2078ss07
2078ss07.doc
EPA's ENERGY STAR Product Labeling (Renewal)
OMB: 2060-0528
SUPPORTING STATEMENT FOR
INFORMATION COLLECTION REQUEST NUMBER 2078.07:
“EPA’S ENERGY STAR® PRODUCT LABELING”
June 17, 2019
Prepared by:
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency
Office of Air and Radiation
Climate Protection Partnerships Division
Table of Contents
1 IDENTIFICATION OF THE INFORMATION COLLECTION 3
1.a TITLE OF THE INFORMATION COLLECTION 3
1.b SHORT CHARACTERIZATION/ABSTRACT 3
2 NEED FOR AND USE OF THE COLLECTION 5
2.a NEED/AUTHORITY FOR THE COLLECTION 5
2.b PRACTICAL UTILITY/USERS OF THE DATA 5
3 NONDUPLICATION, CONSULTATIONS, AND OTHER COLLECTION CRITERIA 5
3.b PUBLIC NOTICE REQUIRED PRIOR TO ICR SUBMISSION TO OMB 6
3.d EFFECTS OF LESS FREQUENT COLLECTION 8
4 THE RESPONDENTS AND THE INFORMATION REQUESTED 8
4.a RESPONDENTS AND NAICS CODES 8
5 INFORMATION COLLECTED: AGENCY ACTIVITIES, COLLECTION METHODOLOGY, AND INFORMATION MANAGEMENT 14
5.b COLLECTION METHODOLOGY AND MANAGEMENT 16
5.c SMALL ENTITY FLEXIBILITY 16
6 ESTIMATING THE BURDEN AND COST OF THE COLLECTION 16
6.a ESTIMATING RESPONDENT BURDEN 16
6.b ESTIMATING RESPONDENT COSTS 17
6.c ESTIMATING AGENCY BURDEN AND COSTS 17
6.d ESTIMATING THE RESPONDENT UNIVERSE AND TOTAL BURDEN AND COSTS 18
6.e BOTTOM LINE BURDEN HOURS AND COSTS 27
1 IDENTIFICATION OF THE INFORMATION COLLECTION
1.a TITLE OF THE INFORMATION COLLECTION
This ICR is entitled “EPA’s ENERGY STAR® Product Labeling.” (EPA ICR No. 2078.07, OMB Control Number 2060-0528)
1.b SHORT CHARACTERIZATION/ABSTRACT
Section 324 of the Energy Policy and Conservation Act directs the Environmental Protection Agency and the Department of Energy1 to implement “a voluntary program to identify and promote energy–efficient products and buildings in order to reduce energy consumption, improve energy security, and reduce pollution through voluntary labeling of or other forms of communication about products and buildings that meet the highest energy efficiency standards.” Operating under this authority, EPA’s ENERGY STAR program is a voluntary public/private partnership program that creates self-sustaining markets for energy efficient products. The centerpiece of the program is the ENERGY STAR label, a registered certification label that helps consumers identify products that save energy, save money, and help protect the environment without sacrificing quality or performance. In order to protect the integrity of the label and enhance its effectiveness in the marketplace, EPA must ensure that products carrying the label meet appropriate program requirements.
EPA partners with retailers, energy efficiency program sponsors (EEPS), and product brand owners who wish to use the ENERGY STAR label to differentiate products as more energy efficient. Retailers, EEPS, and product brand owners sign and submit a Partnership Agreement Form and Participation Form2 to indicate that they voluntarily agree to fulfill the relevant program requirements. These forms are collectively referenced in this ICR as a Partnership Application (PA).3 Products that are labeled as ENERGY STAR by product brand owner partners undergo third-party certification. EEPS Partners agree to promote energy efficiency as an easy and desirable option for organizations and consumers to prevent pollution, protect the global environment, and save on energy bills. Retail partners sell, market, and promote ENERGY STAR certified products.
Prior to labeling a product as ENERGY STAR, partners have eligible products tested in an EPA-recognized laboratory and certified by an EPA-recognized third-party certification body (CB). To minimize the burden on Partners, EPA maintains an automated data exchange with CBs. The CBs share information with EPA on products they review from EPA-recognized laboratories during the certification process. The XML-based data exchange allows the CBs to automatically transmit information on certified products to EPA from their database via web services. This automated system eliminates the need for paper submissions. EPA runs a series of automated validations to ensure the integrity of the data and confirm the credentials of the organizations associated with the data prior to incorporating it into the ENERGY STAR product database. EPA then provides the relevant information to consumers and purchasers in user-friendly formats that facilitate the purchase of energy efficient products.
The certification process also includes requirements for CBs to report to EPA products that were reviewed, but not eligible for certification, as well as to conduct post-market verification testing of a sampling of ENERGY STAR certified products. CBs complete a minimum amount of verification testing and share information with EPA on products verified twice a year. CBs report to EPA any post-market test data indicating a product may no longer meet the program requirements. This process helps maintain consumer confidence in the ENERGY STAR label and protect the investment of Partners.
While
most product-related information is provided by CBs, Partners are
asked to submit to EPA annual unit shipment data for their ENERGY
STAR
certified products. EPA is flexible as to the methods Partners may
use to submit unit shipment data. For example, if Partners already
submit this type of information to a third party, such as a trade
association, they are given the option of arranging for shipment
data to be sent to EPA via this third party to avoid duplication of
efforts and to ensure confidentiality.
Finally, Partners that wish to receive recognition for their efforts in ENERGY STAR may submit an application for the Partner of the Year Award. Partners that have ENERGY STAR certified central air conditioners, air-source heat pumps, furnaces, geothermal heat pumps, and windows that meet the ENERGY STAR Most Efficient criteria may submit an application to gain ENERGY STAR Most Efficient recognition.
Today, more than 90% of the American public recognizes the ENERGY STAR label. Thus, even though participation in the ENERGY STAR program is voluntary, most producers seek to satisfy its criteria. Currently ENERGY STAR has over 1,800 manufacturing Partners covering more than 60,000 certified product models in more than 75 product categories. Americans purchased more than 300 million ENERGY STAR certified products and more than 300 million ENERGY STAR certified light bulbs in 2017. Partners see the ENERGY STAR label as a useful and effective marketing tool for highlighting the energy efficiency of their products to consumers and others. In addition, ENERGY STAR provides Partners with recognition as environmental leaders. More than 700 utilities, state and local governments, and nonprofits leverage ENERGY STAR in their efficiency programs, reaching roughly 95% of households in all 50 states. By choosing ENERGY STAR, a typical household can save about $575 on their energy bills. With the help of ENERGY STAR, Americans prevented approximately 290 million metric tons of greenhouse gas emissions and $30 billion in energy costs in 2017 alone.4
2 NEED FOR AND USE OF THE COLLECTION
2.a NEED/AUTHORITY FOR THE COLLECTION
Section103(g) of the Clean Air Act directs EPA to "develop, evaluate, and demonstrate nonregulatory strategies and technologies for air pollution prevention… with opportunities for participation by [stakeholders]… including SOx, NOx… CO2… including end-use efficiency, and fuel-switching to cleaner fuels." (42 USC Section 7403g)
In 2005, Congress enacted the Energy Policy Act. Section 131 of the Act amends Section 324 of the Energy Policy and Conservation Act, and directed the Environmental Protection Agency and the Department of Energy to implement “a voluntary program to identify and promote energy–efficient products and buildings in order to reduce energy consumption, improve energy security, and reduce pollution through voluntary labeling of or other forms of communication about products and buildings that meet the highest energy efficiency standards.” The Act further directs EPA and DOE to “(1) promote ENERGY STAR compliant technologies as the preferred technologies in the marketplace for (A) achieving energy efficiency; (B) and reducing pollution; (2) work to enhance public awareness of the ENERGY STAR label, including providing special outreach to small businesses; (3) preserve the integrity of the ENERGY STAR label; (4) regularly update Energy Star product criteria for product categories;” and to solicit comments from interested parties prior to establishing/revising ENERGY STAR product categories, specifications, or criterion. (42 USC Section 6294a)
Collecting information from ENERGY STAR Partners and their representatives is necessary to achieve this mandate and document results.
2.b PRACTICAL UTILITY/USERS OF THE DATA
EPA uses information from organizations joining the program to ascertain basic identification information about them and verify their commitment to the program. EPA may also use partnership information for program implementation purposes, such as maintaining up-to-date listings of products and services available to the public. Further, ENERGY STAR’s tools (e.g., Product Finder, EPA-Recognized Bodies Search Tool, Rebate Finder) are available online for the public to find and compare ENERGY STAR certified product performance, third-party EPA-recognized bodies, and rebate offerings. Finally, EPA uses certified product data primarily to document and inform consumers about which products qualify for the ENERGY STAR label, fulfilling a fundamental purpose of the program – making it easy for consumers to identify and choose energy efficient products that are good for the environment. This data also informs the process by which ENERGY STAR performance specifications are established and revised, and factors into EPA’s assessment of whether and how the ENERGY STAR label can continue to effectively differentiate efficient products in the market. EPA and others use this information to evaluate ENERGY STAR and ensure continued success and benefits to Partners. EPA recognition enhances the image of organizations as national leaders in energy performance.
3 NONDUPLICATION, CONSULTATIONS, AND OTHER COLLECTION CRITERIA
3.a NONDUPLICATION
The information collected under this ICR is not collected by any other organization. In addition, the information collected is based on a particular point in time; therefore, information that is not up-to-date is not sufficient. EPA ensures that the information collected will not duplicate any ongoing recordkeeping or reporting functions requested under other Agency programs. For example, Energy Efficiency Program Sponsors (EEPS) can participate in one or more ENERGY STAR programs (e.g., Products, C&I). EPA designed its Partnership Agreement to enable an EEPS to complete and submit it once and select the specific program(s) it wants to partner with, rather than submitting it to each program separately.
3.b PUBLIC NOTICE REQUIRED PRIOR TO ICR SUBMISSION TO OMB
In compliance with the Paperwork Reduction Act, EPA solicited public comments on this ICR through an announcement in the Federal Register on April 10, 2019 (84 FR 14372). No comments were received on this notice.
3.c CONSULTATIONS
In May 2019, EPA contacted four individuals in Partner organizations to request their input on the ICR’s burden estimates. The purpose of the consultations was to determine if the burden estimates (e.g., EPA recognition applications) should be updated or revised in preparing ICR 2078.07. The table identifies the points of contact (POCs) and their organizations. EPA selected these organizations because of their substantial experience in carrying out collections under the ENERGY STAR program. Generally, the estimates provided by the Partners were consistent with EPA expectations of the labor burden. EPA averaged Partner responses for the labor burden estimates.
POC Name |
Organization Name |
Phone Number |
|
Johnson Choo |
LG Electronics |
201-266-2419 |
johnson.choo@lge.com |
Jack Marstellar |
Polaris Technologies |
330-726-7000 |
jmarstellar@polaristechnologies.com |
Jenny Giron |
Intertek |
847-871-1054 |
jenny.giron@intertek.com |
David Piecuch |
UL LLC |
847-664-3760 |
David.Piecuch@ul.com |
Following is a summary of EPA’s questions, POCs’ comments and EPA’s responses (e.g., if and how the Agency incorporated the comments into ICR 2078.07):
Joining the ENERGY STAR program and Related Activities: EPA provided two POC’s with the ICR’s burden estimates for completing a Product Brand Owner Partnership Application and asked if they are reasonable. EPA provided two POC’s with the ICR burden estimates for completing an Application for Lab Recognition, Application for Lab Scope Expansion, Application for Witnessed/Supervised Manufacturing Testing Laboratories (W/SMTL) Recognition, Application for CB Recognition, and Application for CB Scope Expansion and asked if they are reasonable. The POC’s discussed their experiences conducting these activities and indicated that most of the estimates are reasonable. The POC’s indicated that the estimates for Applications for W/SMTL Recognition and Applications for CB Scope Expansion are slightly high. EPA revised these estimates by taking the average of the Partner responses, which resulted in a slightly decreased estimate. The POC’s indicated that no capital or operations and maintenance costs are involved with these activities because the materials are downloaded and completed online and submitted to EPA via email.
Certified Product Maintenance Activities: EPA provided two POC’s with the ICR’s burden estimates for third-party certified product information activities and asked if they are reasonable. The third-party certified product information activities include submitting certified model data, submitting verification testing data, submitting testing failure information, and submitting ineligible product information. EPA provided one POC with the ICR’s burden estimates for Unit Shipment Data. The POCs discussed their experiences conducting these activities and indicated that the burden estimates are reasonable. EPA did not revise its estimates. The POC’s indicated that no capital or operations and maintenance costs are involved with these activities because the materials are downloaded and completed online and submitted to EPA via email or online platform.
POY and ENERGY STAR Most Efficient Recognition: EPA provided one POC with the ICR’s burden estimates for the POY Application and the ENEGY STAR Most Efficient HVAC Narrative Guide and asked if they are reasonable. The POC discussed their experience conducting the activities and indicated that the burden estimates are reasonable. EPA did not revise its estimate. EPA provided one POC with the ICR’s burden estimate for the ENERGY STAR Most Efficient Windows Application and asked if it is reasonable. The POC discussed their experience conducting the activity and indicated that the burden estimate is slightly high. EPA reduced the estimate to reflect the POC’s estimate and feedback. The POC’s indicated that no capital or operations and maintenance costs are involved with these activities because the materials are downloaded and completed online and submitted to EPA via email or online platform.
3.d EFFECTS OF LESS FREQUENT COLLECTION
EPA has carefully considered the information collection burden under the ENERGY STAR program. EPA is confident that those activities requested of respondents are necessary, and to the extent possible, the Agency has minimized the burden. A number of the requested activities, for example, will be performed once (e.g., one-time submittal of a Partnership Application). In addition, respondents can satisfy many of the collections in this ICR by submitting readily available information. For example, brand owner partners submit Unit Shipment Data on an annual basis in order to monitor and evaluate the program annually to ensure continued program success and benefits to Partners. EPA believes strongly that, if the information collections in this ICR are not performed at the requested frequency, EPA’s ability to implement the ENERGY STAR program and the public’s ability to benefit from the program’s tools and resources could be hampered significantly.
3.e GENERAL GUIDELINES
With the following exception, information collections performed under this clearance will follow all of OMB’s General Guidelines regarding federal data collection.
EPA intends to omit the expiration date from instruments associated with this collection. The information requested on the forms is modified infrequently and these documents are already in wide distribution. It would be impracticable for the Agency to fully replace its stock of instruments every three years and unproductive to even try if, except for the expiration date, the documents remain correct and useful.
3.f CONFIDENTIALITY
Participation in the ENERGY STAR program is voluntary and may be terminated by participants or EPA at any time. If a claim of confidential business information (CBI) is asserted, EPA will manage that information in accordance with EPA’s provisions on confidentiality. 40 CFR Part 2, Subpart B establishes EPA’s general policy on the public disclosure of information and procedures for handling CBI claims.
3.g SENSITIVE QUESTIONS
No questions of a sensitive nature are asked of participants under the ENERGY STAR program.
4 THE RESPONDENTS AND THE INFORMATION REQUESTED
4.a RESPONDENTS AND NAICS CODES
Respondents for this information collection request include ENERGY STAR Partners, who are product manufacturers. The following list of North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) codes includes, but is not limited to industry segments which may be potential respondents to the information collections.5
NAICS |
Industries |
221111 |
Hydroelectric Power Generation |
313320 |
Fabric Coating Mills |
322211 |
Corrugated and Solid Fiber Box Manufacturing |
323113 |
Commercial Screen Printing |
324122 |
Asphalt Shingle and Coating Materials Manufacturing |
325992 |
Photographic Film, Paper, Plate, and Chemical Manufacturing |
327123 |
Other Structural Clay Product Manufacturing |
327211 |
Flat Glass Manufacturing |
327993 |
Mineral Wool Manufacturing |
332321 |
Metal Window and Door Manufacturing |
333298 |
All Other Industrial Machinery Manufacturing |
333311 |
Automatic Vending Machine Manufacturing |
333313 |
Office Machinery Manufacturing |
333319 |
Other Commercial and Service Industry Machinery Manufacturing |
333414 |
Heating Equipment (except Warm Air Furnaces) Manufacturing |
333415 |
Air-Conditioning and Warm Air Heating Equipment and Commercial and Industrial Refrigeration Equipment Manufacturing |
334113 |
Computer Terminal Manufacturing |
334119 |
Other Computer Peripheral Equipment Manufacturing |
334210 |
Telephone Apparatus Manufacturing |
334220 |
Radio and Television Broadcasting and Wireless Communications Equipment Manufacturing |
334310 |
Audio and Video Equipment Manufacturing |
334512 |
Automatic Environmental Control Manufacturing for Residential, Commercial, and Appliance Use |
335110 |
Electric Lamp Bulb and Part Manufacturing |
335121 |
Residential Electric Lighting Fixture Manufacturing |
335129 |
Other Lighting Equipment Manufacturing |
335222 |
Household Refrigerator and Home Freezer Manufacturing |
335224 |
Household Laundry Equipment Manufacturing |
423440 |
Other Commercial Equipment Merchant Wholesalers |
423740 |
Refrigeration Equipment and Supplies Merchant Wholesalers |
441310 |
Automotive Parts and Accessories Stores |
443111 |
Household Appliance Stores |
443120 |
Computer and Software Stores |
444110 |
Home Centers |
493120 |
Refrigerated Warehousing and Storage |
541380 |
Testing Laboratories |
4.b INFORMATION REQUESTED
This section describes the information collections under this ICR, including data items and respondent activities.
Joining the ENERGY STAR Program and Related Activities
Partnership Application (PA)
Data Item
Partner name
Programs for which they are partnering with EPA (participation form)
Information on main contact person
Information on marketing/PR contact person
Signature of company official
Recordkeeping Item
There are no recordkeeping data items required pertaining to the Partnership Application.
ii Respondent Activity
Review the instructions of the PA
Complete and review the information requested by the PA
Submit the PA
Submit the joint statement between the brand owner and licensee, if applicable
Joint Statement between Brand Owner and Licensee, if applicable
Data Item
Partner and Brand Owner name
Information on brand involved in license agreement
Information on expiration date of license agreement
Information on main contact person at each organization
Signatures of company officials
Recordkeeping Item
There are no recordkeeping data items required pertaining to the Joint Statement.
ii Respondent Activity
Review the joint statement template
Complete and review information requested in the template
Submit as a supplement to the Partnership Application if applicable
Application
for AB, CB, Lab, and W/SMTL Recognition and Scope Expansion
i Data Item
Organization’s name
Organization’s address
Contact name, address, email, phone
Preparer’s name, title, date
Programs (product categories) for which they are partnering with EPA
Organization’s relevant reference documents
Recordkeeping Items
The
Accreditation Body maintains a record of quality management
documentation as required by ISO 17011.
The Laboratory
maintains a record of their accreditation certificate and scope of
accreditation.
The Certification Body maintains a record of
their accreditation certificate and scope of accreditation.
ii Respondent Activity
Review the instructions in the application
Complete and review application
Submit the application
Certified Product maintenance Activities
Third-Party Certified Product Information
i Data Item
Company Name
Product Name and model number
Product energy consumption attributes
Other key product specific information according to the relevant ENERGY STAR product Eligibility Requirements
Certified laboratories and certification bodies associated with the product.
Recordkeeping Items
The Certification Body maintains a certification record, and test reports on file for all products that undergo certification testing.
ii Respondent Activity
Organize certified model data into format for automated submission
Submit summary of verification testing data
Submit testing failure information
Submit information on ineligible products
Partner Response Forms (PRFs)
i Data Item
Company name and contact information
Case number
Product name and model number
OEM name
Notification date
Manufactured dates and sales information
Downstream distribution chain information
Additional affected model numbers and sales information
Representative signature
Recordkeeping Items
There are no recordkeeping data items required pertaining to Partner Response Forms.
ii Respondent Activity
Complete and submit “Disputable” version of the PRF
Complete and submit “Non-disputable” version of the PRF
Complete and submit Certification Error PRF
Complete and submit CFL Disputable PRF
Unit Shipment Data
i Data Item
Number of ENERGY STAR certified units shipped that year by product sub-type
Total U.S. shipments that year (requested but not required)
Recordkeeping item
There are no recordkeeping data items required pertaining to Unit Shipment Data.
ii Respondent Activity
Review instructions regarding Unit Shipment Data
Gather annual Unit Shipment Data
Compile and review USD by ENERGY STAR product category
Submit Unit Shipment Data form
Partner of the year (pOY) and Most Efficient Recognition
Partner of the Year Application
i Data Item
Name of the organization
Name of the organization as it should appear on the award
Information on the primary contact person
Information on the communications contact
Information on the organization CEO
Information on the organization headquarters
Information on the award category
Information on the number of products labeled, number of ENERGY STAR certified homes built, benchmarks reached or surpassed in energy management, benchmarks reached or surpassed in EE program delivery
Information on training, communication and outreach efforts
Information on other special endeavors or services provided
Recordkeeping Item
There are no recordkeeping data items required pertaining to Partner of the Year award applications.
ii Respondent Activity
Review the eligibility requirements and instructions on the application
Gather data
Complete and review the information and narrative descriptions in the application
Submit the application
Submit original examples of communication materials
ENERGY STAR Most Efficient Windows Application
i Data Item
Company Name
Contact’s name, address, and email
Company’s Most Efficient webpage
Product line name(s) and model number(s)
Product energy consumption attributes
Other key product specific information
Recordkeeping Items
There are no recordkeeping data items required pertaining to the ENERGY STAR Most Efficient Windows Application.
ii Respondent Activity
Review the eligibility requirements for model recognition and instructions on application
Gather data and test report
Complete the and review the information on the application
Submit the application and NAFS test report cover page(s)
ENERGY STAR Most Efficient HVAC Narrative Guide
i Data Item
Product Name and model number
Narrative description of automatic setup capabilities
Narrative description of access to system fault history
Narrative description of alerts of servicing
Narrative description of capabilities to facilitate installation and maintenance
Narrative description of compressor(s) and staging
Narrative description of capability to measure external static pressure
Recordkeeping Items
There are no recordkeeping data items required pertaining to the ENERGY STAR Most Efficient HVAC Narrative Guide.
ii Respondent Activity
Review the eligibility requirements and instructions on the application
Gather data
Complete and review the narrative descriptions in the application
Submit the application
5 INFORMATION COLLECTED: AGENCY ACTIVITIES, COLLECTION METHODOLOGY, AND INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
5.a AGENCY ACTIVITIES
This section describes EPA’s activities under ENERGY STAR.
Joining the ENERGY STAR Program and Related Activities
Partnership Application
EPA must perform the following activities related to the Partnership Application:
Modify PA to be submitted by applicants
Post the PA templates on the website
Review the completed PA
Send the joint statement template for the brand licensee and brand owner to sign, if a brand licensee is applying for partnership
Enter the information contained in the PA into EPA database. (Include information from the joint statement, if applicable.)
Send email welcoming them to the program
Application for AB, CB, Lab, and W/SMTL Recognition and Scope Expansion
EPA must perform the following activities related to recognition of these entities:
Modify application to be submitted by AB/CB/Labs
Disseminate via the internet
Review the completed application
Enter the information into EPA database
Certified Product maintenance Activities
Third-Party
Certified Product Information
EPA must perform the following activities related to third-party certified product information:
Maintain web services and incorporate model data from CBs into database
Review and ensure accuracy of testing failure information
Review and ensure accuracy of verification testing
Review and ensure accuracy of verification testing summary report
Maintain ineligible products list
Partner Response Forms:
EPA must perform the following activities related to Partner Response Forms:
Review “Disputable” version of the PRF
Review “Non-disputable” version of the PRF
Review Certification Error PRF
Review CFL Disputable PRF
Unit Shipment Data
EPA must perform the following activities related to Unit Shipment Data:
Review Unit Shipment Data
Compile information in aggregate form per product category
Evaluate aggregate data to determine ENERGY STAR success and/or need for program adjustment
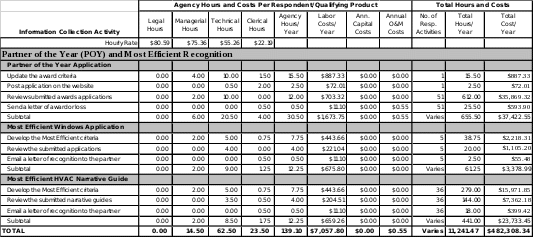
partner of the year (POY) and ENERGY STAR Most Efficient Recognition
Partner of the Year Application
EPA must perform the following activities related to Partner of the Year application:
Update the award criteria
Post application on the website
Review submitted awards applications
Send a letter of award or loss
ENERGY STAR Most Efficient Windows Application
EPA must perform the following activities related to Most Efficient Windows Application:
Develop the Most Efficient criteria
Review the submitted applications
Email a letter of recognition to the partner
ENERGY STAR Most Efficient HVAC Narrative Guide
EPA must perform the following activities related to Most Efficient HVAC Narrative Guide:
Develop the Most Efficient criteria
Review the submitted narrative guides
Email a letter of recognition to the partner
5.b COLLECTION METHODOLOGY AND MANAGEMENT
In collecting and analyzing the information associated with this ICR, EPA will use a telephone system, personal computers, the Internet, and applicable database software. EPA will ensure accuracy and completeness of collected information by reviewing and validating each submittal. Respondents can submit the information electronically (e.g., via email), without the use of postal mail. EPA will enter the information obtained into a database and will aggregate data obtained in order to make that information available to the public and monitor the progress of program implementation.
5.c SMALL ENTITY FLEXIBILITY
EPA expects that small entities will participate in ENERGY STAR product labeling. EPA has designed information requirements to minimize respondent burden while obtaining sufficient and accurate information. Under EPA’s ENERGY STAR product certification process, EPA gives organizations the flexibility to use their own in-house laboratory for testing or contract with an independent laboratory. EPA believes this ensures small businesses have plenty of options when searching for a third-party entity to conduct testing and certification of their products. Third-party certification bodies and laboratories submit certifications directly to EPA, reducing the burden on brand owner partners from needing to submit certification information.
5.d COLLECTION SCHEDULE
EPA collects initial information in the Partnership Agreement, which is completed and submitted by every Partner participating in ENERGY STAR. EPA also collects from brand licensees a joint statement with the brand owner prior to signing the Partnership agreement. In order to be recognized by EPA as an ENERGY STAR appropriate Accreditation Body, Laboratory and/or Certification Body, entities must provide EPA with the relevant documentation to provide assurance of their competence to perform these tasks. CBs must provide EPA with a summary of verification testing completed twice a year and report information on ineligible products and products that fail verification testing as they occur. EPA also requests that Product Brand Owner Partners submit information on their unit shipments of ENERGY STAR labeled products annually by March 1st for shipments during the previous calendar year. EPA requests this information the first week of January and reminds partners in February in advance of the annual deadline. Partners interested in receiving recognition for their efforts on ENERGY STAR submit a Partner of the Year Award application.
6 ESTIMATING THE BURDEN AND COST OF THE COLLECTION
6.a ESTIMATING RESPONDENT BURDEN
EPA conducted consultations with ENERGY STAR Partners to estimate respondent burden hours for the activities covered by this ICR. The responses EPA received were averaged to estimate the hourly burden for each activity. Exhibit 1 presents the estimated annual respondent burden for information collection activities associated with ENERGY STAR product labeling.
6.b ESTIMATING RESPONDENT COSTS
Exhibit 1 presents the estimated annual respondent costs for information collection activities associated with ENERGY STAR product labeling. The estimated annual respondent costs are discussed below.
Estimating Labor Costs
EPA estimates an average hourly respondent labor cost ($2019) of $115.16/hr for legal staff, $100.18/hr for managerial staff, $47.21/hr for technical staff, and $29.96/hr for clerical staff. To derive these hourly estimates, EPA referred to the May 2017 National Occupational Employment and Wage Estimates published by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics.6 This publication summarizes the unloaded (base) hourly rate for major occupational groups.7 EPA then applied the standard government overhead factor of 1.6 to the unloaded rate to derive loaded hourly rates. Finally, EPA updated the loaded hourly rates to December 2018 levels using Employment Cost Indexes developed by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics.8
Estimating Capital and Operations and Maintenance (O&M) Costs
EPA does not expect Partners to incur capital or operations and maintenance costs to meet the information requests of ENERGY STAR because Partners conduct the activities online and submit the information via email or an online platform.
6.c ESTIMATING AGENCY BURDEN AND COSTS
The hourly Agency labor rates used in this ICR were obtained from the 2019 Salary Tables for federal civilian employees, which are published by the Office of Personnel Management.9 EPA estimates an average hourly labor cost of $80.59/hr for legal staff, $75.36/hr for managerial staff, $55.26/hr for technical staff, and $22.19/hr for clerical staff. The labor costs are based on the following GS levels and steps: legal labor rates were based on GS Level 15, Step 1, managerial labor rates were based on GS Level 14, Step 4, technical labor rates were based on GS Level 12, Step 5, and clerical labor rates were based on GS Level 5, Step 1. To derive hourly estimates, EPA multiplied hourly rates by the standard government overhead factor of 1.6. Agency burden and costs are estimated in Exhibit 2.
EPA anticipates one instance of Agency O&M costs associated with ENERGY STAR product labeling information collection activities. This corresponds to the cost of $0.55 to mail a letter of award or loss to Partners who submit Partner of the Year applications.
6.d ESTIMATING THE RESPONDENT UNIVERSE AND TOTAL BURDEN AND COSTS
In this section, EPA describes its estimates of the number of respondents carrying out the information collections under the ENERGY STAR product labeling program. In developing its estimates, EPA referred to its databases and other documentation in order to understand historical trends in the number of new and existing respondents. Based on this understanding, EPA has estimated the average annual number of respondents associated with each of the information collections under the program.
In total, EPA estimates approximately 2,732 respondents participate under the ENERGY STAR products labeling program annually. In deriving this estimate, EPA referred to its databases to determine the current number of respondent Partners, including Product Brand Owners, Retailers, EEPS10, ABs, CBs, and Labs. EPA notes that most respondents in this ICR are current Partners. EPA next identified the number of new organizations expected to join the program each year for the next three years, based on historical trends over the last three years.
These organizations are discussed further below.
Joining the ENERGY STAR Program and Related Activities (exhibit 1)
Partnership Application
EPA has developed a Partnership Application process for product brand owners, retailers, and EEPS wishing to join the ENERGY STAR product labeling program, which consists of a partnership agreement form and a participation form. It is expected that 250 new brand owner, retailers, and EEPS Partners will join each year for the three years of this ICR, as reflected in Exhibit 1.11 One joint statement template for brand owners and brand licensees has been developed by EPA for ENERGY STAR product labeling. It is expected that 15 Brand Owner templates will be submitted along with the Partnership Application each year, for the three years of this ICR.
Partnership Type |
Number of Annual Respondents |
Product Brand Owner |
200 |
Retailer |
35 |
EEPS |
15 |
Total |
250 |
Application for AB, CB, and Lab Recognition and Scope Expansion
As reflected in Exhibit 1, EPA estimates that it will receive 25 applications for lab recognition, 40 applications for lab scope expansion, and 15 applications for W/SMTL recognition each year.
Further, the number of Accreditation Bodies and Certification Bodies has changed minimally over the last three years because most interested stakeholders are already participants. EPA estimates that it will receive 1 application from an AB over the next three years, and 2 applications from CBs each year over the next three years. Because this ICR estimates annual burden over a 3-year period, EPA has annualized the one AB application over three years, to estimate that 0.33 applications will be received annually on average.
Certified Product maintenance Activities (exhibit 2)
Third Party Certified Product Information
Product specifications for over 75 different products are developed and maintained by EPA under the ENERGY STAR product labeling program. Each product category has specific qualifying product information that must be reviewed, certified and shared by the CB. An average of 13,000 products are certified and labeled with the ENERGY STAR annually.
As reflected in Exhibit 1, EPA estimates that 20 CBs will organize their certified model data into a format for automated submission. EPA updates the lists of certified models daily to reflect the most current information that has been transmitted to the EPA database via web services. CBs conduct verification and challenge testing on an ongoing basis and verify a minimum sampling of products each year. In 2018, 20 CBs submitted the summary of the testing they conducted for the year. This number of CBs is representative of how many entities EPA expects to report this information every year. On average CBs reported 355 product failures to EPA in the last three years. This number tends to fluctuate annually and could decrease in future years as product quality control increases. CBs report to EPA information on products reviewed for certification, but not eligible for ENERGY STAR. Based on the average number of ineligible products reported to EPA in the past three years, EPA expects 21 ineligible products to be reported each year under this ICR.
Partner Response Forms
Upon receipt of an official testing failure or delisted product letter from EPA, brand owner Partners complete and submit to EPA a Partner Response Form. There are several versions of this form (e.g., “Disputable” version, “Non-disputable” version). In total, EPA expects 161 Partner Response Forms to be submitted each year under this ICR.
Unit Shipment Data
Each year, ENERGY STAR Partners are asked to submit unit shipment data for their ENERGY STAR labeled products. Based on historical trends of data, EPA estimates that it will receive 1,727 unit shipment reports each year. Unit shipment data will be aggregated for each of the product categories covered by EPA under ENERGY STAR. These estimates are based on aggregates across the 75 product categories.
POY and Most Efficient Recognition (exhibit 3)
Partner of the Year Application
As reflected in Exhibit 1, EPA expects to receive 51 Products Partner of the Year Award applications annually.
ENERGY STAR Most Efficient Windows Application
ENERGY STAR brand owner partners who have ENERGY STAR certified window models that meet the ENERGY STAR Most Efficient Windows Recognition Criteria and wish to apply to gain Most Efficient recognition submit a Most Efficient Windows application. EPA expects to receive 5 Most Efficient Windows applications each year.
ENERGY STAR Most Efficient HVAC Narrative Guide
ENERGY STAR brand owner partners who have ENERGY STAR certified central air conditioner and air source heat pump, furnace, or geothermal heat pump models that meet the ENERGY STAR Most Efficient Recognition Criteria and wish to apply to gain Most Efficient recognition submit an ENERGY STAR Most Efficient HVAC Narrative Guide. EPA expects to receive 36 Most Efficient HVAC Narrative Guides each year.
Exhibit 1
Estimated Annual Respondent Burden and Cost
ENERGY STAR Program: Joining the ENERGY STAR Program and Related Activities
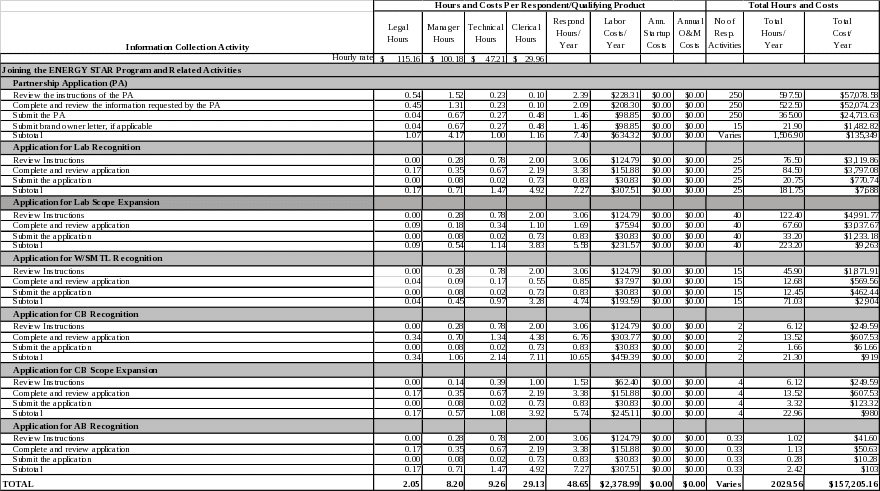
Exhibit 2
Estimated Annual Respondent Burden and Cost
ENERGY STAR Program: Certified Product Maintenance Activities
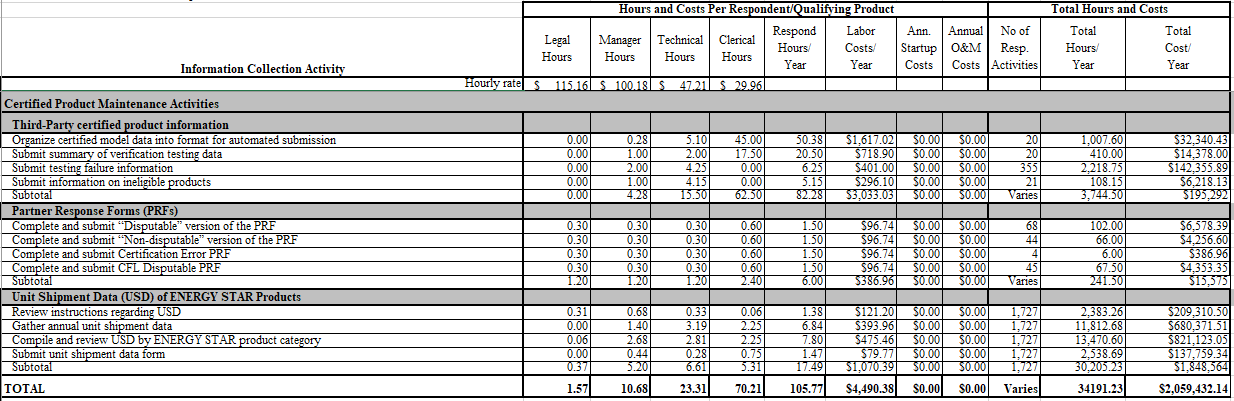
Exhibit 3
Estimated Annual Respondent Burden and Cost
ENERGY STAR Program: Partner of the Year (POY) and ENERGY STAR Most Efficient Recognition
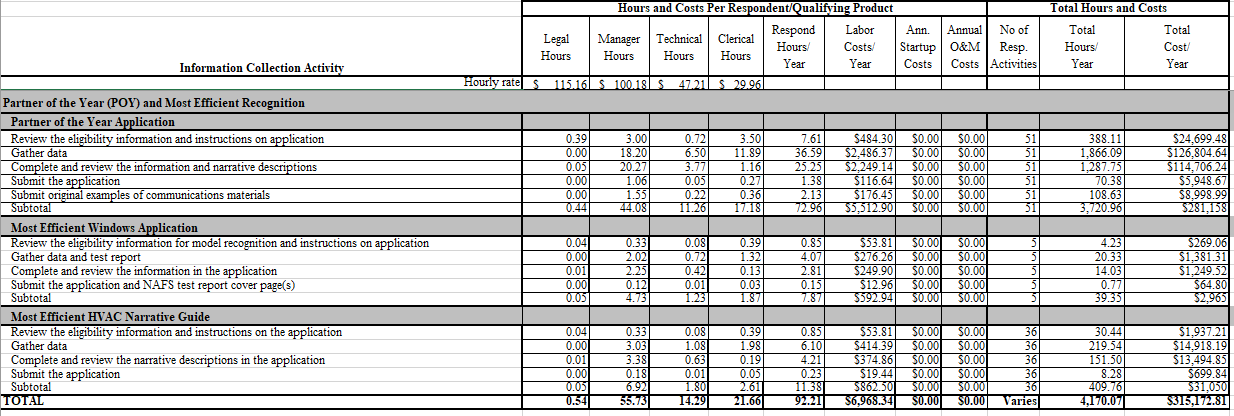
Exhibit 4: Estimated Annual Agency Burden and Cost
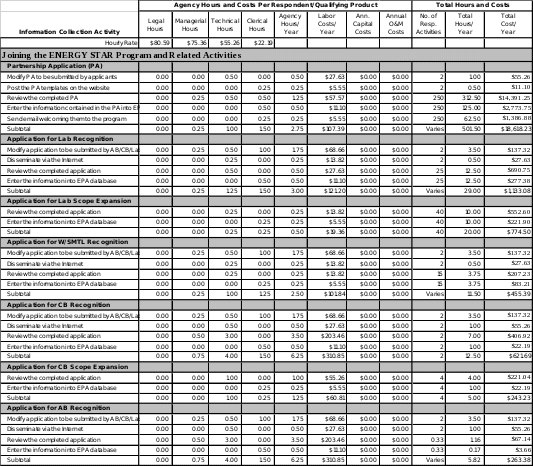
Exhibit 4 Cont.: Estimated Annual Agency Burden and Cost
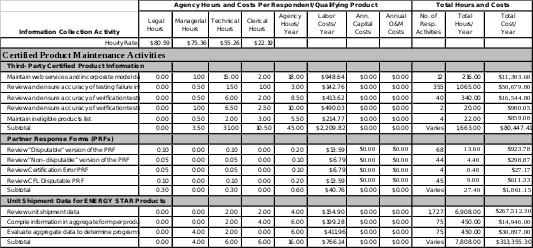
Exhibit 4 Cont.: Estimated Annual Agency Burden and Cost
6.e BOTTOM LINE BURDEN HOURS AND COSTS
(i) Respondent Tally
As shown in Table 1, EPA estimates the total annual hour and cost burden to respondents to be 40,391 hours and $2,531,810. The burden to respondents over the three years of this ICR is estimated to be 121,173 hours and $7,595,430.
Table 1: Total Estimated Annual Respondent Burden and Cost Summary
TABLE 1 |
|||||
TOTAL ESTIMATED ANNUAL RESPONDENT BURDEN AND COST SUMMARY12 |
|||||
Information Collections |
Total Hours Per Year |
Total Labor Cost Per Year |
Total Annual Capital Costs |
Total Annual O&M Costs |
Total Cost Per Year |
Joining the ENERGY STAR Program and Related Activities |
2,030 |
$157,205 |
$0 |
$0 |
$157,205 |
Certified Product Maintenance Activities |
34,191 |
$2,059,432 |
$0 |
$0 |
$2,059,432 |
POY and Most Efficient Recognition |
4,170 |
$315,173 |
$0 |
$0 |
$315,173 |
TOTAL |
40,391 |
$2,531,810 |
$0 |
$0 |
$2,531,810 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(ii) Agency Tally
As shown in Table 2, EPA estimates the total annual hour and cost burden to the Agency to be 11,241 hours and $482,308. The bottom-line burden to the Agency over the three years of this ICR is estimated to be 33,723 hours and $1,446,924.
Table 2: Total Estimated Annual Agency Burden and Cost Summary
TABLE 2 |
|
|||||||||||
TOTAL ESTIMATED ANNUAL AGENCY BURDEN AND COST SUMMARY13 |
|
|||||||||||
Information Collections |
Total Hours Per Year |
Total Labor Cost Per Year |
Total Annual Capital Costs |
Total Annual O&M Costs |
Total Cost Per Year |
|
||||||
Joining the ENERGY STAR Program and Related Activities |
585 |
$22,109 |
$0 |
$0 |
$22,109 |
|
||||||
Certified Product Maintenance Activities |
9,498 |
$395,664 |
$0 |
$0 |
$395,664 |
|
||||||
POY and Most Efficient Recognition |
1,158 |
$64,507 |
$0 |
$28 |
$64,535 |
|
||||||
TOTAL |
11,241 |
$482,280 |
$0 |
$28 |
$482,308 |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
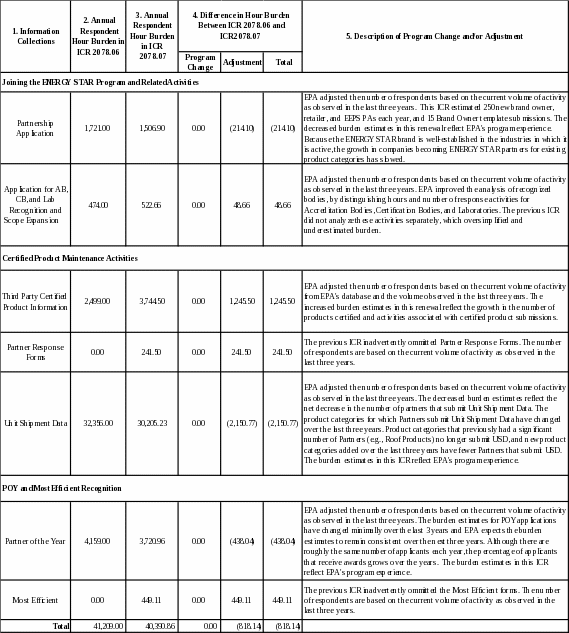
6.f REASONS FOR CHANGE IN BURDEN
EPA estimates a total annual respondent burden in this ICR, 2078.07, of 40,391 hours. This is a decrease of 819 hours from the currently approved burden of 41,210 hours in ICR 2078.06.
Table 3 explains this decrease. Specifically, the table presents the total annual hours estimated in ICR 2078.06 and ICR 2078.07 for each information collection (see columns 1-3). The table then compares their respective hours for each collection to derive the change in hours, and indicates whether this hour-change resulted from a program change and/or adjustment (see column 4). The table also briefly describes the program change and/or adjustment (see column 5). Finally, the table sums up all hour-changes to derive the total annual change in hours for all collections (see the bottom row of the table).
The table shows that there was an 819 hour decrease due to adjustments. There were no program changes.
The number of anticipated responses for Partnership Applications has decreased slightly from 280 in the previous renewal to 250 new Partnership Applications each year and an average of 15 brand owner/licensee agreements. These estimates are based on the average number of Partnership Agreements received over the last three years for Brand Owners, Retailers, and EEPS. Because the ENERGY STAR brand is well-established in the industries in which it is active, the growth in companies becoming ENERGY STAR partners for existing product categories has slowed.
The previous Product Labeling ICR did not include burden estimates for EEPS. ICR, 2078.07, consolidates the burden for the EEPS Partnership Application across all ENERGY STAR programs. As such, EPA ICR 1772.08 no longer estimates burden for EEPS Partnership Applications.
EPA adjusted the number of respondents for third-party certified product information based on the current volume of activity from EPA's database and the volume observed in the last three years. The increased burden estimates in this renewal reflect the growth in the number of products certified and activities associated with certified product submissions.
EPA has put significant investment in working with partners to increase their responses to the request for Unit Shipment Data. The number of responses for the Unit Shipment Data collection activity is approximately 1,727 responses. EPA adjusted the number of respondents based on the current volume of activity as observed in the last three years. The decreased burden estimates reflect the net decrease in the number of partners that submit Unit Shipment Data. The product categories for which Partners submit Unit Shipment Data have changed over the last three years. Product categories that previously had a significant number of Partners (e.g., Roof Products) no longer submit USD, and new product categories added over the last three years have fewer Partners that submit USD.
The previous ICR inadvertently omitted Partner Response Forms and the ENERGY STAR Most Efficient Forms. The number of respondents is this ICR is based on the current volume of activity as observed in the last three years.
EPA revised the number of Partner of the Year Applications from 57 in the previous renewal to 51 in this renewal based on the average number of award applications received over the last three years. The burden estimates for POY applications remain consistent over the years. Although there are roughly the same number of applicants each year, the percentage of applicants that receive awards grows over the years.
Table 3: Comparison of Total Annual Respondent Hours Under ICR 2078.06 and ICR 2078.0714
6.g BURDEN STATEMENT
The public reporting and recordkeeping burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 14 hours per response across all activities.
Burden means the total time, effort, or financial resources expended by persons to generate, maintain, retain, or disclose or provide information to a Federal Agency. This includes the time needed to review instructions; develop, acquire, install, and utilize technology and systems for the purposes of collecting, validating, and verifying information; adjust the existing ways to comply with any previously applicable instructions; search data sources; complete and review the collection of information; and transmit or otherwise disclose the information. An agency may not conduct or sponsor, and a person is not required to respond to, a collection of information unless it displays a currently valid OMB control number. The OMB control numbers for EPA’s regulations are listed in 40 CFR Part 9 and 48 CFR Chapter 15.
To comment on the Agency's need for this information, the accuracy of the provided burden estimates, and any suggested methods for minimizing respondent burden, including the use of automated collection techniques, EPA has established a public docket for this ICR under Docket ID No. EPA-HQ-OAR-2003-0033, which is available for online viewing at www.regulations.gov, or in person viewing at the at the Air and Radiation Docket in the EPA Docket Center (EPA/DC), EPA West, Room 3334, 1301 Constitution Ave., NW, Washington, DC.
The EPA Docket Center Public Reading Room is open from 8:30 a.m. to 4:30 p.m., Monday through Friday, excluding legal holidays. The telephone number for the Reading Room is (202) 566-1744, and the telephone number for the Air and Radiation Docket is (202) 566-1742. An electronic version of the public docket is available at www.regulations.gov. This site can be used to submit or view public comments, access the index listing of the contents of the public docket, and to access those documents in the public docket that are available electronically. When in the system, select “search,” then key in the Docket ID Number identified above. Also, you can send comments to the Office of Information and Regulatory Affairs, Office of Management and Budget, 725 17th Street, NW, Washington, DC 20503, Attention: Desk Office for EPA. Please include the EPA Docket ID No. EPA-HQ-OAR-2003-0033 and OMB Control Number in 2060-0528 in any correspondence.
1 Under the terms of an interagency Memorandum of Understanding, EPA is responsible for implementing the ENERGY STAR Program with technical support from DOE.
2 EPA is in the process of transitioning its database of ENERGY STAR partner and product information to a new platform. Once that transition is complete, which is estimated to take place by the end of 2020, the Participation Form will no longer be used.
3 The term, Partnership Application, is used to collectively refer to the Partnership Agreement Form and the Participation Form throughout the ICR; however, it is not a term used by the Labeled Products program.
4 The source of this information can be found at https://www.energystar.gov/about/origins_mission/energy_star_numbers.
5U.S. Census Bureau. North American Industry Classification System. Accessed on May 20, 2019 https://www.census.gov/eos/www/naics/.
6 U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), Occupational Employment Statistics (OES), May 2017 National Occupational Employment and Wage Estimates. Available online at: https://www.bls.gov/oes/2017/may/oes_nat.htm#23-0000.
7 For purposes of this analysis, the following occupational groups of the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) were used: Legal staff, SOC 23-1011, Lawyers; managerial staff, BLS SOC Code 11-1021, General and Operations Managers; technical staff, BLS SOC Code 17-3027, Mechanical Engineering Technicians; and clerical staff, BLS SOC Code 43-6014, Secretaries and Administrative Assistants, Except Legal, Medical, and Executive.
8 Bureau of Labor Statistics, Economic News Release, “Table 2. Seasonally adjusted: Employment Cost Index for wages and salaries, by ownership, occupational group, and industry.” Available online at: https://www.bls.gov/news.release/eci.t02.htm.
9 See 2019 General Schedule (Base), “SALARY TABLE 2019-GS RATES FROZEN AT 2018 LEVELS EFFECTIVE JANUARY 2019,” available at: https://www.opm.gov/policy-data-oversight/pay-leave/salaries-wages/salary-tables/pdf/2019/GS_h.pdf.
10 The total number of EEPS with ENERGY STAR Partner Accounts is distinct from the number of EEPS Partners actively responding to information collection requests. EPA estimates that around 200 EEPS Partners respond to information collection requests.
11 This ICR estimates the burden for EEPS Partnership Applications across all ENERGY STAR programs (e.g., Products, C&I). All EEPS complete and submit the same Partnership Application to EPA.
12 Table contains rounding.
13 Table contains rounding.
14 Table contains rounding.
| File Type | application/msword |
| Author | EPA |
| Last Modified By | SYSTEM |
| File Modified | 2019-09-25 |
| File Created | 2019-09-25 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy