis of State fiscal year 2024, as specified in items A-230 and
A-240, although data in Part B and Part I are requested as of October
1, 2024.
Health
literacy: Programs that promote the
ability to understand basic health information and builds the
capacity to make appropriate health decisions based on this
information.
Information
literacy: Programs that promote the
ability to recognize the need for information and the ability to
find, evaluate, and use information.
KH
(Key holder): Person at the SLAA who is responsible for collecting
and providing the SLAA’s data for the survey.
LSTA
(The Library Services and Technology Act):
The only federal program exclusively for libraries. State libraries
use the funds to support statewide initiatives and also distribute
the funds through subgrants or cooperative agreements to public,
school, academic, research, and special libraries.
Language
literacy: Programs that promote the
ability to read and write.
Library
Cooperative: A Library Cooperative
is an organization that has its own budget and staff and provides
library and information services for the mutual benefit of
participating or member libraries. The organization’s
participants or members are primarily libraries, which are not under
the organization’s administrative control. The organization may
also be termed a network, system, district, or consortium. A Library
Cooperative may serve single-type or multi-type libraries.
Marketing/Communications:
Includes promoting and communicating the value of libraries and
library services and programs.
Numerical
literacy: Programs that promote the
ability to use, understand, and apply numerical concepts and
techniques.
Outlet:
A unit that provides direct public library service; it may be the
main or central library, a branch library, or a bookmobile. Only one
outlet may be designated as the central outlet.
Public
library: A library that serves all
residents of a given community, district, or region, and (typically)
receives its financial support, in whole or part, from public funds.
Reference
referral: A reference referral
transaction involves the provision of information about a group or
organization and its activities, services or agencies, and calendar.
Such a transaction typically requires the determination of the user's
need and the appropriate group or organization to meet the need. Such
a transaction may require directing the user to persons or
organizations external to the library for an answer to a question
School
library media center: A library that
is an integral part of the educational program of an elementary or
secondary school with materials and services that meet the
curricular, information, and recreational needs of students,
teachers, and administrators.
Special
library: A library in a business
firm, professional association, government agency, or other organized
group; a library that is maintained by a parent organization to serve
a specialized clientele; or an independent library that may provide
materials or services, or both, to the public, a segment of the
public, or to other libraries. Scope of collections and services are
limited to the subject interests of the host or parent institution.
Includes libraries in State institutions.
Statewide
reading programs: A statewide
coordinated program to support, maintain, or improve reading skills.
Summer
reading programs: A statewide
reading promotion campaign typically implemented between school years
to encourage children and young adults to maintain or improve their
reading skills.
Technology/Connectivity:
Includes computing, networking, broadband and related topics.
Youth
services: Services and programs to
engage young persons (under 18) in library programs and services.
Appendix B: Specific Instructions for Data
Elements
Part
A:
State Library
Administrative Agency
Identification
A-010
|
SLAA
name. Enter the full official name of the SLAA.
|
|
Physical
Location Address
|
A-020−
A-050
|
Enter
the address of the physical location of the SLAA. Include the
street address, city, State, and ZIP Code.
|
|
Mailing
Address
|
A-070−
A-100
|
Enter
the mailing address of the SLAA. Include the street address or
post office box, city, State, and ZIP code.
|
A-120
|
Web
address. Enter the web address of the SLAA. The web address is the
Uniform Resource Locator (URL) of the World Wide Web home page of
the SLAA.
|
|
Chief
Officer of SLAA
|
A-130−
A-170
|
Enter
the name, title, telephone number, fax number, and email address
of the chief officer of the SLAA.
|
|
Survey
Respondent
|
A-180−
A-220
|
Enter
the name, title, telephone number, fax number, and email address
of the respondent to this survey.
|
|
Reporting
Period
|
A-230−
A-240
|
Fiscal
year (FY) starting and ending dates. Enter the starting and ending
dates for State FY 2024, which is the period for which data in
this report are requested (except Part B and Part I data). Enter
the month and day in two digits each, and enter the year in four
digits. For example: June 30, 2024, would be entered as
06/30/2024.
|
Part B: Governance
B-010
|
Specify the SLAA’s location in State
government as of October 1, 2024.
|
B-060
|
If the
SLAA is part of a larger agency that is not listed in item B-010,
enter the name of the agency in item B-060.
|
Part C: Allied
Operations, State
Resource
or Reference/Information
Service Center,
and State Center for the
Book
Enter Yes or No for each
item to indicate whether the SLAA is combined with any of the allied
operations listed below.
Note:
An allied operation is an office, bureau, division, center, or other
organizational unit or service within an SLAA with staff, mission,
and resources to provide service not ordinarily considered an SLAA
function. It is characterized by having:
a specific mission, which may be a part
of the SLAA’s overall mission statement;
staff assigned for that mission (that
staff usually includes professionals other than librarians, such as
historians, archivists, curators) appropriate to its mission;
a
high-level manager or supervisor who reports to the SLAA chief
officer or to a deputy designated by the chief officer; and
financial resources clearly identified
and managed for the operation.
Note:
Do not report the following as allied operations: a Library for the
Blind and Print Disabled, a State Center for the Book, a law library,
or a contract with another library or other entity to provide a
service on behalf of the SLAA.
C-010
|
State
archives. This
operation is responsible for preserving and servicing noncurrent
official records of State organizations and institutions that are
of continuing value (1) to the legal and administrative
functioning of State government, (2) for the verification and
protection of the rights of individuals, and (3) for historical
and other research. It usually includes records of antecedent
colonial and territorial governments. Materials are stored,
arranged, and described so that needed records can be found
readily.
|
C-020
|
Primary
State legislative research organization.
This operation conducts research and gathers, digests, and
analyzes information in a close and confidential relationship with
members of the State legislature and their staff.
|
|
Note:
As an allied service, the organization is distinguished from
specialized reference service which an SLAA may provide to
government and other users by responding to reference questions
from legislative personnel, providing information service,
furnishing bibliographic and net search results, and instructing
and guiding users in conducting their research. At the federal
level, the parallel might be the difference between parts of the
Library of Congress: (1) the Congressional Research Service, and
(2) various reference services and subject divisions of the
Library.
|
C-030
|
State
history museum/art gallery.
This operation collects, preserves, and displays cultural
artifacts and/or works of art related to the State’s
political, social, economic, and cultural history.
|
C-040
|
State
records management service. This
operation manages the life cycle of the State’s own records
and records of local government from creation to disposition.
Disposition includes the preservation of certain records as well
as the disposal of nonessential records.
|
C-050
|
Other
allied operation.
If any other operations are allied with the SLAA, enter Yes for
this item.
|
|
Specify.
If any other operations are allied with the SLAA, enter the name
of the operation in this item.
|
C-070
|
Enter Yes or No to indicate whether the SLAA
contracts with a local public library or academic library to serve
as a State resource center or State reference/information service
center.
|
|
State
resource center or State reference/information service center.
This is an operation outside the SLAA, administered by a local
public library or academic library, which provides library
materials and information services to libraries and individuals
throughout the State. It is administratively separate from the
SLAA but receives grant or contract funds from the SLAA for
providing services.
|
C-080
|
Enter
Yes or No to indicate whether the SLAA is the host institution
for, or provides any funding to, a State Center for the Book.
|
|
State
Center for the Book.
The State Center for the Book is part of the Center for the Book
program sponsored by the Library of Congress that promotes books,
reading, and literacy and is hosted or funded by the State.
|
C-090
|
Enter
Yes or No to indicate whether the SLAA is a host institution for,
or provides any funding to, a Library for the Blind and Print
Disabled.
|
|
Library
for the Blind and Print Disabled.
The Library for the Blind and Print Disabled is part of a program
sponsored by the National Library Service to provide braille and
audio materials such as books and magazines to those with low
vision, blindness, or physical disability that makes reading
regular print difficult.
|
C-100
|
Enter
Yes or No to indicate whether the SLAA has a State advisory
council that advises the SLAA on the State’s LSTA program.
|
|
LSTA
program.
Funded by the Institute of Museum and Library Services (IMLS)
under provisions of the LSTA, this program is geared toward the
specific needs of public, academic, and community college
libraries. These federal funds are investments that help libraries
deliver relevant and up-to-to-date services to their communities.
|
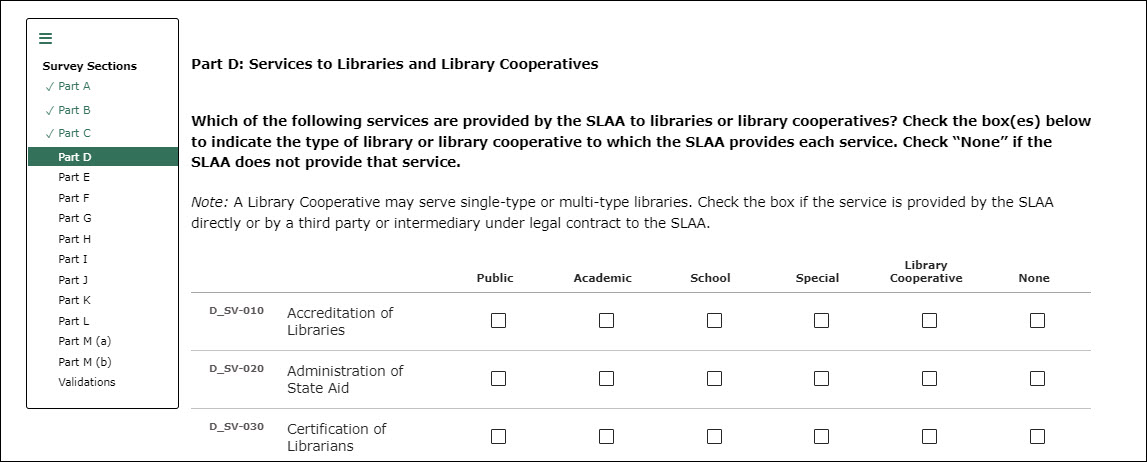
Part D: Services to Libraries and Library Cooperatives
Indicate which of the
specified services the SLAA provides to different types of libraries
or library cooperatives. For each service, check boxes for any type
of library where the service is provided from the options of Public,
Academic, School, Special, Cooperative, or None. More than one type
of library may be selected.
Note: A
Library Cooperative may serve single-type or multi-type libraries.
Report services provided directly by the SLAA are or those provided
by a third party or intermediary under legal contract to the SLAA.
Type of Library
Public Library. A
library that serves all residents of a given community, district, or
region and (typically) receives its financial support, in whole or
part, from public funds.
Academic
Library. A library forming an
integral part of a college, university, or other academic institution
for postsecondary education, organized and administered to meet the
needs of students, faculty, and affiliated staff of the institution.
School Library Media
Center. A library that is an
integral part of the educational program of an elementary or
secondary school with materials and services that meet the
curricular, information, and recreational needs of students,
teachers, and administrators.
Special Library. A
library in a business firm, professional association, government
agency, or other organized group; a library that is maintained by a
parent organization to serve a specialized clientele; or an
independent library that may provide materials or services, or both,
to the public, a segment of the public, or to other libraries. Scope
of collections and services are limited to the subject interests of
the host or parent institution. Includes libraries in State
institutions.
Library Cooperative.
A Library Cooperative is an organization that has its own budget and
staff and provides library and information services for the mutual
benefit of participating or member libraries. The organization’s
participants or members are primarily libraries, which are not under
the organization’s administrative control. The organization may
also be termed a network, system, district, or consortium. A Library
Cooperative may serve single-type or multi-type libraries.
Services
to Libraries and Library Cooperatives
|
D_SV-010
|
Accreditation
of libraries.
The SLAA may endorse or approve officially libraries that meet
criteria specified by the State.
|
D_SV-020
|
Administration
of State aid.
Includes determining compliance with eligibility criteria and
performance standards, overseeing processes through which grant
recipients are determined, announcing grant recipients and
disbursing funds, monitoring and receiving reports from grant
recipients, and other activities involved in the management of
financial assistance provided by the State to libraries.
|
D_SV-030
|
Certification
of librarians.
The SLAA may credential library staff with the rank or title of
librarian by attesting officially to their qualifications. These
qualifications may include a master’s degree from a graduate
program accredited by the American Library Association (ALA),
another level or type of educational attainment, confirmation of
participation in continuing education activities, and/or residency
in the State for a specified period.
|
D_SV-040
|
Collection
of library statistics. Every
SLAA collects statistics on public libraries and participates in
the Federal-State Cooperative
System (FSCS) for Public Library Data, otherwise known as the
Public
Library Statistics Cooperative (PLSC). Many SLAAs collect
statistics on institutional and other special libraries. Some
SLAAs assist in the collection of academic library statistics. A
few SLAAs collect statistics on school library media centers.
These data collections usually involve the design and
administration of survey instruments as well as data entry and
processing and report design and dissemination.
|
D_SV-050
|
Consulting
services. Individual
or small-group contracts to help libraries to attain goals and
objectives and to deal with specific needs and problems.
Consultants provide guidance on problems of concern to local
personnel, assistance in identifying problems not clearly
recognized, and identification of opportunities for increased or
improved performance.
|
Types
of Consulting Services Provided
If any
library type was checked in item D_SV-050, this section will be
displayed. If not, this will be hidden. For these follow-up
questions, the response options are Yes, No, or Don’t Know.
Only one response may be selected.
|
D_SV-050.1.1
|
Construction.
Includes new buildings and structures, as well as additions,
alterations, conversions, expansions, reconstruction, renovations,
rehabilitations, and major replacements.
|
D_SV-050.1.2
|
Library
management/organizational development.
Includes helping libraries to attain goals and objectives and to
deal with specific needs and problems of specific groups, such as
issues of concern to local personnel, assistance in identifying
problems not clearly recognized, and identification of
opportunities for increased or improved performance.
|
D_SV-050.1.3
|
Continuing
education.
Learning activities to increase skills and knowledge of the
library workforce.
|
D_SV-050.1.4
|
Technology/connectivity.
Includes computing, networking, broadband, and related topics.
|
D_SV-050.1.5
|
Marketing/communications.
Includes
promoting
and
communicating
the
value
of
libraries
and
library
services
and programs.
|
D_SV-050.1.6
|
Universal
Service Program/E-Rate.
Universal Service Program for Schools and Libraries.
|
D_SV-050.1.7
|
Adult
literacy.
Basic
reading
and
writing skills
for
adults.
|
D_SV-050.1.8
|
Youth/teen
services.
Services
and programs
to
engage
young
persons
(under
18)
in
library
programs
and
services.
|
D_SV_050.1.11
|
Collection of library statistics.
Support to libraries related to the collection or analysis of
library data and statistics. Libraries
collect various statistics for planning, developing, and
evaluating their services. Some examples are circulation, visits,
collection, acquisitions, electronic resource usage,
reference/chat transactions, and library instruction sessions.
|
D_SV-050.1.9
|
Other.
If the SLAA provides other types of consulting services, please
select Yes as the response and fill in the other services provided
in the write-in box in the survey.
|
|
Specify the type of other consulting
services provided.
|
D_SV-060
|
Library
legislation preparation/review.
Minimally, addresses the governance and financing of the SLAA,
public library services, and library services to blind and
print-disabled persons and residents of State institutions. It
usually permits the types of public library structures, such as
municipal, countywide, regional, federated, cooperative, and
contractual agreements. It may also provide mandates for SLAA
functions, other types of libraries (e.g., academic, school), and
multi-type cooperation.
|
D_SV-070
|
State
standards/guidelines.
The SLAA may promulgate standards or guidelines that define
adequacy, equity, and/or excellence in library services. Standards
or guidelines may be quantitative, qualitative, or both.
Maintaining standards or following guidelines may be a requirement
for receiving State aid and/or LSTA grants.
|
D_SV-080
|
Administration
of library system support.
Includes determining compliance with eligibility criteria and
performance standards, overseeing processes through which funds
are disbursed, monitoring and receiving reports, and other
activities involved in the management of financial assistance
provided by the State. Library systems are defined here as
cooperatives established under State law and supported by public
funding. Systems may be single- or multi-type cooperatives.
|
D_SV-090
|
LSTA
State program grants.
Funds distributed by the SLAA to recipients who meet eligibility
criteria specified by LSTA and the State. Such funds are awarded
for the purposes specified in successful grant proposals. Such
grants may be awarded competitively or on a formula basis. Include
sub-grants made to libraries or outside agencies to provide or
assist in providing such services.
|
|
|
|
|
Services
to Libraries and Library Cooperatives—Operational Assistance
|
D_OA-010
|
Cooperative
purchasing of library materials.
Two or more independent libraries of any type engaging in joint
activities related to purchasing materials, together with the
maintenance of the necessary records of these additions. Also
included are joint activities related to the identification and
verification of titles, fund accounting, processing payments, and
claims.
|
D_OA-020
|
Interlibrary
loan (ILL) services.
Activities involving bibliographic service centers or utilities,
regional systems (federations or cooperatives), consortia, and
resource centers, such as identifying libraries believed to own
requested materials and/or transmitting ILL requests in accordance
with established protocols or prevailing practices.
|
D_OA-030
|
Reference referral services.
Provision of information about or from groups or organizations. A
reference referral transaction involves the provision of
information about a group or organization and its activities,
services or agencies, and calendar. Such a transaction typically
requires the determination of the user’s need and the
appropriate group or organization to meet the need and may require
directing the user to persons or organizations external to the
library for an answer to a question.
|
Services
to Libraries and Library Cooperatives—Coordination/Integration
|
D_CI-010
|
Statewide
coordinated digital program or service.
Activities providing for the digitization of documents,
publications, or sets of records or realia to be made available
for public use (e.g., digitization of a series of city reports,
local newspapers, or genealogical records).
|
D_CI-020
|
Statewide
public relations/library promotion campaigns. A
public relations program usually organized around a particular
theme or issue, with specific objectives, and using a variety of
techniques in concert (e.g., press releases, events,
publications, exhibits).
|
D_CI-030
|
Statewide
virtual reference service.
Reference service supported by chat-based web technology that
provides access for all or a significant portion of the residents
of the State through libraries or remotely, typically on a
24-hours-per-day/7-days-a-week basis.
|
D_CI-040
|
Universal
Service Program
for Schools and Libraries.
The schools and libraries Universal Service Support Program,
commonly known as the E-Rate program, helps schools and libraries
to obtain affordable broadband. The E-Rate program is
administered by the Universal Service Administrative Co. under
the direction of the Federal Communications Commission (FCC)
under the Telecommunications Act of 1996.
|
D_CI-050
|
Statewide
resource sharing.
Organized efforts that enable and support the sharing of services
and materials through coordination and collaboration (e.g.
databases, e-books, ILL, cataloging).
|
D_CI-060
|
Involvement
in the acquisition of other federal program funds.
Providing technical assistance to receive federal assistance
funds. Involvement in the acquisition of technical assistance
funds includes determining compliance with eligibility criteria
and performance standards, overseeing processes through which
funds are disbursed, monitoring and receiving reports, and other
activities involved in the management of financial assistance
provided by the federal government from an agency other than
IMLS.
|
From
which federal agencies other than IMLS do you apply for funding?
Please answer each of the questions below by selecting one of the
choices provided.
This
section will only be displayed if a library type was selected for
D_CI-060.
|
D_CI-060.1.1
|
U.S.
Department of Education.
Funding received from the Department of Education. Examples
include Vocational Educational National Programs and Recreational
Programs.
|
D_CI-060.1.2
|
U.S.
Department of Agriculture (USDA). Funding
received from the Department of Agriculture. Examples include
USDA’s Rural Development Community Facilities Grant
Program, Community Facilities Program, and Rural Utility Service.
|
D_CI-060.1.3
|
Federal
Communications Commission/Universal Service Administrative
Company.
Funding or discounted services received or provided from the FCC
or the Universal Service Fund. Examples include the Schools and
Library Program (E-Rate program) This program makes discounts
available to eligible schools and libraries for
telecommunications services, Internet access, and internal
connections so that schools and libraries may have access to
affordable telecommunications and information services.
|
D_CI-060.1.4
|
U.S.
Department of Labor.
Funding received from the Department of Labor. Examples include
Labor Literacy Innovations Grant and Project Compass.
|
D_CI-060.1.7
|
National
Endowment for the Humanities (NEH).
Funding received from NEH. Examples include Humanities
Collections and Reference Resources Grants, NEH Preservation and
Access Research and Development Grants.
|
D_CI-060.1.5
|
Other.
Funding received from some other federal agency.
|
|
Specify
name of other federal agency
in the write-in box in the survey.
|
Services
to Libraries and Library Cooperatives—Program
Assistance
|
D_PA-010
|
Continuing
education programs.
Includes staff development events for library personnel at all
levels as well as training events for trustees and other State
and local government
officials
who
have
authority
over
or
responsibility
for
libraries.
|
D_PA-020
|
Library
planning/evaluation/research. Activities
involved in designing and assessing library programs and services
and studying issues facing libraries. Examples include the Public
Library Association (PLA) planning for the results process for
public libraries and the outcome-based evaluation process.
|
D_PA-030
|
Literacy programs.
A statewide program to assist individuals with limited skills to
develop skills that enable them to function in society without
assistance from others.
|
D_PA-030.1
|
Types of literacy programs.
This
section will only be displayed if a library type was selected for
D_PA-030.
|
D_PA-030.1.1
|
Language
literacy.
Programs
that promote
the ability
to read
and
write.
|
D_PA-030.1.2
|
Numerical
literacy.
Programs that promote
the ability
to use,
understand,
and
apply
numerical
concepts
and
techniques.
|
D_PA-030.1.3
|
Information
literacy.
Programs that
promote
the
ability to recognize
the need
for
information
and
the
ability
to
find,
evaluate, and use
information.
|
D_PA-030.1.4
|
Digital
literacy.
Programs
that
promote
the ability
to effectively
find,
evaluate,
and
create
information
using
digital
technology.
|
D_PA-030.1.5
|
Financial
literacy.
Programs
that
promote
the ability
to understand
personal
financial
matters.
|
D_PA-030.1.6
|
Health
literacy.
Programs
that
promote
the
ability
to
understand
basic
health
information
and
build
the
capacity
to
make
appropriate
health
decisions
based
on
this
information.
|
D_PA-030.1.7
|
Family/intergenerational
literacy.
Programs
that
promote
the incorporation
of the
spoken
and
written
word
into
meaningful
activities
with
the
family
unit.
|
D_PA-030.1.8
|
Other literacy types.
|
|
Specify the type(s) of the other types of
literacy programs in the write-in box in the survey.
|
D_PA-040
|
Preservation/conservation services
(physical objects). Specific
measures undertaken for the repair, maintenance, restoration, or
protection of library materials, including (but not limited to)
binding and rebinding, materials conversion (e.g., to microform),
deacidification, and lamination.
|
D_PA-100
|
Digitization.
Measures taken to convert information into a digital (i.e.,
computer-readable) format.
|
D_PA-110
|
Digital object preservation.
Digital Object Preservation refers
to the processes and activities involved in ensuring the
long-term maintenance, accessibility, and usability of digital
objects. These objects can include digital files, databases,
multimedia, software, and other forms of digital information. The
goal of digital preservation is to protect digital content from
obsolescence, corruption, and loss over time, ensuring that it
remains accessible and usable for future generations.
|
D_PA-050
|
Summer reading programs.
A statewide reading promotion campaign typically implemented
between school years to encourage children and young adults to
maintain or improve their reading skills.
|
D_PA-060
|
Statewide reading programs. A
statewide coordinated program to support, maintain, or improve
reading skills.
|
|
Do you support the following statewide
reading programs for target populations listed below? Please mark
those that apply.
This
section will only be displayed if a library type was selected for
D_PA-060.
|
D_PA-060.1.1
|
Children
(ages 0–5
years)
|
D_PA-060.1.2
|
Children
(ages 6–11
years)
|
D_PA-060.1.3
|
Young
adults (ages 12–18
years)
|
D_PA-060.1.4
|
Adults
(ages 19–65
years)
|
D_PA-060.1.5
|
Older
adults (ages 65+ years)
|
D_PA-120
|
Community workforce development.
Programming that encourages
workforce skill development and training for existing and
potential workers and that enables them to pursue employment
opportunities.
|
D_PA-130
|
Emergency preparedness.
Programs on how libraries and library staff can prepare for
emergencies or natural disasters within their own buildings and
their communities, ranging from preparation to recovery and
preservation.
|
D_PA-090
|
Did the SLAA engage in partnerships with
any government agencies or departments outside your SLAA to
provide services? Enter Yes or No.
|
D_PA-090.1
|
If
yes, describe how the SLAA partnered with other government
agencies or departments to provide services.
___________________________________________
Note:
Include partnerships between your SLAA and other government
agencies or departments that provided library-related or
non-library-related services. These may be special partnerships
or initiatives that are outside of the normal scope for your
SLAA. Examples could include partnering with a health department
to provide health outreach and materials, partnering with a labor
department on unemployment forms or information, or coordinating
with election boards on voter registration, outreach, or
materials
|
Part E:
Public Service
Hours, Outlets, and
User Groups
Enter in
the spaces provided the total hours open in a typical week for all
SLAA outlets (main or central, bookmobiles, and other outlets),
regardless of whom they serve. Do not report an allied operations
outlet as an SLAA outlet. For example, if the SLAA has a main
outlet with no bookmobile or other outlets and is open for public
service 40 hours in a typical week, report 40 hours. If the
SLAA has a main outlet, a bookmobile, and two other outlets open
40, 20, 35, and 35 hours, respectively, in a typical week, report
130 hours (40 + 20 + 35 + 35 = 130 hours
per typical week).
The
far-right column indicates the total hours open in a typical week
recorded in the previous reporting period.
Note:
Main or central outlet, bookmobiles, and other outlets (excluding
bookmobiles) are defined in the instructions to items E-050,
E-060, and E-070. Report total hours open in a typical week for
all SLAA outlets, regardless of whom they serve and regardless of
whether they are open on a walk-in or referral basis. Exclude data
for a local public or academic library serving as a State resource
center or State reference/information service center under
contract with the SLAA. Do not report data for non-SLAA outlets,
even though the SLAA may provide funding or services to such
outlets.
A “typical week” is a time
that is neither unusually busy nor unusually slow. Avoid holidays,
vacation periods, and days when unusual events are taking place in
the community or in the library. Choose a week in which the
library is open its regular hours. Include seven consecutive
calendar days from Sunday through Saturday or whenever the library
is usually open.
|
E-010
|
Total
hours/week
(all
SLAA
outlets,
regardless
of
whom
they
serve).
Sum
of
hours
open
during
a
typical
week
for
all
SLAA
outlets
(main
or
central,
bookmobiles,
and
other
outlets),
regardless
of
whom
them serve. Do
not
report
an allied
operations
outlet
as
an
SLAA
outlet.
|
|
Enter
in
the
spaces
provided
the
total
hours
that
the main or
central SLAA outlet is open in a typical week
to
serve
the
general
public
or
State government employees, by the specified categories. Only one
outlet may be designated as the main or central outlet.
Note:
Main
or
central
outlet
is
defined
in
items
E-050, E-60, and E-070. Report public service hours for the main
or central SLAA outlet, regardless of whether the outlet is open
on a walk-in or referral basis. Exclude data for a local public or
academic library serving as a State resource center or State
reference/information service center under contract with the SLAA.
Exclude service hours if the outlet only serves blind and
physically handicapped individuals through the National Library
Service for the Blind and Print Disabled, Library of Congress.
Also
exclude service hours if the outlet only serves residents of State
correctional institutions or residents of other State institutions
unless the outlet is administered and staffed by the SLAA. Do not
report data for a non-SLAA outlet, even though the SLAA may
provide funding or services to such an outlet.
|
|
E-020
|
Total
hours/week
(main
or
central
outlet). Sum of
hours
open during
a
typical
week
for
the
main
or
central outlet. If there is no main or central outlet, or the main
or central outlet does not provide services to the general public
or State government employees, select “Not applicable.”
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Enter in
the spaces provided the total number of SLAA outlets by type,
regardless of whom they serve. Only one outlet may be designated
as the main or central outlet. Do not report an allied operations
outlet as an SLAA outlet. Enter the total number of outlets for
each type.
Note:
An SLAA outlet has regular hours of service in which SLAA staff
are present to serve its users. The staff and all service costs
are paid by the SLAA as part of its regular operation. A loan of
books or total collections (whether permanent or short term) to
another agency, library, or school does not constitute an SLAA
outlet because it is not administered and staffed by the SLAA.
|
|
E-050
|
Main
or
central
outlet. A
single
unit
library
or
the
unit
where
the
principal
collections
are
located
and
handled.
Note:
An
SLAA
administrative
center
that
is separate
from
the
principal
collections
and is not
open
to users should not be included as an outlet. Only one outlet may
be designated as the main or central outlet. When two or more
outlets are considered main or central outlets, one outlet should
be designated as the central outlet, and the others should be
designated as “other outlets (excluding bookmobiles).”
|
|
E-060
|
Other outlets (excluding bookmobiles).
Units that have all of the following: (1) separate quarters, (2) a
permanent basic collection of books and/or other materials, (3) a
permanent paid staff, and (4) a regular schedule of hours open to
users.
|
|
E-070
|
Bookmobiles.
Trucks or vans specially equipped to carry books and other library
materials. They serve as traveling branch libraries. Count
vehicles in use rather than the number of stops each vehicle
makes.
|
|
E-080
|
Total outlets.
Sum of items E-050, E-060, and E-070. The web system will
calculate and display this total.
|
|
Enter in
the spaces provided the total number of SLAA outlets that serve
the following user groups, in whole or in part, by type of outlet.
The web system will calculate and display the totals.
Note:
Main
or central outlet, bookmobiles, and other outlets (excluding
bookmobiles) are defined in items E-050, E-060, and E-070.
|
|
E-090
|
Blind and physically
handicapped
individuals.
Outlets serving this
user group may contain talking
books on discs and tapes and books in braille made available from
the National Library Service for the Blind and Print Disabled,
Library of Congress. In addition, such outlets may contain large
print books for the visually handicapped and captioned films for
the deaf. These outlets provide such library materials and library
services to blind or physically handicapped residents who have
been certified by a competent authority as unable to read or to
use conventional printed materials due to physical limitations.
|
|
E-100
|
Residents of State correctional
institutions. Outlets serving
this user group provide books, other library materials, and access
to other information resources as well as other library services
to residents of prisons, reformatories, and other correctional
institutions operated or substantially supported by the State.
|
|
E-110
|
Residents of other State institutions.
Outlets serving this user group provide books, other library
materials, and access to other information resources as well as
other library services to patients or residents of residential
training schools, hospitals, nursing homes, and other general or
special institutions operated or substantially supported by the
State.
|
|
E-120
|
State government employees (executive,
legislative, or judicial).
Outlets serving this user group provide books, other library
materials, and access to other information resources as well as
other library services to employees of all branches of State
government.
|
|
E-130
|
General public.
Report all SLAA outlets that serve the general public, regardless
of whether they are open on a walk-in or referral basis. Outlets
serving this user group function as the State-level equivalent of
a local public library, providing books, other library materials,
and digital access to locally mounted and remote information
resources for all State residents.
|
|
Part F: Collections
Enter in
the spaces provided the total number of volumes or physical units
in the specified formats in all SLAA outlets (main or central,
bookmobiles, and other outlets) that serve the general public
and/or State government employees.
Note:
Main or central outlet, bookmobiles, and other outlets (excluding
bookmobiles) are defined in items E-50, E-60, and E-70. Report
collections for all SLAA outlets that serve the general public,
regardless of whether they are open on a walk-in or referral
basis. Exclude data for a local public or academic library
serving as a State resource center or State reference/information
service center under contract with the SLAA. Exclude collections
of braille and talking books owned by the National Library
Service for the Blind and Print Disabled, Library of Congress.
Also exclude collections that are specifically intended to serve
only residents of State correctional institutions or residents of
other State institutions unless such outlets are administered and
staffed by the SLAA. In every category below (F-010,
F-020, F-030, F-040, and F-050), include
only physical units.
|
F-010
|
Book and serial volumes
(exclude microforms) (exclude collections of braille books owned
by the National Library Service for the Blind and Print Disabled,
Library of Congress). Books are non-periodical printed
publications bound in hard or soft covers, or in loose-leaf
format, of at least 49 pages, exclusive of the cover pages; or
juvenile non-periodical publications of any length bound in hard
or soft covers. Serials are publications issued in successive
parts, usually at regular intervals, and, as a rule, intended to
be continued indefinitely. Serials include periodicals
(magazines, newspapers, annual reports, yearbooks, etc.),
memoirs, proceedings, and transactions of societies. Except for
the current volume, count unbounded serials as volumes when the
library has at least half of the issues in a publisher’s
volume.
|
F-020
|
Audio materials
(exclude collections of talking books owned by the National
Library Service for the Blind and Print Disabled, Library of
Congress). These are materials on which sounds (only) are stored
(recorded) and that can be reproduced (played back) mechanically
or digitally, or both. Included are records, audiocassettes,
audio cartridges, audiodiscs, audioreels, talking books, and
other sound recordings.
|
F-030
|
Video materials.
These are materials on which pictures, sound, or both are
recorded. Digital playback reproduces pictures, sounds, or both
using a television receiver or monitor.
|
F-040
|
Current serial subscriptions
(titles, not individual issues; include print subscriptions only)
(exclude microform, electronic, and digital subscriptions). These
include current subscriptions received, both purchased and gifts.
This count does not include the number of individual issues but
rather each serial title.
Report the total number
of titles subscribed to, including duplicates. Do not report
individual issues. Report print subscriptions only. Exclude
microform, electronic, and digital subscriptions.
|
F-050
|
Government documents
(include only government documents not accessible through the
library catalog and not reported elsewhere). For government
documents not accessible through the library catalog and not
reported on other lines, report the number of volumes or physical
units of such materials in all formats. A government document is
a publication in any format bearing a government imprint.
Includes publications of federal, State, local, tribal, and
foreign governments and intergovernmental organizations to which
governments belong and appoint representatives (e.g., United
Nations, Organization of American States).
|
Is the SLAA designated as a federal or
State depository library for government documents? Enter Yes or
No for each item (F-060–F090)
to indicate whether the SLAA is designated as a federal or State
depository library for government documents and whether it is a
regional or selective federal depository.
|
F-060
|
State depository library.
A library officially designated as a depository of publications
bearing the imprint of the State government.
|
F-070
|
Federal depository library.
A library officially designated as a depository of publications
bearing the imprint of the federal government. These libraries
receive publications issued by the executive, judicial, and
legislative branches at no charge in exchange for providing free
public access. Enter Yes or No to items 108 and 109 to indicate
if the SLAA is a regional or selective depository.
|
F-080
|
Regional.
Regional depositories receive one copy of all materials
distributed by the federal government.
|
F-090
|
Selective.
Selective depositories receive only those materials they select.
|
Part G: Library Service Transactions
Enter in
the spaces provided the ANNUAL totals for the specified types of
service transactions for all SLAA outlets (main or central,
bookmobiles, and other outlets) that serve the general public
and/or State government employees.
Note:
Main or central outlet, bookmobiles, and other outlets (excluding
bookmobiles) are defined in items E-50, E-60, and E-70. Report
library service transactions for all SLAA outlets that serve the
general public, regardless of whether they are open on a walk-in
or referral basis. Exclude data for a local public or academic
library serving as a State resource center or State
reference/information service center under contract with the SLAA.
Exclude service transactions for outlets or outlet service points
that only serve blind and physically handicapped individuals
through the National Library Service for the Blind and Print
Disabled, Library of Congress. Also exclude service transactions
for outlets that only serve residents of State correctional
institutions or other State institutions unless such outlets are
administered and staffed by the SLAA.
|
G-010
|
Circulation
(exclude items checked out to another library). These are
transactions that involve lending a physical item from the State
Library collection or borrowed from another library by a patron
for use generally, although not always, outside the library. This
activity includes charging materials manually or digitally. Also
report each renewal as a circulation transaction. Exclude in-house
use resulting from counting items in the collection as they are
re-shelved after use and without any formal tracking system.
Exclude items checked out to another library.
|
Interlibrary Loan/Document Delivery
|
G-020
|
Provided to other libraries.
These are library materials, or copies/scans of materials, loaned
from the SLAA collection to a patron at another library upon
request. Do not include loans or copies of materials from one SLAA
outlet to another SLAA outlet.
|
G-030
|
Received from other libraries and
document delivery services. These
are library materials, or copies of materials, borrowed by the
SLAA from another library or obtained by the SLAA from a
commercial document delivery service. Do not include loans or
copies of materials from one SLAA outlet to another SLAA outlet.
|
G-040
|
Reference transactions.
A reference transaction is an information contact that involves
the knowledge, use, recommendations, interpretation, or
instruction in the use of one or more information sources by a
member of the SLAA staff. The term includes information and
referral services. Information sources include printed and
non-printed materials, machine-readable databases (including
computer-assisted instruction), catalogs and other records of
holdings and through communication or referral, other libraries,
and institutions and persons both inside and outside the library.
When a staff member utilizes information gained from previous use
of information sources to answer a question, report as a reference
transaction even if the source is not consulted again during the
transaction. If necessary, multiply a typical week by 52. Exclude
directional transactions. (See definition of typical week in
question 6.)
|
G-050
|
Library
visits.
This
is
the
total number
of
persons
per
year
entering
SLAA
outlets,
including
persons
attending
activities
or meetings
and
those
persons
requiring
no
staff
services.
If
necessary,
multiply
a typical
week
by
52.
A
“typical
week” is
defined
in the
instructions
to
question
6.
|
Part H: Library
Development Transactions
Enter in the spaces provided the ANNUAL
totals for the specified types of library development transactions
of the SLAA.
|
H-010
|
LSTA and State grants: Grants awarded.
Report the total annual number of LSTA and State grants awarded by
the SLAA during State FY 2024. For grants or grant programs that
are awarded to multiple recipients, count each grant agreement as
a separate grant.
|
H-020
|
Continuing education programs: Number of
events. Report the total number
of continuing education events (workshops, training sessions,
virtual events, etc.) that (1) the SLAA sponsored and itself
presented, and (2) another agency presented with the help of SLAA
funding and planning support. Do not count events for which the
SLAA is only a nominal sponsor. Do not count events for an allied
operation.
Where an event is offered via video
conferencing, consider presentation simulcast to multiple
locations as one event. If a presentation is offered multiple
times, each offering should be counted as a separate event. Where
delivery is via synchronous web presentation and the number of
concurrent participants is limited and they must sign up to
participate, count each offering of the web training as one event.
Where delivery is via the web with asynchronous participation and
no limitation of participants, count web event as one event. For
the headcount of a virtual event, count the number of participants
logged in.
|
H-030
|
Total attendance at events.
Report the total annual attendance at continuing education events
reported in item H-020. Attendance should include total number of
participants in events regardless of delivery method. If web event
is delivered asynchronously, recommend counting only participants
who complete the continuing education offering.
|
Part I:
Staff
Enter
total number of SLAA staff in full-time equivalents (FTEs) to two
decimal places, by type of service. Report all staff on the
payroll as of October 1, 2024, and unfilled but budgeted
positions.
Note:
Forty hours per week is the measure of full-time employment for
this survey. FTEs of employees in any category may be computed by
taking the number of hours worked per week by all employees in
that category and dividing it by 40. Report staff based on the
SLAA organization chart. A given position (e.g., State Data
Coordinator) may be part of administration in one agency, library
development in another, and library services in another agency. If
an employee provides more than one service, allocate the FTE among
appropriate categories. Enter total number of SLAA staff in FTEs
(to two decimal places), by type of service. Report all staff on
the payroll as of October 1, 2024, and unfilled but budgeted
positions.
Type
of Position
Librarians
with ALA-MLS.
Librarians with master’s degrees from programs of library
and information studies accredited by ALA.
Librarians
other than ALA-MLS librarians employed by the SLAA.
This includes staff employed by the SLAA in the librarian
occupational category who have a master’s degree in Library
Science from programs not accredited by ALA and librarians who do
not have MLS degrees.
Other
professional and non-professional staff.
These are staff, employed by the SLAA, who are not in the
librarian occupational category, regardless of degree or
training, such as archivists, accountants, business managers,
public relations, and human resources staff and other employees
paid from the SLAA budget, including plant operations, security,
and maintenance staff.
Total
staff.
Sum of items a–c.
The web system will calculate and display these totals.
|
Type of Service
|
I-010
|
Administration.
Usually includes the chief officer of the SLAA and his or her
immediate staff. May include officers responsible for the SLAA’s
fiscal affairs; public relations; and planning, evaluation, and
research.
|
I-020
|
Library development.
Usually includes staff responsible for the development of public
library services. May include staff responsible for administering
State and LSTA grant programs; providing consulting and continuing
education services; and promoting resource sharing and other forms
of interlibrary cooperation. (See Part D instructions for
definitions of types of libraries.)
|
I-030
|
Library services.
Staff responsible for providing library service from the SLAA.
Includes public, technical, and other library services.
|
I-040
|
Other services.
Includes staff not reported in items I-010, I-020, and I-030, such
as staff in allied operations.
|
I-050
|
Total
staff. Sum
of
items
I-010–I-040.
The web system will calculate and display these totals.
|
I-110
|
Enter
the total number of staff FTEs that are employed directly by the
State.
|
I-120
|
Enter
the total number of staff FTEs that are for contracted employees
(i.e., not State employees).
|
Part J: Revenue
Enter Yes
or No to indicate whether all public library funds from State
sources are administered by the SLAA.
Note:
Answer this question based on State funds distributed to
individual public libraries and library cooperatives serving
public libraries in State FY 2024. If no State funds are reported
in Part K in items K_FA-01(b) or K_FA-020(b), the answer should be
No.
|
J-010
|
SLAA administration of all public library
State funds
|
Enter Yes
or No to indicate whether any funds from State sources are
administered by the SLAA for the following types of libraries.
Note:
Answer this question based on State funds distributed to libraries
and library cooperatives in State FY 2024. If no State funds are
reported in Part K in related items K_FA-010(b) to K_FA-050(b) or
K_FA-070(b), the answer should be No.
|
J-020
|
Academic libraries
(definition
is
provided
in
Part
D)
|
J-030
|
School
library
media
centers
(definition is
provided
in
Part
D)
|
J-040
|
Special
libraries (definition
is provided
in
Part
D)
|
J-050
|
Library
cooperatives
(definition
is
provided
in Part
D)
|
Enter in
the spaces provided the total funds received as revenue by the
SLAA during the reporting period specified in items A-230 and
A-240. EXCLUDE carryover funds. Include revenue for allied
operations only if the revenue is part of the SLAA budget. Include
all funds distributed to libraries and library cooperatives if the
funds are administered by the SLAA.
Note:
Exclude carryover when reporting revenue. Carryover means funds
carried forward from the previous year, sometimes called an
“opening balance” or a “fund balance.”
|
Federal
Revenue
|
J-070
|
Library Services and Technology Act
(LSTA) Grants to States program.
Report the funds drawn down from the federal government from the
LSTA Grants to States program during State FY 2024, whether
drawn from one or more federal fiscal year allotments. Do not
include IMLS Discretionary funds such as National Leadership
Grants, Laura Bush 21st Century Librarian Program, or Sparks!
Ignition—report
these grants in items J-080.1–J-080.10 (Other Federal
revenue).
|
J-080
|
Other federal revenue.
Report revenue in this item if the SLAA received federal revenue
other than LSTA Grants to States funds (e.g., National Endowment
for the Humanities grants, National Historical Publications and
Records Commission grants, LSTA National Leadership Grants, Laura
Bush 21st Century Librarian grants). If your State acts as the
fiscal agent for a multi-state grant, report only the funds
designated for your State.
|
J-080.1–
J-080.10
|
Specify program(s), title(s), and funding
amount for each source of revenue if other federal revenue is
reported in item J-080. Up to 10 programs may be reported.
|
J-090
|
Total federal revenue.
Sum of items J-070 and J-080. The web system will calculate and
display this total.
|
State and Other Revenues
|
J-100
|
SLAA operation.
Report revenue received from the State to support operation and
services of the SLAA. Do not include revenue received for major
capital expenditures, contributions to endowments, or revenue
passed through to another agency or for funds unspent in the
previous fiscal year.
|
J-110
|
State aid to libraries.
Report revenue received from the State for distribution to
libraries, library cooperatives, and agencies. Include funds
derived from State sources (exclusive of federal funds) and
appropriated by a State legislature to an SLAA for payment or
transfer to an individual library; a group of libraries; or an
agency or library, other than the SLAA, that provides a statewide
service to libraries or citizens. Exclude State funds used to
administer the SLAA or to deliver statewide services to libraries
or citizens where the service is administered directly by the
SLAA; State funds allocated for school library operations when the
SLAA is under the State education agency; and federal funds.
|
J-120
|
Other State revenue.
Report revenue received from the State for any other purpose, such
as interagency transfers.
|
J-130
|
Total State revenue.
Sum of items J-100, J-110, and J-120. The web system will
calculate and display this total.
|
J-140
|
Other revenue.
Include (1) any other revenue from public sources; (2) revenue
received from private sources, such as foundations, corporations,
Friends of the Libraries groups, and individuals; and (3)
SLAA-generated revenue, such as fines and fees for services.
|
J-150
|
Total revenue.
Sum of items J-090, J-130, and J-140. The web system will
calculate and display this total.
|
Part K: Expenditures
Total SLAA
expenditures, by source of revenue and type of expenditure.
|
Enter in
the spaces provided (a–c)
the total SLAA expenditures, by source of revenue and type of
expenditure. Include all LSTA expenditures. Include expenditures
for allied operations only if the expenditures are from the SLAA
budget. Include all funds distributed to libraries and library
cooperatives if the funds are administered by the SLAA.
Note:
These are the current and recurrent costs necessary to the
provision of services by the SLAA. Include LSTA expenditures for
statewide services (item L-010) conducted directly by the SLAA.
Include LSTA expenditures for LSTA administration (item L-030).
Exclude LSTA expenditures for grants (item L-020).
Do
not include funds distributed to libraries and library
cooperatives; report them instead in items K_FA-010–K_FA-080.
Enter
the total SLAA expenditures for each type of expenditure (d). The
web system will calculate and display these totals.
|
Expenditures for Statewide Digital
Resources
|
K-M160_A
K-M160_B
K-M160_C
|
Research databases:
Research databases are organized collections of electronic data or
records (e.g., facts, abstracts, articles, bibliographic data,
texts, photographs) that can be searched for to retrieve
information.
Online
learning platforms: Online
learning platforms primarily provide instruction, tools, and
resources to enhance education, lifelong learning, and skill
building. Platforms may offer homework assistance, language
learning, test preparation, professional development, resume
assistance, hobby instruction, etc. Do not consider resources
available for free when answering the following questions.
Total
Expenditures for statewide research databases and online learning
platforms; If
your state does not itemize the expenditures for research
databases and online learning platforms, please enter the total
amount for these expenditures in K-M160_C, by source.
|
Operating Expenditures for SLAA and
Allied Operations
|
K_AO-010
|
Salaries and wages. Salaries and wages
for all SLAA staff, including plant operation, security, and
maintenance staff for the reporting year. Include salaries and
wages before deductions but exclude employee benefits. The web
system will calculate and display the total for column (d).
|
K_AO-020
|
Employee benefits. Benefits
outside of salaries and wages paid and accruing to employees,
including plant operation, security, and maintenance staff,
regardless of whether the benefits or equivalent cash options are
available to all employees. Include amounts spent by the SLAA for
direct, paid employee benefits, including Social Security,
retirement, medical insurance, life insurance, guaranteed
disability income protection, unemployment compensation, worker’s
compensation, tuition, and housing benefits. Only that part of any
employee benefits paid out of the SLAA budget should be reported.
The web system will calculate and display the total for column
(d).
|
K_AO-030
|
Total staff expenditures.
Sum of items K_AO-010 and K_AO-020. The web system will calculate
and display these totals.
|
K_AO-040
|
Collection expenditures.
Includes all expenditures for materials purchased or leased for
use by SLAA users, including electronic materials, print
materials, microforms, machine-readable materials, audiovisual
materials, etc. The web system will calculate and display the
total for column (d).
|
K_AO-050
|
Other operating expenditures.
Includes all operating expenditures not reported in items
K_AO-010, K_AO-020, and K_AO-040. The web system will calculate
and display the total for column (d).
|
K_AO-060
|
Total operating expenditures.
Sum of items K_AO-030, K_AO-040, and
K_AO-050. The web
system will calculate and display these totals.
|
Other Expenditures for SLAA and Allied
Operations Only
|
K_OE-010
|
Capital outlay.
Funds for the acquisition of or additions to fixed assets such as
building sites, new buildings and building additions, new
equipment (including major computer installations), initial book
stock, furnishings for new or expanded buildings, and new
vehicles. Exclude replacement and repair of existing furnishings
and equipment, regular purchase of library materials, and
investments for capital appreciation. Exclude the amount reported
for this item from all other items except item K_TE-010. Include
construction aid expended on the SLAA. Exclude construction aid
expended on other libraries and library cooperatives. Include
expenditures for allied operations only if the expenditures are
from the SLAA budget. The web system will calculate and display
the total for column (d).
Note:
State accounting practices shall determine whether a specific item
is a capital expense or an operating expense, regardless of the
examples in this definition.
|
K_OE-020
|
Other expenditures.
These are expenditures not reported elsewhere. Exclude
construction aid. Include expenditures for allied operations only
if the expenditures are from the SLAA budget. The web system will
calculate and display the total for column (d).
|
Financial Assistance to Libraries and
Library Cooperatives
Note:
Include all funds distributed to libraries and library
cooperatives if the funds are administered by the SLAA.
|
K_FA-010
|
Individual public libraries.
Financial assistance to individual public libraries for services
to their population of legal service area. These are libraries
that are governed exclusively by a single board or political
subdivision. Municipal libraries, county libraries, consolidated
multi-county libraries, and library districts are considered
individual libraries if there is only one administrative entity.
Exclude construction aid. The web system will calculate and
display the total for column (d).
|
K_FA-020
|
Library cooperatives serving public
libraries only. Financial
assistance to library cooperatives serving public libraries only
for services to their population of legal service area. Exclude
construction aid. The web system will calculate and display the
total for column (d).
|
K_FA-030
|
Other individual libraries.
Financial assistance to other individual libraries for services to
their population or constituency. These are libraries other than
public libraries and school library media centers. Exclude grants
to public libraries and to school library media centers. Report
financial assistance to school library media centers in item
K_FA-070. Exclude construction aid. The web system will calculate
and display the total for column (d).
|
K_FA-040
|
Library cooperatives serving more than
one type of library. Financial
assistance to library cooperatives serving more than one type of
library for services to their population of legal service area.
Exclude construction aid. The web system will calculate and
display the total for column (d).
|
K_FA-050
|
Single agency or library providing
statewide service. Financial
assistance to a single entity (agency, library, library
cooperative, etc.) for services offered to all libraries in the
State, or all State residents, or a significant portion of all
libraries or State residents. Exclude funds administered directly
by the SLAA to provide such services. Exclude construction aid.
The web system will calculate and display the total for column
(d).
|
K_FA-060
|
Library construction.
Do not report data for this item in items K_FA-010–
K_FA-050,
K_FA-070, or K_OE-010. Includes construction of new buildings;
acquisition, expansion, remodeling, and alteration of existing
buildings; and purchase, lease, and installation of equipment of
any such buildings; or any combination of such activities
(including architects’ fees and the cost of acquisition of
land). Equipment includes information and building technologies,
video and telecommunications equipment, machinery, utilities, and
built-in equipment and any necessary enclosures or structures to
house them. Exclude construction aid expended on the SLAA. The web
system will calculate and display the total for column (d).
|
K_FA-070
|
Other assistance.
Expenditures for other assistance to libraries and library
cooperatives not reported in items K_FA-010–K_FA-060, such
as financial assistance to school library media centers. Exclude
construction aid. The web system will calculate and display the
total for column (d).
|
K_FA-080
|
Total financial assistance.
Sum of items K_FA-010–K_FA-070. The web system will
calculate and display these totals.
|
K_TE-010
|
Total expenditures.
Sum of items K_AO-060, K_FA-080, K_OE-010, and
K_OE-020. The
web system will calculate and display these totals.
|
Part L: LSTA State Program Expenditures
Enter in the spaces provided the total LSTA
State program expenditures, by type of expenditure. Report
expenditures in one and only one category. These expenditures
should also be reported in Part K.
|
L-010
|
Statewide services
(exclude sub-grants to single libraries or agencies providing
statewide services). Funds expended by the SLAA to provide
services to libraries and individuals throughout the State.
Include expenditures for statewide services conducted directly by
the SLAA. Exclude sub-grants made to single libraries or other
outside agencies to provide or assist in providing such services.
Note:
These expenditures should also be reported in Part K, under
operating expenditures (items K_AO-010–K_AO-060), capital
outlay (item K_OE-010), or other expenditures (item K_OE-020), as
appropriate. DO NOT report them as financial assistance to
libraries and library cooperatives (items K_FA-010–K_FA-080).
|
L-020
|
Grants
(include sub-grants to single libraries or agencies providing
statewide services). Funds distributed by the SLAA to recipients
who meet eligibility criteria specified by LSTA and the State.
Such funds are usually awarded for purposes specified in
successful grant proposals. Such grants may be awarded
competitively or on a formula basis. Include sub-grants made to
single libraries or other outside agencies to provide or assist in
providing statewide services.
Note:
These expenditures should also be reported in Part K, under
financial assistance to libraries and library cooperatives (items
K_FA-010–K_FA-080), as appropriate. DO NOT report them as
SLAA operating expenditures (items K_AO-010–K_AO-060),
capital outlay (item K_OE-010), or other expenditures (item
K_OE-020).
|
L-030
|
LSTA administration.
Expenditures of LSTA funds for administrative costs in connection
with programs and services carried out under this act.
Note:
These are the costs associated with the SLAA’s management,
oversight, and administration of the IMLS LSTA Grants to States
program and are costs that would be considered administrative
costs and subject to the 4% cap.
|
L-040
|
Total LSTA expenditures.
Sum of items L-010, L-020, and L-030. The web system will
calculate and display this total.
|
Part M (a): Digital Services and Information
Enter Yes or No for each item to indicate
whether the SLAA funds or facilitates the specified digital
networking functions at the State level.
Note:
A State-level digital information network involves the wide-area
use of telecommunications to link libraries via microcomputers or
terminals to automated library systems. The network may include
online public access catalogs and other library applications;
locally mounted or online databases (bibliographic, full text, or
data); bibliographic utilities; and other information resources.
Access to such networks may be via modem (i.e., dial access) or
dedicated lines (i.e., hard-wired). Such a network may or may not
be connected to the Internet.
|
M-010
|
Network planning or monitoring.
Includes drafting Statewide plans, requests for proposals, and
contracts and monitoring contracts for network development.
|
M-020
|
Network operation.
Includes acquiring, maintaining, or replacing substantial
technological equipment necessary to provide access to information
in digital and other formats made possible by new information and
communication technologies. May include hosting or sharing a
mainframe, minicomputer, or file server or facilitating reciprocal
borrowing agreements and document delivery systems necessary to
fully exploit such a network. Such a network may or may not be
connected to the Internet.
|
Database Development
Note:
Activities may include creation of new databases or conversion of
existing databases into electronic format. Includes bibliographic
databases as well as full-text or data files.
|
M-030
|
Bibliographic databases.
Includes machine-readable catalog records, other electronic
indexes, and other databases that contain only references to or
condensed surrogates for original materials.
|
M-040
|
Full-text or data files.
Full-text files are files in which the information consists of the
content of one or more complete intellectual products initially
expressed primarily through the written word. Data files report
the content of one or more complete intellectual products
expressed primarily with numbers.
|
Enter Yes
or No for each item to indicate whether the SLAA funds or
facilitates digitization or digital programs or services in any of
the following instances.
Note:
Digitization and digital programs or services include activities
providing for the digitization of documents, publications, or sets
of records or realia to be made available for public use.
|
M-050
|
For the
SLAA itself
|
M-060
|
Via grants or contracts to other State
agencies
|
M-070
|
Via grants or contracts to other libraries
or library cooperatives
|
Enter Yes
or No for each item to indicate whether the SLAA funds or
facilitates library access to any of the following programs or
services. In this item, “facilitate” means to make a
process or action easier or smoother by providing assistance or
resources.
|
M-081
|
Makerspace(s)
|
M-082
|
Virtual reality
|
M-083
M-086
M-087
|
Wi-Fi hotspots
3D
Printing: a process of creating physical objects layer by layer
from digital designs.
Technology
or tech kits: a technology/tech kit refers to a collection of
technology-related items or tools that are often designed to
provide hands-on learning experiences for a specific purpose. Tech
kits can include hardware devices, software programs,
instructional materials, or access to online resources or training
modules. In the context of libraries or educational institutions,
tech kits promote digital literacy and technological proficiency
related to STEM, digitization, podcasts, digital media, coding,
virtual reality (VR), green screen, drones, and others.
|
|
|
M-085
|
Other recent or emerging technologies or
programs: Other recent or emerging technologies or programs may
cover a variety of services including but
not limited to artificial
intelligence and machine learning, augmented reality, blockchain,
internet of things, robotic process automation, voice
assistants/natural language processing, biometric authentication,
5G technology, quantum computing, and edge computing.
|
Enter Yes
or No for each item to indicate whether the SLAA funds or
facilitates library access to the Internet in any of the following
ways.
Note:
The Internet is the global network of networks that, via a
standardized addressing system and a common primary command
structure, enables individuals and organizations to communicate
via email, to access a host of online databases and other digital
information resources, and to transfer files electronically.
|
M-090
|
State library end users.
Includes all activities that facilitate Internet awareness and use
by actual or potential State library end users.
|
M-100
|
Providing direct funding for Internet
access. Includes any grants of
State, federal, and/or other SLAA funds to libraries or related
organizations that facilitate (1) establishing Internet accounts
for library-related individuals or organizations; (2) acquiring
computer hardware, software, or peripherals necessary for Internet
access; and (3) training or consulting with actual and potential
Internet users.
|
M-110
|
Providing equipment.
Includes computer hardware, software, and peripherals necessary
for Internet access. Critical types of equipment, beyond basic
hardware and operating system software, include modems and
telecommunications software.
|
M-120
|
Providing access to directories,
databases, or online catalogs via the Internet.
Includes bibliographic files, locator files, and/or full-text
databases produced or licensed by the SLAA and available via the
Internet.
|
M-130
|
Managing a website, file server, bulletin
boards, or electronic mailing lists.
Includes the development and maintenance of Internet menu systems,
operation of equipment that provides Internet access to multiple
files, or posting of electronic messages via the Internet.
Note:
This item focuses on the structure through which content is
available via the Internet.
|
Enter in the spaces provided the number
of workstations that are used for Internet access by the general
public in all SLAA outlets that serve the public, by the specified
categories. Include terminals used by both SLAA staff and the
public. Exclude terminals that are for SLAA staff use only.
Note:
Report data only for all SLAA outlets that serve the general
public. Exclude data for: (a) a local public or academic library
serving as a State resource center or State reference/information
service center under contract with the SLAA; (b) outlets that only
serve blind and physically handicapped individuals through the
National Library Service for the Blind and Print Disabled, Library
of Congress; (c) outlets that only serve residents of State
correctional institutions or residents of other State
institutions; (d) outlets that only serve State government
employees; and (e) non-SLAA outlets, even though the SLAA may
provide funding or services to such outlets.
|
M-140
|
Number of library-owned public-access
graphical workstations that connect to the Internet for a
dedicated purpose (e.g., to access an Online Public Access Catalog
[OPAC] or specific database, or to train the public) or multiple
purposes. (For this count, the
term “library-owned” includes computers leased by the
State library agency.)
|
M-150
|
Number of all other public access
Internet workstations in the library.
(Report non-library computers placed in the library by other
agencies or groups. Report non-graphical workstations.)
|
Part M (b): Digital Services and Information
|
|
|
Enter Yes
or No for each item to indicate whether your statewide research
databases or online learning platforms, paid for by the funds
reported in K-M160-B, include access by the following groups.
Enter Yes if any
of the databases are available to a group.
|
M-170
|
Public libraries
(definition is provided in Part D)
|
M-180
|
Academic libraries
(definition is provided in Part D)
|
M-190
|
School library media centers
(definition is provided in Part D)
|
M-200
|
Special libraries
(definition is provided in Part D)
|
M-210
|
Library cooperatives
(definition is provided in Part D)
|
M-220
|
Other State agencies
|
M-230
|
Remote users.
Authorized users having access to and use of licensed database(s)
from sites outside of a library building
|
Enter Yes
or No to indicate whether the SLAA facilitates or subsidizes
digital access to the bibliographic records or holdings of other
libraries in the State, by the specified categories.
|
M-240
|
Web-based union catalog (international,
national, statewide, multi-state, and regional). A
web-based union catalog makes the aggregated digital holdings of
libraries in a nation, region, a library cooperative serving more
than one type of library, or a State available via the World Wide
Web. Holdings and indexes for a web-based union catalog are
mounted on a server that is connected to the Internet. Access to
the bibliographic information in a web-based union catalog is
available to any user with an Internet connection and a standard
web browser. National union catalogs include The Library of
Congress and OCLC. OCLC also provides the holdings of libraries
outside the United States.
Note:
Report access to a web-based
union catalog via a Z39.50 gateway in this item because it is a
web-based protocol.
|
M-250
|
Other types of digital access.
If the SLAA facilitates or subsidizes a type of digital access to
the holdings of other libraries in the State not covered in item
M-240, enter Yes for this item.
|
|
If Yes was indicated for item M-250, enter
the type of digital access in this item.
|
Enter Yes or No to indicate whether the
SLAA is an applicant for the Universal Service Fund (also known as
the E-Rate discount program).
|
M-270
|
Applicant for Universal Service Program
(E-Rate). The Universal Service
Program was established by the FCC under the Telecommunications
Act of 1996. To be considered an applicant, the SLAA must have an
FCC Form 470 and Form 471 on file with the FCC.
|
Appendix C: Auto-Sum
The following survey items
use auto-summing to calculate totals.
Section
|
Line
Item for Auto-Sum
|
Total
is the sum of these Line Items
|
E
|
E-080
|
E-050 +
E-060 + E-070
|
E
|
E-080B
|
E-050b +
E-060b + E-070b
|
E
|
E-080C
|
E-050c +
E-060c + E-070c
|
E
|
E-090d
|
E-090a +
E-090b + E-090c
|
E
|
E-100d
|
E-100a +
E-100b + E-100c
|
E
|
E-110d
|
E-110a +
E-110b + E-110c
|
E
|
E-120d
|
E-120a +
E-120b + E-120c
|
E
|
E-130d
|
E-130a +
E-130b + E-130c
|
I
|
I-010d
|
I-010a +
I-010b + I-010c
|
I
|
I-020d
|
I-020a +
I-020b + I-020c
|
I
|
I-030d
|
I-030a +
I-030b + I-030c
|
I
|
I-040d
|
I-040a +
I-040b + I-040c
|
I
|
I-050a
|
I-010a +
I-020a + I-030a + I-040a
|
I
|
I-050b
|
I-010b +
I-020b + I-030b + I-040b
|
I
|
I-050c
|
I-010c +
I-020c + I-030c + I-040c
|
I
|
I-050d
|
I-010d +
I-020d + I-030d + I-040d
|
J
|
J-090
|
J-070 +
J-080
|
J
|
J-130
|
J-100 +
J-110 + J-120
|
J
|
J-150
|
J-090 +
J-130 + J-140
|
K
|
K_AO-010d
|
K_AO-010a
+ K_AO-010b + K_AO-010c
|
K
|
K_AO-020d
|
K_AO-020a
+ K_AO-020b + K_AO-020c
|
K
|
K_AO-030a
|
K_AO-010a
+ K_AO-020a
|
K
|
K_AO-030b
|
K_AO-010b
+ K_AO-020b
|
K
|
K_AO-030c
|
K_AO-010c
+ K_AO-020c
|
K
|
K_AO-030d
|
K_AO-030a
+ K_AO-030b + K_AO-030c
|
K
|
K_AO-040d
|
K_AO-040a
+ K_AO-040b + K_AO-040c
|
K
|
K_AO-050d
|
K_AO-050a
+ K_AO-050b + K_AO-050c
|
K
|
K_AO-060a
|
K_AO-030a
+ K_AO-040a + K_AO-050a
|
K
|
K_AO-060b
|
K_AO-030b
+ K_AO-040b + K_AO-050b
|
K
|
K_AO-060c
|
K_AO-030c
+ K_AO-040c + K_AO-050c
|
K
|
K_AO-060d
|
K_AO-060a
+ K_AO-060b + K_AO-060c
|
K
|
K_OE-010d
|
K_OE-010a
+ K_OE-010b + K_OE-010c
|
K
|
K_OE-020d
|
K_OE-020a
+ K_OE-020b + K_OE-020c
|
K
|
K_FA-010d
|
FA-010a +
FA-010b + FA-010c
|
K
|
K_FA-020d
|
FA-020a +
FA-020b + FA-020c
|
K
|
K_FA-030d
|
FA-030a +
FA-030b + FA-030c
|
K
|
K_FA-040d
|
FA-040a +
FA-040b + FA-040c
|
K
|
K_FA-050d
|
FA-050a +
FA-050b + FA-050c
|
K
|
K_FA-060d
|
FA-060a +
FA-060b + FA-060c
|
K
|
K_FA-070d
|
FA-070a +
FA-070b + FA-070c
|
K
|
K_FA-080a
|
FA-010a +
FA-020a + FA-030a + FA-040a + FA-050a + FA-060a + FA-070a
|
K
|
K_FA-080b
|
FA-010b +
FA-020b + FA-030b + FA-040b + FA-050b + FA-060b + FA-070b
|
K
|
K_FA-080c
|
FA-010c +
FA-020c + FA-030c + FA-040c + FA-050c + FA-060c + FA-070c
|
K
|
K_FA-080
|
FA-080a +
FA-080b + FA-080c
|
K
|
K_TE-010a
|
K_AO-060a
+ K_OE-010a + K_OE-020a + FA-080a
|
K
|
K_TE-010b
|
K_AO-060b
+ K_OE-010b + K_OE-020c + FA-080d
|
K
|
K_TE-010c
|
K_AO-060c
+ K_OE-010c + K_OE-020c + FA-080c
|
K
|
K_TE-010d
|
K_TE-010a
+ K_TE-010b + K_TE-010c
|
L
|
L-040
|
L-010 +
L-020 + L030
|
M
|
M-160d
|
M-160a +
M-160b + M-160c
|
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| Author | Activate_KMP |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 2024-09-12 |



