ECLS Att D-6 Spr1TchrC-Lvl Paper_Redact
Early Childhood Longitudinal Study, Kindergarten Class of 2023-24 (ECLS-K:2024) Kindergarten and First-Grade Field Test Data Collection, National Sampling, and National Recruitment
ECLS Att D-6 Spr1TchrC-Lvl Paper_Redact
Early Childhood Longitudinal Study, Kindergarten Class of 2023-24 (ECLS-K:2024) Kindergarten and First-Grade Field Test Data Collection, National Sampling, and National Recruitment
OMB: 1850-0750
Early Childhood Longitudinal Study, Kindergarten Class of 2023-24
(ECLS-K:2024)
Kindergarten and First-Grade Field Test Data Collection, National Sampling, and National Recruitment
OMB# 1850-0750 v.24
Attachment D-6 Spring First-Grade Child-Level
Teacher Paper Survey
National Center for Education Statistics
U.S. Department of Education
August 2021
Note: Some items in these surveys are copyright protected and as such are redacted in public review copies.
2022

T
C 






Link_ID
P |
|
|
Completing this survey will help us learn more about children and their experiences in different schools and classrooms.
Thank you for your time!
To show our appreciation, we have included with your invitation a check that equals $20 for the teacher background survey plus $7 for every child for whom you’ve been asked to complete a survey.
Please return the survey to your school coordinator or an ECLS staff member. The survey should be sealed in the envelope we provided you. Do not mail this survey unless you are provided with an additional mailing envelope.
Photo is for illustrative purposes only. Any person depicted in the photo is a model.
The
National
Center
for
Education
Statistics
(NCES)
is
authorized
to
conduct
the
Early
Childhood
Longitudinal
Study
(ECLS)
by
the
Education
Sciences
Reform
Act
of
2002
(ESRA
2002,
20
U.S.C.
§9543).
The
data
are
being
collected
for
NCES
by
Westat,
a
U.S.-based
research
organization.
All
of
the
information
you
provide
may
be
used
only
for
statistical
purposes
and
may
not
be
disclosed,
or
used,
in
identifiable
form
for
any
other
purpose
except
as
required
by
law
(20
U.S.C.
§9573 and 6 U.S.C. §151). According to the Paperwork
Reduction Act of 1995, no persons are required to respond to a
collection of information unless it
displays
a valid OMB control number. The valid OMB control number for this
voluntary information collection is 1850-0750 v.24. The time
required to complete
this
information collection is estimated to average approximately 16
minutes per child-level survey including the time to review
instructions and complete and
review
the
information
collection.
If
you
have
any
comments
concerning
the
accuracy
of
the
time
estimate,
suggestions
for
improving
this
information
collection,
or
any comments or concerns regarding the status of your individual
submission of these data, please write directly to: Early Childhood
Longitudinal Study,
National
Center
for
Education
Statistics,
PCP,
550
12th
St.,
SW,
4th
floor,
Washington,
DC
20202.
OMB
No.
1850-0750,
v.24.
Approval
expires
xx/xx/xxxx
TQC1A-FT
Early Childhood Longitudinal Study First-Grade Teacher Survey (Child Level)
Fall 2022 - Form TQC1A-FT
INTRODUCTION
Dear Teacher,
Your school has agreed to participate in the Early Childhood Longitudinal Study (ECLS), a nationwide study of elementary-aged children, their schools, teachers, and parents. As part of the study, we are asking teachers at your school to complete surveys. You have been asked to complete this survey because one or more of the children in your class(es) are participants in this study. The child who is the subject of this survey is identified on the cover. This survey contains questions about this child’s skills and abilities.
The ECLS collects information from teachers of children who are in the study to investigate the relationship between children’s academic progress and various school, classroom, teacher, and home characteristics.
Taking part in the study is voluntary. You may stop at any time or choose not to answer a question you do not want to answer. However, only you can provide this information.
Although we realize you are very busy, we urge you to complete this survey as completely and accurately as possible.
THANK YOU VERY MUCH FOR YOUR HELP.




28
TQC1A-FT
MARKING DIRECTIONS

PLEASE READ CAREFULLY AND USE A BLACK OR BLUE BALL POINT PEN TO COMPLETE THIS SURVEY. DO NOT USE PENCIL OR FELT-TIP PEN.

It is important that you mark an “X” in the box next to your answers and print clearly.
Shown below is the correct way to mark your answers, along with examples of incorrect ways.
Correct Mark:
![]()
Incorrect Marks:


Light
and thin, outside
the box,
thick or
scrawled.
How to Change an Answer:
Completely black out the box of the incorrect answer and mark an “X” in the box next to the correct
answer.
![]()



Answers should be printed clearly and
should not touch or cross any of the box lines. Do not
cross zeroes or sevens. That
is, do not write a zero with a line through it like this – 0,
and do not
write
a
seven with a
line
through it
like
this
–
7.
Write one number per box like this:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
0









Write words like this:
John Smith

TQC1A-FT
ACADEMIC RATING SCALE
First, we would like for you to rate this child's current skills, knowledge, and behaviors within language and literacy (section 1), science (section 2), and mathematical thinking (section 3), based on your experience with him or her. If you are not the primary teacher in any of these areas, you may want to consult with the person most familiar with the child's progress in the area when completing the scales.
 This
is NOT
a test
and should
NOT be
administered directly to
the child.
This
is NOT
a test
and should
NOT be
administered directly to
the child.
 Examples
are meant to help you think of the range of situations in which the
child may demonstrate the
identified skills and behaviors. These examples do not
exhaust all the ways the child may demonstrate
what he or she knows or can do. The examples do,
however, indicate a level of proficiency a child should
have reached in order to receive the highest ratings. Some of
these examples describe a very high level of
performance (beyond typical students) in order to evaluate
achievement levels of the highest performing
students.
Examples
are meant to help you think of the range of situations in which the
child may demonstrate the
identified skills and behaviors. These examples do not
exhaust all the ways the child may demonstrate
what he or she knows or can do. The examples do,
however, indicate a level of proficiency a child should
have reached in order to receive the highest ratings. Some of
these examples describe a very high level of
performance (beyond typical students) in order to evaluate
achievement levels of the highest performing
students.
 Rate
this child
compared to
other children
of the
same age
level. Please
consider the
full range
of ratings
when answering.
Rate
this child
compared to
other children
of the
same age
level. Please
consider the
full range
of ratings
when answering.
The following five-point scale is used for each of the questions. It reflects the degree to which a child has acquired and demonstrated the targeted skills, knowledge, and behaviors.
Not yet Beginning
In progress Intermediate Proficient
Not applicable or Skill not yet taught
= Child has not yet demonstrated skill, knowledge, or behavior.
= Child is just beginning to demonstrate skill, knowledge, or behavior but does so very inconsistently.
= Child demonstrates skill, knowledge, or behavior with some regularity but varies in level of competence.
= Child demonstrates skill, knowledge, or behavior with increasing regularity and average competence but is not completely proficient.
= Child demonstrates skill, knowledge, or behavior competently and consistently.
= Skill, knowledge, or behavior has not been introduced in classroom setting.
If this child has limited English proficiency or is an English language learner, answer with his or her native language in mind if he or she does not yet demonstrate skills in English but does demonstrate them in his or her native language.
If this child has a disability, it may be necessary to consider adaptations for some questions to make them more inclusive for this child's skills and/or use of adaptive equipment. Some children may utilize alternative forms of verbal communication (for example, sign language, communication boards) or written communication (for example, word processors, Braille, dictation). Please answer the questions with these adaptations in mind.




29
TQC1A-FT
SECTION 1: LANGUAGE AND LITERACY
A1.
First, please rate this child's current skills, knowledge, and behaviors in LANGUAGE AND LITERACY.
MARK ONE RESPONSE ON EACH ROW.
Not
THIS CHILD...
Contributes relevant information to classroom discussions – for example, during a class discussion, can express an idea or a personal opinion on a topic and the reasons behind the opinion.
Engages in higher-level thinking and reasoning during classroom discussions – for example, answers questions that are not just an explicit recall of facts, makes inferences, asks
on-topic questions, and can have a cohesive exchange of ideas that are centered on a given topic for at least three conversational turns.
Uses correct endings on verbs and nouns when speaking – for example, says "dog plays" and "dogs play" or uses present tense ("she runs" or "she is running") and past tense correctly for both regular and irregular verbs ("he walks" and "he walked"; "I run" and "I ran").
Uses morphemes to figure out the meanings of words – for example, knows that “–s” means “more than 1” as in “trucks”; “–er” means a “person who” as in “farmer” and “painter”; “un” means “not” as in “unlike” and “unfriendly”; or “re” means “again” as in “reread” and “replay.”
Uses morphemes to decode new words – for example, decodes “jellyfish” by recognizing it is made up of two familiar words “jelly” and “fish” or decodes “preheat” as “pre” and “heat” and “fearless” as “fear” and “less.”
Uses complex sentence structures – for example, says "If she had brought her umbrella, she wouldn't have gotten wet," or "Yesterday it was raining cats and dogs," or "Why can't we go on the field trip at the same time as the first grade?"
Understands and interprets a story or other text read to him/her – for example, by writing a sequel to a story, or dramatizing part of a story, or posing a question about why a particular story event occurred as it did.
Not yet



Beginning



In progress



Intermediate



Proficient



applicable or
Skill not
yet taught





 1 TQC1A-FT
1 TQC1A-FT
A1. (Cont.) Please rate this child's current skills, knowledge, and behaviors in LANGUAGE AND LITERACY.
MARK ONE RESPONSE ON EACH ROW.
THIS CHILD...
Reads first-grade books independently with comprehension – for example, reads most words correctly and answers questions about what was read, makes predictions while reading, and retells a story after reading it.
Reads first-grade books fluently – for example, easily reads words in meaningful phrases rather than reading word by word.
Demonstrates beginning writing skills – for example writes sentences to express ideas while correctly spelling many short words like "hop" or "bed," and, if necessary, attempts approximate phonetic spelling for more difficult words (for example, "vakashun" for "vacation.")
Composes a story with a clear beginning, middle, and end.
Composes informative/explanatory text – for example, uses a combination of drawing, dictating, and writing to state what is being written about, supply some information about the topic, and provide some sense of closure.
Not yet


Beginning


In progress


Intermediate


Proficient


Not applicable or
 Skill
not
Skill
not
yet taught


Demonstrates an understanding of some of the conventions of print – for example, by appropriately using question marks, exclamation points, and quotation marks.





 Finds
meaningful units
in words
such as
prefixes, suffixes,
and base
words.
Finds
meaningful units
in words
such as
prefixes, suffixes,
and base
words.
SECTION 2: SCIENCE
B1. Next, please rate this child's current skills, knowledge, and behaviors in SCIENCE.
MARK ONE RESPONSE ON EACH ROW.
 Not
applicable
or
Not
applicable
or
Skill not
THIS CHILD...
Uses his/her senses to explore and observe – for example, observes how a push or pull can change the way an object is
moving, or observes and describes properties of rocks, soil, and water, or uses tools (such as hand lenses, thermometers, rulers) to gather information about objects.
Forms explanations based on observations and explorations – for example, explains the best growing conditions for a plant after investigating with light and water.
Classifies and compares living and non-living things in different ways – for example, classifies vegetables that grow above or below the ground, or measures objects and classifies them by size or weight.
Makes logical predictions when pursuing scientific investigations – for example, predicts whether or not objects are magnetic based on the materials they are made of.
Communicates scientific information – for example, records data from measurement tools (for example, clocks, thermometers, etc.), or constructs bar graphs.
Shows curiosity about the world by asking how and why things happen – for example, asks how rocks are formed or why it is warmer in the daytime than at night.
Generates different strategies to solve a problem – for example, when a design solution does not work as intended, tries other tools, materials, or methods to solve the problem.
Shows an understanding of cause and effect – for example, knows if he or she pushes a ball harder, it will go faster.
Not yet




Beginning




In progress




Intermediate




Proficient




yet taught




SECTION 3: MATHEMATICAL THINKING
C1.
Now, please rate this child's current skills, knowledge, and behaviors in MATHEMATICAL THINKING.
MARK ONE RESPONSE ON EACH ROW.
Not
THIS CHILD...
Applies properties of operations as strategies to add and subtract – for example, if 8 + 3 = 11 is known, then 3 + 8 = 11 is also known (commutative property of addition); to add 2 + 6 + 4, the second two numbers can be
added to make a ten, so 2 + 6 + 4 = 2 + 10 = 12 (associative property of addition). (Child does not need to use the formal terms for these properties.)
Fluently adds and subtracts within 10.
Fluently adds and subtracts within 20 using a variety of mental strategies – for example, making 10 ( 8 + 6 = 8 + 2 + 4 = 10 + 4 = 14); using the relationship between addition and subtraction (for example, knowing that
8 + 4 = 12, one knows 12 – 8 = 4); and creating equivalent but easier or known sums (for example, adding 6 + 7 by creating the known equivalent 6 + 6 + 1 = 12 + 1 = 13).
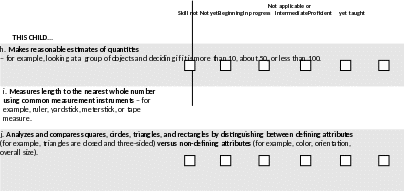
Demonstrates an understanding of place value – for example, by explaining that fourteen is ten plus four, or using two stacks of ten and five single cubes to represent the number 25.
Reads and writes numbers to 1000 using base-ten numerals, number names, and expanded form – for example, reads or writes “537” as “five hundred thirty seven,” writes “one hundred six” as “106,” and writes that 289 = 200 + 80 + 9.
Uses addition and subtraction (within 20) to solve problems involving unknown parts
and unknown total – for example, 4 + = 9, 12 + 7 = , 15 – = 4, and 10 – 3 = .
Surveys, collects, and organizes data into simple graphs – for example, by making tally marks to represent the number of children who want to play jump rope at recess, or making a picture, bar, line, or circle graph to show the different kinds of fruit children bring to school and the quantity of each type.
Not yet



Beginning



In progress



Intermediate



Proficient



applicable or
Skill not
yet taught



C1.
(Cont.) Please rate this child's current skills, knowledge, and behaviors in MATHEMATICAL THINKING.
 MARK
ONE
RESPONSE
ON
EACH
ROW.
MARK
ONE
RESPONSE
ON
EACH
ROW.






SECTION 4: EARLY LANGUAGE SKILLS
D1.
For this set of questions, please focus on this child’s early language skills in English based on your experience with this child at school. Think about your experience with this child at school. Mark the response option that best indicates how often this child exhibits the following early language skills when at school. Your best guess is fine. MARK ONE RESPONSE ON EACH ROW.
How Often?
-
THIS CHILD...
Never
Rarely
Some-
times
Often
Very
often
a.
Recalls and communicates personal experiences he/she has had to peers in a logical way.





b.
Answers questions that are not just an explicit recall of facts but that require some higher-level thinking.





c.
Is a good listener in conversations with peers.





d.
Uses a varied vocabulary in spoken language.





e.
Responds to questions in a thoughtful way that makes sense.





f.
Uses grammatically correct sentences when speaking.





g.
Recalls and communicates the meaning of a story or other experiences/events which he/she has heard.





h.
Uses correct endings on verbs and nouns when speaking – for example, says “dog plays” and “dogs play” or uses present tense (“she runs” or “she is running”) and past tense correctly for both regular and irregular verbs (“he walks” and “he walked”; “I run” and “I ran”).





i.
Asks on-topic questions that are relevant to the discussion in the classroom.





j.
Uses complex sentences with two or more clauses of various types (for example, independent, dependent) in spoken language, rather than using only simple, short sentences with a subject and a verb.





k.
Is a good listener in conversations with adults.





l.
Instructs peers in tasks which need to be done in a certain order.





m.
Uses academic language learned in the classroom when speaking.





D1. (Cont.) For this set of questions, please focus on this child’s early language skills in English based on your experience with this child at school. Think about your experience with this child at school. Mark the response option that best indicates how often this child exhibits the following early language skills when at school. Your best guess is fine. MARK ONE RESPONSE ON EACH ROW.
How Often?
THIS CHILD... Never Rarely
Some-
times Often
Very
often





 Tries
repeatedly to communicate information
which
has
not
been
understood.
Tries
repeatedly to communicate information
which
has
not
been
understood. Uses
evidence from a text or word problem to
support his
or
her answer.
Uses
evidence from a text or word problem to
support his
or
her answer.



 Uses
morphemes
to
figure
out
the
meanings
of
words –
for example, knows that “–s” means
“more
than 1”
as in
“trucks”;
“–er” means a
“person
who” as in “farmer” and “painter”;
“un”
means “not”
as in “unlike” and “unfriendly”; or
“re”
means
“again”
as
in
“reread”
and
“replay.”
Uses
morphemes
to
figure
out
the
meanings
of
words –
for example, knows that “–s” means
“more
than 1”
as in
“trucks”;
“–er” means a
“person
who” as in “farmer” and “painter”;
“un”
means “not”
as in “unlike” and “unfriendly”; or
“re”
means
“again”
as
in
“reread”
and
“replay.” Uses
long sentences with descriptive language
and
connecting words in a grammatically
appropriate
way
when
speaking.
Uses
long sentences with descriptive language
and
connecting words in a grammatically
appropriate
way
when
speaking.





Asks questions about information which is unclear to him/her.
u. Tries out new words (for example, heard in stories or from teacher) when speaking.









 Relates
and communicates personal experiences
in
a logical
way
or
“in a
way that
makes sense."
Relates
and communicates personal experiences
in
a logical
way
or
“in a
way that
makes sense." Uses
descriptive vocabulary such as adjectives
and/or
adverbs
when speaking
to
provide
detail.
Uses
descriptive vocabulary such as adjectives
and/or
adverbs
when speaking
to
provide
detail.



 Rephrases
questions or asks follow-up questions
if he/she does
not get the information he/she
wanted.
Rephrases
questions or asks follow-up questions
if he/she does
not get the information he/she
wanted. Uses
morphemes to decode new words – for
example,
decodes “jellyfish” by recognizing it is
made up of two
familiar words “jelly” and “fish”
or decodes
“preheat” as “pre” and “heat”
and
“fearless”
as
“fear”
and
“less.”
Uses
morphemes to decode new words – for
example,
decodes “jellyfish” by recognizing it is
made up of two
familiar words “jelly” and “fish”
or decodes
“preheat” as “pre” and “heat”
and
“fearless”
as
“fear”
and
“less.”
D1. (Cont.) For this set of questions, please focus on this child’s early language skills in English based on your experience with this child at school. Think about your experience with this child at school. Mark the response option that best indicates how often this child exhibits the following early language skills when at school. Your best guess is fine. MARK ONE RESPONSE ON EACH ROW.
How Often?
THIS CHILD... Never Rarely
Some-
times Often
Very
often





 bb.
Actively contributes
within a classroom
discussion.
bb.
Actively contributes
within a classroom
discussion.

D2.
Next, please think about this child's written language. Which of the following writing levels (ordered below from lowest to highest) best describes the highest level at which this child is currently performing (independently, without teacher help)? MARK ONE RESPONSE.


 Scribbling
Drawing a
picture
Scribbling
Drawing a
picture
Can copy his or her name


 Can
copy sentences from the board
Write his
or her name
without copying
Can
copy sentences from the board
Write his
or her name
without copying

 Can
write most letters when asked to write the letter
Write initial
sounds for
many words
Can
write most letters when asked to write the letter
Write initial
sounds for
many words
Write simple 2-4 letter words with invented spelling
 Write
multi-syllabic words
with invented
spelling with
most sounds
represented
Write
multi-syllabic words
with invented
spelling with
most sounds
represented
 Compose
and write
a full
sentence with
invented spelling
with most
sounds represented
Compose
and write
a full
sentence with
invented spelling
with most
sounds represented
 Compose
and write 2 or more consecutive full sentences with invented
spelling with most sounds
represented
Compose
and write 2 or more consecutive full sentences with invented
spelling with most sounds
represented
 Other
(Please specify):
Other
(Please specify):

D3. How much does this child enjoy writing? MARK ONE RESPONSE.




 Not
at all
A little bit Somewhat
Quite a bit Very
much
Not
at all
A little bit Somewhat
Quite a bit Very
much
SECTION 5: SOCIAL SKILLS AND APPROACHES-TO-LEARNING
E1.
For this set of items, please think about this child's behavior during the past month or two. Decide how often the child demonstrates the behavior described. MARK ONE RESPONSE ON EACH ROW.
Never Sometimes Often
Very often
 No
opportunity
No
opportunity
→ Child never exhibits this behavior.
→ Child exhibits this behavior occasionally or sometimes.
→ Child exhibits this behavior regularly but not all the time.
→ Child exhibits this behavior most of the time.
→ No opportunity to observe this behavior.
-
How Often?
Some- Very
Never times Often often
No opportunity
to observe
a. Xxxxxx xxxx xxxxxx.





b. Xxxxxxxxx xxxx xxxxxx.
c. Xxxx xxxxxx.
d. Xxxx xxxxx xxxxxx.
e. Xxxxxxxx xxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxx.
f. Keeps belongings organized.
g. Xxxx xxx xxxxxx xxxxx xxxx.
h. Shows eagerness to learn new things.
i. Works independently.
j. Xxxx xxxxxxxxxxx.
k. Xxxxxx xxxx xxxxxx.
l. Easily adapts to change in routines.
m. Xxxx xxx xx xxxxxxxxx.





n. Persists in completing tasks.





o. Pays attention well.





p. Follows classroom rules.





q. Xx xxxxxxxxxx xxxxxx xxxxxx xx xxxxxxx.





r. Xxxxxxxx xxxxx xx xxxxxxxx.





s. Xxxx xxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxx.





Source: Social Skills Rating System (SSRS). Copyright © 1990, NCS Pearson. Adapted with permission. All rights reserved; Social Skills Improvement System (SSIS). Copyright © 2008, NCS Pearson. Adapted with permission. All rights reserved.
E1.
(Cont.) For this set of items, please think about this child's behavior during the past month or two. Decide how often the child demonstrates the behavior described. MARK ONE RESPONSE ON EACH ROW.
Never Sometimes Often
Very often
No opportunity
→ Child never exhibits this behavior.
→ Child exhibits this behavior occasionally or sometimes.
→ Child exhibits this behavior regularly but not all the time.
→ Child exhibits this behavior most of the time.
→ No opportunity to observe this behavior.
Source: Social Skills Rating System (SSRS). Copyright © 1990, NCS Pearson. Adapted with permission. All rights reserved; Social Skills Improvement System (SSIS). Copyright © 2008, NCS Pearson. Adapted with permission. All rights reserved.
SECTION 9: SCHOOL LIKING AND AVOIDANCE
I1.
For the items below, please indicate how often each of these items applies to this child.
MARK ONE RESPONSE ON EACH ROW.
Doesn't apply Seldom displays this behavior
Sometimes applies Occasionally displays this behavior
Certainly applies Often displays this behavior





b. Dislikes
school.
d. Likes being in school.






 f. Enjoys
most classroom
activities.
f. Enjoys
most classroom
activities.

Source: School Liking and Avoidance Questionnaire. Adapted from Ladd and Price, 1987 and Ladd, 1990. Used with permission.
SECTION 10: STRATEGIC PLANNING
J1.
Please read the statements below and indicate how often each applies to this child’s behaviors observed across the past month. MARK ONE RESPONSE ON EACH ROW.
Does
not
apply Sometimes
applies
Consistently
applies
b. Xxxxxxxx xxx xxxx xx xxxxxxx xx xxxxxxxx




xxx
xx xxxxx xx xxxx xxxxxxxx xxxxxx xxx
xxxx xxx xxx.
d. Xxxxxxxxxx xxx xxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxx xx




x
xxxxxxxxxx xxx xx xxxxx (xxx xxxxxxx, "Xx X
xxxx xxx xxxx,
xxxx xx xxx
xxx.").
f. Xxxxxxxx x xxxx xxx xxxxx-xxxx xxxxxxxx (xxx







xxxxxxx,
"Xxxxx, X'x xxxxx xx xxxx xx xxx
xxxx. Xxxx,
X xxxx
xxx xxx
xxxx xxx
xxxx xx.").
h. Xxxxxxx xxxxxxx xxxxx x xxx xxxx xx xxxxx.



 j. Xxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxx xxxxxxxx xxx xxxx xxxx
xxxx xxx
xxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx.
j. Xxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxx xxxxxxxx xxx xxxx xxxx
xxxx xxx
xxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx.
Source: Adapted from the Learning-to-Learn Scales © 2019 by Edumetric and Clinical Science. All rights reserved. Used with permission. McDermott, P. A. (2018). Learning-To-Learn Scales. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania and Edumetric and Clinical Science.
SECTION 11: PEER RELATIONSHIPS
K1.
Please indicate how often each of these items applies to this child, particularly in the context of his or her behavior with peers. MARK ONE RESPONSE ON EACH ROW.
Doesn't apply Seldom displays this behavior
Sometimes applies Occasionally displays this behavior
Certainly applies Often displays this behavior





b. Xx
xxx xxxxxx
xx xxxxxxxx
xx xxxxx.
d. Xx xxxx xxxxxx xxxxx.











f. Xx
xxxxxxxxxxx xxxx xxxxx.
h. Xx xxxxxxx xx xxxxx.

Source: Adapted from the Child Behavior Scale © 2010 Gary W. Ladd. Used with permission.
K2.
During this school year, how often have other students ... MARK ONE RESPONSE ON EACH ROW.
Never
Rarely
Sometimes
Often
Very
often







b. Told
lies or
untrue stories
about this
student?
d. Intentionally excluded or left this student out from playing with him or her?




 K3.
K3.
During this school year, how often has this student ... MARK ONE RESPONSE ON EACH ROW.
Never
Rarely
Sometimes
Often
Very
often












b. Told
lies or
untrue stories
about other
students?
d. Intentionally excluded or left other students out from playing with him or her?
Source: Espelage, D. L. and Holt, M. (2001). Bullying and peer victimization during early adolescence: Peer influences and psychosocial correlates. Journal of Emotional Abuse, 2: 123-142. Adapted and used with permission.
SECTION 12: STUDENT INFORMATION
L1.
In which grade is this child enrolled? MARK ONE RESPONSE.
Kindergarten includes regular kindergarten, transitional (or readiness) kindergarten, transitional first (or pre-first) grade, or a program that is a kindergarten equivalent but is ungraded or has multiple grades.
A transitional kindergarten (TK) program is an extra year of school before kindergarten starts. It is different from preschool, Head Start, and prekindergarten.
Transitional first (or pre-first grade) is a school program between kindergarten and the first grade. It is for children who have attended kindergarten, but need more time to be ready for the first grade.



 Kindergarten
(Full-day program) Kindergarten
(Part-day program) First
grade
Kindergarten
(Full-day program) Kindergarten
(Part-day program) First
grade
Second grade
 Third
grade or higher
Third
grade or higher
 This
is an ungraded
classroom
This
is an ungraded
classroom
L2.
How long has this child been in your classroom this school year? MARK ONE RESPONSE.
 Entire
school year
Entire
school year


 More
than one semester but less than the entire school year
More than one
quarter but less
than one semester
More
than one semester but less than the entire school year
More than one
quarter but less
than one semester
Less than one quarter of the school year
L35.
Are you this child's primary teacher in the following subject areas? MARK ALL THAT APPLY.
A primary teacher is the teacher who is responsible for all learning in that subject area. The primary teacher writes all lesson plans and handles all activities and assessments in that subject area. If you co-teach a subject area with another teacher but think you could report about this child, please report that you are this child's primary teacher for that subject area.


 Reading/Language
Arts Mathematics
Reading/Language
Arts Mathematics
 Science
Social Studies
Science
Social Studies
L36.
Please fill in the boxes below with the date the survey was completed.
2
0
2
2
MONTH DAY YEAR
Thank you very much for answering these questions and for taking the time to participate in the
Early Childhood Longitudinal Study.
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 0000-00-00 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy