2019 Urban Rate Study Statistical Methodology 3060-1192 (003)
2019 Urban Rate Study Statistical Methodology 3060-1192 (003).docx
Survey for Urban Rates for Fixed Voice and Fixed Broadband Residential Services
OMB: 3060-1192
3060-1192
June 2019
SUPPORTING STATEMENT
Part B: Statistical Methodology:
B.1. The specifics of the survey design described here (e.g., strata definitions, sample sizes) were based on data collected in the 2018 Urban Rate Survey. The methodology is essentially the same as the 2016 Urban Rate Survey methodology. The required sample sizes for both voice and broadband surveys also remain the same. The difference is that we will add more stratifications to the broadband survey to account for wider selection of broadband service plans on the market.
The specific example described here serves as the general template for designs of current Urban Rate Surveys. The respondent universe is providers of fixed voice or fixed broadband services in urban census tracts of the 50 United States, the District of Columbia, and Puerto Rico. We estimate the respondent universe as 694 urban providers of fixed voice services and 1,344 providers of fixed broadband services in 58,000 urban census tracts. Each (service provider, census tract) pair will be assigned a “measure of size” reflecting the number of potential subscribers offered service by the provider in the census tract. This number of potential subscribers will be calculated as:
Number of Potential Subscribers = Provider Presence Ratio x (households in the census tract)
where
Provider Presence Ratio = 1/(1 + 10 –Y),
Y = 2.289 + 0.776 Log10(X/(1-X)) + bn * staten 1, and
X = residential subscribers for provider in the tract / households in the tract. 2
The survey will collect a sample of urban rates for voice services and a separate sample of urban rates for broadband services. In both cases, the sampling unit will be a (service provider, census tract) pair and the sampling frame will be constructed from FCC Form 477.
For the voice survey, we will implement a Stratified Probability Proportional to Size (PPS) sampling, where the selection probability is a function of measure of size. Measure of size is the number of potential subscribers from a provider in a given census tract, as described earlier.
The sampling units will be divided into two strata depending on whether the service provider is an incumbent local exchange carrier (ILEC) or Non-ILEC. The total number of samples is 500. The sample size allocation between ILEC and Non-ILEC will be a proportionate allocation, where the sample size in each stratum is proportional to that of the total number of potential subscribers. A sample of 217 ILEC and 283 Non-ILEC sampling units will be selected randomly from their respective strata.
For the broadband survey, same as the voice survey, we will implement a Stratified PPS sampling, where the selection probability is a function of the number of potential subscribers from a provider in a given tract. The sampling units will be divided into 28 strata. The total number of samples is 500.
Past Urban Rate Surveys demonstrated that for many of the service providers (particularly the large national service providers), the rates offered for broadband services did not vary across census tracts. Stratification will allow us to reduce the number of survey responses requested in such cases while still capturing the offered rates in accordance with their estimated effect on the reasonable comparability benchmark. The terrestrial fixed wireless providers exhibit high price variations and their number of potential customers in a service area is limited by geographic constraints (line of sight). A terrestrial fixed wireless stratum will allow us to produce more precise price estimates. The Alaska strata will allow us to develop Alaska-specific benchmarks. The high bandwidth strata will allow us to develop benchmarks for service plans with download bandwidth up to 1 Gbps.
The following 28 strata will be used:
Service download bandwidth < 500 Mbps
AT&T (AT&T Services, Inc.)
CenturyLink (CenturyLink, Inc., CenturyLink Communications, LLC)
Charter (Charter Communications, Inc.)
Comcast (Comcast Cable Communications, INC.)
Cox (Cox Communications)
CSC Holdings (CSC Holdings LLC)
Frontier (Frontier Communications Corporation)
Verizon (Verizon New York Inc., Verizon Pennsylvania LLC, Verizon New Jersey Inc., Verizon California Inc., Verizon New England Inc., Verizon Virginia LLC, Verizon Maryland LLC, Verizon Florida LLC, Verizon Delaware LLC, GTE Southwest Incorporated dba Verizon Southwest, Verizon Washington, DC Inc.)
WideOpenWest (Knology, WideOpenWest, and Wiregrass Telcom) Windstream (service providers identifying Windstream as their holding company)
Terrestrial Fixed Wireless
Other Major
Other Minor
Service download bandwidth >= 500 Mbps (high bandwidth strata)
AT&T
CenturyLink
Charter
Comcast
Cox
CSC Holdings
Frontier
Verizon
WideOpenWest
Windstream
Terrestrial Fixed Wireless
Other Major
Other Minor
Alaska
Fixed services
Terrestrial Fixed Wireless
The Other Major and Other Minor strata will be divided3 depending on the number of potential subscribers, the number of occupied housing units to which the provider offers service, and Provider Presence Ratio in the sampling unit, based on Partitioning Around Medoids.4
For each sampling unit, except for the Terrestrial Fixed Wireless providers, the number of potential subscribers is calculated as:
Number of Potential Subscribers = Provider Presence Ratio x (Number of households in the sampling unit’s census tract)
For each sampling unit of the Terrestrial Fixed Wireless providers, the number of potential subscribers is calculated as:
Number of Potential Subscribers = 2 x (Number of residential subscribers)
Provider Presence Ratio is calculated as the fraction of housing units in the census tract for which the provider offered fixed broadband service.
Sample size allocation will be an optimum allocation with fixed cost, where the sample size for each stratum is proportional to the standard deviation of the distribution of the rates. This allocation is designed to minimize possible sampling variance. The sample size is calculated as:
nh = n * ( Nh * σh * wi) / [ Σ ( Nh * σi * wi) ]
where nh is the sample size for stratum h, n is total sample size, Nh is the population size for stratum h, σh is the Stratum standard deviation (SD) of stratum h, and wi is the square root of number of potential subscribers per unit for stratum h. The purpose of wi is to give extra weight to those units with larger number of potential subscribers in the census tract. Nh and wi are derived from the frame data.
Stratum SD (σh) is an estimate of the standard deviation of rates by service plan for the service providers in the stratum. Stratum SD is based on fixed broadband service rates provided in last year’s Urban Rate Survey. The Stratum SDs are calculated based on service plans with download bandwidths greater than or equal to 2 Mbps.
For a particular stratum identified with a service provider, all service rates are partitioned by service plan according to download bandwidth, upload bandwidth, and usage allowance. The variance of rates is calculated for each service plan. The Stratum SD is calculated as the square root of the average of these variances.5 For the Other Major, Other Minor, and high bandwidth strata, the standard deviation is calculated by applying the above procedure to all service plans, assigned to the current Other Major, Other Minor, and high bandwidth strata, from the last year’s broadband Urban Rate Survey.
Once each sample is selected, the survey will be organized by provider so that each provider surveyed is given a list of census tracts for which the appropriate urban service rate is to be provided.
We anticipate the high response rates from the voice and broadband surveys will continue. We contact directly any provider that is sent a survey notification that does not complete the online survey form within 30 days. Because compliance is mandatory, failure to comply may lead to enforcement action, including forfeiture penalties, pursuant to the Communications Act of 1934, as amended, and other applicable law.
B.2.
The survey will collect a sample of urban rates for voice services and a separate sample of urban rates for broadband services. In both cases, the sampling unit will be a (service provider, census tract) pair.
For the voice survey, the sampling units will be divided into two strata depending on whether the service provider is an incumbent local exchange carrier (ILEC) or Non-ILEC. The total number of samples is 500. The sample size allocation between ILEC and Non-ILEC will be a proportionate allocation, where the sample size in each stratum is proportional to that of the total number of potential subscribers. A sample of 217 ILEC and 283 Non-ILEC sampling units will be selected randomly from their respective strata.
For the broadband survey, the sampling units will be divided into 28 strata. The total number of samples is 500. Past Urban Rate Surveys demonstrated that for many of the service providers (particularly the large national service providers), the rates offered for broadband services did not vary across census tracts. Stratification will allow us to reduce the number of survey responses requested in such cases while still capturing the offered rates in accordance with their estimated effect on the reasonable comparability benchmark. The terrestrial fixed wireless providers exhibit high price variations and their number of potential customers in a service area is limited by geographic constraints (line of sight). A terrestrial fixed wireless stratum will allow us to produce more precise price estimates. The Alaska strata will allow us to develop Alaska-specific benchmarks. The high bandwidth strata will allow us to develop benchmarks for service plans with download bandwidth up to 1 Gbps.
The following 28 strata will be used:
Service download bandwidth < 500 Mbps
AT&T (AT&T Services, Inc.)
CenturyLink (CenturyLink, Inc., CenturyLink Communications, LLC)
Charter (Charter Communications, Inc.)
Comcast (Comcast Cable Communications, INC.)
Cox (Cox Communications)
CSC Holdings (CSC Holdings LLC)
Frontier (Frontier Communications Corporation)
Verizon (Verizon New York Inc., Verizon Pennsylvania LLC, Verizon New Jersey Inc., Verizon California Inc., Verizon New England Inc., Verizon Virginia LLC, Verizon Maryland LLC, Verizon Florida LLC, Verizon Delaware LLC, GTE Southwest Incorporated dba Verizon Southwest, Verizon Washington, DC Inc.)
WideOpenWest (Knology, WideOpenWest, and Wiregrass Telcom)
Windstream (service providers identifying Windstream as their holding company)
Terrestrial Fixed Wireless
Other Major
Other Minor
Service download bandwidth >= 500 Mbps (high bandwidth strata)
AT&T
CenturyLink
Charter
Comcast
Cox
CSC Holdings
Frontier
Verizon
WideOpenWest
Windstream
Terrestrial Fixed Wireless
Other Major
Other Minor
Alaska
Fixed services
Terrestrial Fixed Wireless
The Other Major and Minor strata will be divided depending on the number of potential subscribers, the number of occupied housing units to which the provider offers service, and Provider Presence Ratio in the sampling unit, based on Partitioning Around Medoids.
For each sampling unit, except for the Terrestrial Fixed Wireless providers, the number of potential subscribers is calculated as:
Number of Potential Subscribers = Provider Presence Ratio x (Number of households in the sampling unit’s census tract)
For each sampling unit of the Terrestrial Fixed Wireless providers, the number of potential subscribers is calculated as:
Number of Potential Subscribers = 2 x (Number of residential subscribers)
Provider Presence Ratio is calculated as the fraction of housing units in the census tract for which the provider offered fixed broadband service.
Sample size allocation will be an optimum allocation with fixed cost, where the sample size for each stratum is proportional to the standard deviation of the distribution of the rates. This allocation is designed to minimize possible sampling variance. The sample size is calculated as:
nh = n * ( Nh * σh * wi) / [ Σ ( Nh * σi * wi) ]
where nh is the sample size for stratum h, n is total sample size, Nh is the population size for stratum h, σh is the Stratum standard deviation (SD) of stratum h, and wi is the square root of number of potential subscribers per unit for stratum h. The purpose of wi is to give extra weight to those units with a greater number of potential subscribers in the census tract. Nh and wi are derived from the frame data.
Stratum SD (σh) is an estimate of the standard deviation of rates by service plan for the service providers in the stratum. Stratum SD is based on fixed broadband service rates provided in last year’s Urban Rate Survey. The Stratum SDs are calculated based on service plans with download bandwidths greater than or equal to 2 Mbps.
For a particular stratum identified with a service provider, all service rates are partitioned by service plan according to download bandwidth, upload bandwidth, and usage allowance. The variance of rates is calculated for each service plan. The Stratum SD is calculated as the square root of the average of these variances. For the Other Major, Other Minor, and high bandwidth strata, the standard deviation is calculated by applying the above procedure to all service plans, assigned to the current Other Major, Other Minor, and high bandwidth strata, from the last year’s broadband Urban Rate Survey.
Once each sample is selected, the survey will be organized by provider so that each provider surveyed is given a list of census tracts for which the appropriate urban service rate is to be provided.
The goal of the survey is to estimate the mean and standard deviation of the distribution of offered urban rates for a given service. These estimates will then be used to estimate upper and lower limits for carrier rates; for example, the mean plus twice the standard deviation is a possible upper limit based on the approximate 97.5 percentile of a normal distribution.
The estimate of the mean is
 =
=
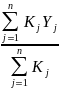
where Yj is the rate and Kj is the weight of the jth sampled rate. Similarly, the estimate of the standard deviation is
 =
=
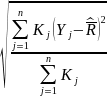
For both voice and broadband surveys, the sample will be selected based on probability proportional to the number of potential subscribers of each sampling unit. Kj will reflect the sampling weight which is the inverse of the selection probability for each sampling unit and the nonresponse weight to compensate for unit nonresponse in each stratum.
B.3. We anticipate the high response rates from the voice and broadband surveys will continue. We contact directly any provider that is sent a survey notification that does not complete the online survey form within 30 days. Because compliance is mandatory, failure to comply may lead to enforcement action, including forfeiture penalties, pursuant to the Communications Act of 1934, as amended, and other applicable law. Based on the sampling methodology described above and an anticipated high rate of compliance, the information collected should be both sufficiently accurate and reliable for the purpose of determine the rate floor and rate comparability benchmarks.
B.4. The total sample size for the voice survey will be similar to past years’ Urban Rate Survey. The sample size allocation between two strata (ILEC and Non-ILEC) will be a proportionate allocation, where the sample size in each stratum is proportional to that of the total number of potential subscribers.
The total sample size for the broadband survey will be similar to past years’ Urban Rate Survey.
The sample size allocation for the broadband survey will be an optimum allocation with fixed cost, where the sample size for each stratum is proportional to the standard deviation of the distribution of the rates. This allocation is designed to minimize possible sampling variance. The sample size is calculated as:
nh = n * ( Nh * σh * wi) / [ Σ ( Nh * σi * wi) ]
where nh is the sample size for stratum h, n is total sample size, Nh is the population size for stratum h, σh is the Stratum standard deviation (SD) of stratum h, and wi is the square root of number of potential subscribers per unit for stratum h. The purpose of wi is to give extra weight to those units with more number of potential subscribers in the census tract. Nh and wi are derived from the frame data.
Stratum SD (σh) is an estimate of the standard deviation of rates by service plan for the service providers in the stratum. Stratum SD is based on fixed broadband service rates provided in last year’s Urban Rate Survey. The Stratum SDs are calculated based on service plans with download bandwidths greater than or equal to 2 Mbps.
For a particular stratum identified with a service provider, all service rates are partitioned by service plan according to download bandwidth, upload bandwidth, and usage allowance. The variance of rates is calculated for each service plan. The Stratum SD is calculated as the square root of the average of these variances. For the Major, Minor, and high bandwidth strata, the standard deviation is calculated by applying the above procedure to all service plans, assigned to the current Major, Minor, and high bandwidth strata, from the last year’s broadband Urban Rate Survey.
Finally, adjustments will be made to the sample sizes so that a minimum of 5 sampling units is in each stratum.
B.5. The individuals within the agency who consulted on the statistical aspects of the design are:
Cha-Chi Fan, Mathematical Statistician, 202-418-1554
Craig Stroup, Industry Economist, 202-418-0989
Rodger Woock, Supervisory Industry Economist and Division Chief, 202-418-1560
The survey data will be collected and analyzed by these same individuals and other Industry Analysis Division of the Office of Economics and Analytics staff. We do not anticipate seeking assistance from outside the agency unit.
1 The bn is the coefficient for nth state.
2 We used a regression model to estimate the proportion of the census tract’s households to which a service provider offers service. The regression was developed from data relating broadband provider presence to broadband provider subscription. Linear regression was used to regress Log10 (p/(1-p)) on Log10 (s/(1-s)), where p is the fraction of housing units covered by the broadband provider in the census tract and s is the provider’s broadband subscriber fraction of households in the tract. This assumes that the relationship of voice provider presence to voice subscribership is similar to that of broadband provider presence to broadband subscribership.
3 The choice of two groups is determined by maximizing mean silhouette information according to a given clustering in k clusters. Silhouette Width is a measure to estimate the dissimilarity between clusters. A higher silhouette width is preferred to determine the optimal number of clusters. See reference for details: Rousseeuw, P.J. 1987. Silhouettes: A graphical aid to the interpretation and validation of cluster analysis. J. Comput. Appl. Math., 20, 53–65.
4 Partitioning Around Medoids is a type of cluster analysis to identify data clusters based on dissimilarities between clusters. See references for details: 1) Kaufman, L. and Rousseeuw, P.J. 1990. Finding Groups in Data: An Introduction to Cluster Analysis. Wiley, New York. 2) Park, H.S. and C.H. Jun. 2009. A simple and fast algorithm for K-medoids clustering. Expert Systems with Applications. 36(2):3336–3341.
5 Service plans with only one rate are ignored in the calculation.
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| Author | Suzanne Yelen |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 2021-01-16 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy