SHTG-FY-20-02 (Training and Educational Materials Develo
DOL Generic Solution for Funding Opportunity Announcements
4. CTS 10286 FY 2020 SH FOA 2 (4-22-2020)
2020 Susan Harwood Training Grant Program Funding Opportunity Announcement
OMB: 1225-0086
U.S. DEPARTMENT OF LABOR
Occupational Safety And Health Administration
Funding Opportunity Announcement/Notice Of Available Funding:
Susan Harwood Training Grant Program, FY 2020 Funding
Catalog of Federal Domestic Assistance Number: 17.502
Funding Opportunity Number: SHTG-FY-20-02
Grant Category: Training and Educational Materials Development
Action: This Funding Opportunity Announcement (FOA)/Notice of Available Funding is for eligible nonprofit organizations to develop classroom quality occupational safety and health training for workers and employers on one of the OSHA-specified topics. Successful applicants must test the training materials in a classroom environment.
Eligible Applicants: Non-profit organizations including qualifying labor unions, community-based and faith-based organizations, employer associations that are not an agency of a state or local government, institutions of higher education supported by a State or local government, Indian tribes, tribal organizations, Alaska Native entities, Indian-controlled organizations serving Indians, and Native Hawaiian organizations may apply.
Application Requirements: Applicants must follow the guidelines stated in this FOA before submitting a complete application package including attachments at www.Grants.gov (Grants.gov). Submission instructions are available at Grants.gov.
Application Deadline: This FOA closes on Month XX, 2020, at 11:59 p.m. eastern time. Applications not validated by Grants.gov, or submitted after this deadline, are ineligible for consideration.
Notice of Concurrent Funding Opportunity Announcement: This FOA
(SHTG-FY-20-02) is for Training and Educational Materials Development grant applicants. Applicants competing for a Targeted Topic Training grant (SHTG-FY-20-01) or for a Capacity Building Developmental or Pilot grant (SHTG-FY-20-03) must submit their application under the appropriate FOA. Applications submitted under the wrong FOA number are invalid and will not be considered.
Further Information: This FOA does not itself obligate any federal funds.
Information about the Susan Harwood Training Grant Program is located on the OSHA website at www.osha.gov/dte/sharwood/index.html. Email your FOA questions to HarwoodGrants@dol.gov, or call 847-725-7805, weekdays between 9:00 a.m. and 5:00 p.m. eastern time.
The Grants.gov Support webpage, www.grants.gov/web/grants/support.html, may have answers to your questions or problems regarding your application submission. In addition, you may contact them by email, Support@grants.gov, or telephone, 1-800-518-4726, 24 hours a day, 7 days a week (except federal holidays).
SHTG-FY-20-02 Training and Educational Materials Development Grant Instructions – Table of Contents
II. Program Overview and Funding Opportunity Description 6
D. 2020 Training and Educational Materials Development Topics 8
F. Targeted Training Audiences 11
IV. Grant Application and Submission 11
C. Required Application Content 12
1. SF-424 Application for Federal Assistance 12
2. SF-424A Budget Information – Non-Construction Programs 13
3. SF-424B Assurances – Non-Construction Programs 13
4. Project/Performance Site Location(s) 13
5. Grants.gov Certification Regarding Lobbying Form 13
6. SF-LLL, Disclosure of Lobbying Activities (if applicable) 13
7. Application Summary (not to exceed 2 pages) 13
8. Program Abstract (not to exceed 1/2 page) 13
9. Technical Proposal (not to exceed 20 double-spaced pages – see Appendix H) 14
Table 1: Training projections by training type and audience 19
Table 2: Training numbers for trainees and training contact hours 20
10. Fiscal Responsibility and Program Budgeting 20
D. Meetings, Reporting, and Documentation 22
Table 3: Grantee reporting due dates 23
F. Intergovernmental Review 25
G. Application Evaluation Criteria, Review, and Selection Process 25
H. Anticipated Award Announcement Date and Notification 25
I. Request for Application Comments 26
V. Post Award Administration 26
B. Grant Program Conditions 27
Appendix A – FY 2020 Training and Educational Materials Development Topics 30
Appendix A – FY 2020 Training and Educational Materials Development Topics (cont.) 31
Appendix A – FY 2020 Training and Educational Materials Development Topics (cont.) 32
Appendix B – Targeted Audiences 33
Appendix B – Targeted Audiences (cont.) 34
Appendix C – Application Checklist 35
Appendix D – Grants.gov Application Submission and Receipt Procedures 36
Appendix D – Grants.gov Application Submission and Receipt Procedures (Cont.) 37
Appendix D – Grants.gov Application Submission and Receipt Procedures (Cont.) 38
Appendix D – Grants.gov Application Submission and Receipt Procedures (Cont.) 39
Appendix E – Non-Viable Applications 40
Appendix F – Administrative and Program Costs Definition 41
Appendix F – Administrative and Program Costs Definition (Cont.) 42
Appendix F – Administrative and Program Costs Definition (Cont.) 43
Appendix G – Example of Budget Forms 44
Appendix G – Example of Budget Forms (Cont.) 45
Appendix H – Application Formatting Requirements 46
Appendix I – Application Summary Document Sample Outline 47
Appendix J – Program Abstract Narrative Example 48
Appendix K – Allowable/Unallowable Use of Grant Funds 49
Appendix K – Allowable/Unallowable Use of Grant Funds (Cont.) 50
Appendix L – Training and Educational Materials Development Criteria 51
Appendix M – Grant Funded Materials Submittal Process 52
Appendix M – Grant Funded Materials Submittal Process (Cont.) 53
Appendix M – Grant Funded Materials Submittal Process (Cont.) 54
I. Executive Summary
Under the authority of Section 21(c) of the Occupational Safety and Health Act of 1970
(OSH Act), the U.S. Department of Labor (DOL) Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) established its discretionary grant program in 1978. In 1997, OSHA renamed the program in honor of the late Susan Harwood, former director of the OSHA Office of Risk Assessment. The grant program offers opportunities for nonprofit organizations to compete annually for funding so they may develop and conduct training and educational programs for small business employers and workers on the recognition, avoidance, and prevention of occupational safety and health hazards in their workplaces, and to inform workers of their rights and employers of their responsibilities under the OSH Act.
The Susan Harwood Grant Program awards funds to qualifying organizations who have demonstrated capabilities to achieve the program’s performance expectations outlined in this FOA. This includes experience in employing subject matter experts, delivering and administering adult training programs, recruiting students, and managing grants. Following the grant awards, OSHA monitors each organization’s progress in achieving their performance goals and training targets. OSHA accomplishes this by conducting orientation meetings, training material reviews, training observations, program and financial monitoring visits, and quarterly and year-end report reviews.
For FY 2020, OSHA announces the availability of approximately $11.5 million to fund new Susan Harwood Training Program grants. Susan Harwood Training Program grants are subject to the availability of federal funding and appropriations. OSHA expects to award multiple grants to eligible nonprofit organizations under this competitive Funding Opportunity Announcement (FOA). Program funding is for a 12-month period beginning no later than September 30, 2020, and ending on September 30, 2021. The maximum award for a Training and Educational Materials Development grant is $75,000.
Applications submitted under this FOA are competing for a Training and Educational Materials Development grant. This FOA does not itself obligate any federal funds. The obligation of funds occurs when grant recipients acknowledge receipt and acceptance of award documents.
Applicants must propose to develop new training materials addressing one of the OSHA-specified training topics. The materials must include learning objectives, course matrices, presentation/training materials including videos, instructor and participant guides, student handouts, training evaluations, and learning assessments. Grantees must validate the training materials in a live classroom training session.
Organizations are restricted to one Susan Harwood Training grant award in a fiscal year. If an organization submits multiple applications, OSHA will review the last complete and viable application package submitted. Once submitted, applications are not available for additions, corrections, or revisions. To make changes to a submitted application, the organization must submit a new application package.
Eligible nonprofit applicants include qualifying labor unions, community-based and faith-based organizations, and employer associations that are not an agency of a state or local government. An institution of higher education supported by a state or local government is eligible to apply in accordance with OMB 2 CFR 200 and DOL exceptions in 2 CFR 2900. Indian tribes, tribal organizations, Alaska Native entities, Indian-controlled organizations serving Indians, and Native Hawaiian organizations are eligible to apply in accordance with Executive Order 13175.
Ineligible applicants are individuals, for profit organizations, 501(c)(4) nonprofit organizations, and FY 2019 Susan Harwood grantees with more than a 90-day time extension to their grant.
Information and forms needed to apply for this funding opportunity announcement are published on the www.grants.gov website (hereinafter “Grants.gov”). Prior to submitting an application, the applicant’s registration must be accurate, up-to-date, and active with Grants.gov and the System for Award Management (SAM). To maintain an active registration in the SAM database, an applicant must review and update their information every 12 months. Inaccurate or expired information may result in rejection of the grant application.
If an applicant is using Grants.gov for the first time, it is strongly recommended that the organization completes the steps to “Register as an Organization” with Grants.gov as soon as possible at www.grants.gov/web/grants/applicants/organization-registration.html. It can take up to five weeks to complete the registration process. Grants.gov requires applicants to have a DUNS number that may be acquired in one or two business days from the Dun & Bradstreet at fedgov.dnb.com/webform. The required SAM registration may take from two to more than five weeks to complete, and requires an employer identification number (EIN) and a notarized letter from the organization’s authorized representative. It is free to register with SAM at www.sam.gov.
To avoid delays that could result in the rejection of the application, the applicant must factor these processes into their plans for submitting their application. It is strongly recommended that applicants/organizations register with SAM themselves, and not rely on third parties to engage in SAM registration on their behalf. Third parties may misrepresent (intentionally or unintentionally) that they have obtained a SAM registration for the applicant/organization when they have not in fact done so. In cases where an applicant does not obtain and maintain an active bona-fide SAM registration, a grant application will be denied even if the applicant relied in good faith on a third party’s representation that an active bona-fide SAM registration was obtained. Additional information about these requirements is located in Appendix D.
II. Program Overview and Funding Opportunity Description
The Susan Harwood Training Grant Program funds eligible nonprofit organizations to develop training and educational materials on the recognition, abatement, and prevention of occupational safety and health hazards in workplaces. When developing and disseminating occupational safety and health training materials, consider these four program emphasis areas:
training that focuses on identifying and preventing occupational safety and health hazards in high-hazard industries;
training on new OSHA standards;
training on workplace hazards identified by the DOL Strategic Plan, OSHA special emphasis program, or other OSHA priorities (www.osha.gov/); and
training workers and employers in small businesses with 250 or fewer employees.
Applicants who demonstrate in their proposal that at least one census tract within their physical service area is designated by the Secretary of Treasury as a qualified Opportunity Zone will receive 2 points toward their overall application score. Applicants will not receive additional points for multiple Opportunity Zones within the proposed physical service area. For more information on Opportunity Zones, go to www.irs.gov/newsroom/opportunity-zones-frequently-asked-questions.
Please be aware the IRS list provides the full 11-digit census tract numbers. Use the example below to identify your census tract number(s):
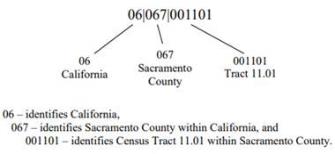
III. Award Information
OSHA may award a grant with or without negotiations with the applicant. Funding for the Susan Harwood Training Grant Program is subject to the availability of federal funding and appropriations.
Grants awarded under this FOA are for the development of occupational safety and health training and educational materials. Proposals must emphasize developing new training and educational materials on one OSHA-specified topic. Training must reach workers and employers from multiple small businesses.
Do not duplicate existing materials without a justification. New materials must fill an unmet need and be relevant and useful to a wide-range of trainers and trainees. New materials must include training goals, terminal, learning, and enabling objectives, course matrix, presentation materials, instructor manual/notes, PowerPoint presentations containing speaker notes, student materials, pre- and post-tests, and other useful resources. Applicants must describe how they will develop, evaluate, and validate new classroom-quality training and educational materials. To evaluate and validate the effectiveness of the new materials, grantees must conduct a pilot training to a targeted audience using the new materials.
Grant awards are for a 12-month performance period beginning no later than
September 30, 2020, and ending on September 30, 2021.
There is approximately $11.5 million available for new FY 2020 Susan Harwood Training grants. This includes $4.5 million for Capacity Building grants and approximately $7 million for Targeted Topic grants and Training and Educational Materials Development grants. Training and Educational Materials Development applicants may request federal funding up to $75,000. Applicants may commit non-federal resources, but it is not a grant requirement.
OSHA selected the following training topics for FY 2020. Training must address federal OSHA requirements for the recognition, abatement, and prevention of occupational safety and health hazards on the topic selected. Applicants must propose to develop training on one of the targeted topics listed below. Selecting more than one topic will make the application non-compliant and ineligible for consideration.
Agricultural safety and health – training materials covering hazards and preventive measures for farm and dairy workers, such as lockout/tagout, struck-by/caught between, falls, grain handling, grain bin entry, entrapment, combustible dust, and fires (may not include rescue training).
Bloodborne pathogens – training materials covering safeguards to protect workers against the health hazards from exposure to blood and other potentially infectious materials, and to reduce their risk from exposure.
Confined space – training materials covering confined space entry and hazards in construction, maritime, or general industry.
COVID-19 – training materials covering worker protection as it pertains to COVID-19 including personal protective equipment (PPE).
Drug misuse and hazards in the workplace – training materials covering the recognition of and hazards associated with drug misuse (abuse) in the workplace. This would include resources for employers and workers. Medical treatment and administration of neutralizing agents are beyond the scope of this topic.
Excavation/trenching – training materials covering proper excavation and trenching procedures including prevention of cave-in, collapse, entrapment, and related hazards.
Fire safety – training addresses fire hazards in the workplace, means of egress, and preparation for a fire emergency.
Healthcare – training materials for workers who provide health services to individuals. Safety and health hazards may include safe patient handling, workplace violence, and exposure to chemicals, gases, infectious diseases, bloodborne pathogens, and proper use of personal protective equipment.
Ladders and stairway safety – training materials covering the proper construction, use, placement, and care in using ladders and stairways.
Lockout/tagout – training materials covering procedures to protect workers from unexpected energizing or startup of machinery and equipment, including release of hazardous energy during servicing and maintenance.
Machine guarding/amputation prevention – training materials covering the operation of stationary equipment, press brakes, saws, shears, slicer, etc., guarding points of operations, and related hazards.
Maritime – training materials covering dock safety hazards such as dock edge protection, working over water, lifting equipment, cargo handling, mooring operations, gangways, fall protection, lifesaving equipment, traffic safety; marine terminal and longshoring industry hazards covering topics in 29 CFR 1917 and 29 CFR 1918; or shipyard safety such as electrical hazards, arc flash, ergonomics, personal protective equipment (PPE), flotation devices; or emergency procedures.
Natural disaster response and cleanup – training materials covering worker exposure and protection during disaster response and cleanup.
Noise/hearing conservation – training materials covering the identification, control, and protection of workers exposed to hazardous noise in construction, maritime, or general industry.
Oil and gas production – training materials covering hazards related to hydraulic fracturing, confined space, falls, explosions, fires, struck-by/caught-in/caught-between, and other hazardous exposures.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) – training materials covering the identification of hazards requiring PPE including the selection and proper use of PPE to protect workers from exposure and injury in the workplace.
Powered industrial trucks – training materials covering safety and health hazards when using, inspecting, and maintaining powered industrial trucks (e.g., forklifts, powered platforms, aerial lifts, and vehicle-mounted work platforms).
Residential construction hazards – training materials covering general safety and health hazards such as falls, electrical, hand/power tools, struck-by/caught-in/caught-between, drywall dust/respiratory protection, PPE, hazard communication, ladders, or scaffolds.
Respiratory protection – training materials covering the identification and use of proper protection to prevent worker injury, infection, and exposure to air contaminants such as harmful dusts, fog, fumes, mists, gases, smoke, vapors, or sprays.
Safety and health training for women – training materials covering occupational safety and health hazards for women in the workplace.
Safety and health training for youth – training materials covering workplace hazards for youth and workers new to the industry.
Scaffolding – training materials covering the proper construction and use of scaffolds including erecting and dismantling of scaffolds, fall protection, guardrails and cross bracing.
Silica – training materials covering the identification, evaluation, and control of silica exposure in construction, general, or maritime industries.
Other special emphasis or emerging industry topic – training materials covering an occupational safety and health topic identified by the applicant (applicant must include a persuasive argument to support the need for training materials for their chosen topic).
OSHA covers most private sector employers and workers. Under this grant program, grantees may train eligible workers and employers covered under the OSH Act of 1970, SEC. 4, codified at 29 U.S.C. 653 (Appendix B). Grant funds may not be used to train the applicant’s staff and employees.
This grant program does not cover activities that benefit state and local government employees unless the employees are responsible for occupational safety and health duties within their agency. These employees include agency’s safety and health trainers/program managers/committee members, or other employees who may be responsible for the abatement of unsafe and unhealthy working conditions in their agency. Most state and local government employees are ineligible trainees under this program, including those who may have occupational safety and health protection under a state operated OSHA-approved State Plan occupational safety and health program. For information about OSHA-approved State Plan occupational safety and health programs, go to www.osha.gov/dcsp/osp/index.html.
Training and educational materials must be in a language the participants can understand, and be appropriate for employers and workers in multiple small businesses. The focus of training and educational materials developed for this program is to reach workers and employers who are impacted by one or more of the following:
working in high-hazard industries;
working in industries with high fatality rates;
working in small new businesses (employing fewer than 250 employees); or
working with limited access to occupational safety and health training (young workers (ages 16-24), temporary, minority, low literacy, limited-English speaking, or other hard-to-reach workers).
IV. Grant Application and Submission
This announcement includes instructions for developing and organizing the application package. Application submission information and standard forms are available on the Grants.gov website. An organization may receive only one Susan Harwood training grant in any fiscal year; therefore, applicants should apply for only one grant under this FOA. If an organization submits more than one application for this funding opportunity, OSHA will review the last application accepted by Grants.gov.
Eligible applicants are limited to nonprofit organizations. Individuals, 501(c)(4) nonprofit organizations, and Susan Harwood grantees with a time extension to their
FY 2019 grant performance period of more than 90 days are not eligible for a FY 2020 award. Eligible applicants include qualifying labor unions, community-based and faith-based organizations, employer associations (may not be an agency of a state or local government), institutions of higher education supported by a state or local government, and Indian tribes, tribal organizations, Indian-controlled organizations serving Indians, Alaska Native entities, and Native Hawaiian organizations.
All organizations listed in an application as a partner, or as a part of a consortium, must be eligible to be a grantee as defined by this FOA, and must adhere to program requirements. An organization cannot be a grantee and a partner/subcontractor for another grantee during the same grant year. Grant duties may not be sub-awarded or passed through to other organizations or contractors. If contracting services, provide a description of the duties of each contractor and justify why the contractor is necessary and how the contractor will support grant goals. These contracts may require a full and open competition to meet the requirements of the award and 2 CFR 200.
The applicant is the lead partner and must have the ability, or develop the ability, to perform the program activities. The authorized representative and the financial certifying official must be identified in the application and employed by the lead partner. The authorized representative must have the authority to enter into a grant agreement, and will be the primary contact for OSHA communications regarding the grant.
Ineligible applicants are individuals and FY 2019 Susan Harwood grantees with more than a 90-day time extension to their grant. Additionally, 501(c)(4) nonprofit organizations that engage in lobbying activities are not eligible to receive federal funds that constitute an award, grant, or loan.
Prepare your grant application package using the checklist in Appendix C. After reviewing the Grants.gov application submission and receipt procedures in Appendix D, submit your application at www.Grants.gov (Grants.gov) prior to this announcement’s closing date and time. Refer to Appendix E for important information about application viability.
For Grants.gov questions, use the online answers section at Grants.gov Support (www.grants.gov/web/grants/support.html), or contact Grants.gov Applicant Support by emailing Support@grants.gov, or calling 1-800-518-4726. Grants.gov support is available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week except federal holidays.
If applying online poses a hardship, applicants must contact the OSHA Directorate of Training and Education (DTE) office at least three weeks prior to the application closing date. An OSHA representative will advise the applicant on how to submit an application online prior to the closing date. Send an email to HarwoodGrants@dol.gov, or call the Susan Harwood Grants Coordinator at 847-725-7805, weekdays between 9:00 a.m. and 5:00 p.m. eastern time excluding federal holidays.
OSHA will review complete applications only. Use the checklist in Appendix C to ensure you submit all the required documents listed below.
Funds requested must be rounded to the nearest dollar.
The amount entered on the SF-424, box 18a, is the official federal funding request.
The applicant information must be consistent on all application documents.
The authorized representative’s electronic signature on the SF-424, block 21, constitutes a binding offer by the applicant.
The authorized representative listed on the SF-424 must be the same authorized representative listed on the application summary document.
The projected budget must cover the 12-month performance period.
The projected budget must be allocated by cost categories on the SF-424A and the detailed budget support documentation.
Projected costs in each cost category must be shown as either a program or an administrative cost (defined in Appendix F).
Budget information provided on the SF-424A must match the information provided by the applicant on the detailed budget support and budget narrative documents. Examples of the SF-424A and the detailed budget support documents are in Appendix G.
The authorized representative’s electronic signature certifies the applicant’s agreement to comply with federal laws, executive orders, regulations, policies, grant requirements, certifications, and assurances governing this program.
The completed form identifies the sites and locations where grant activities will take place.
The authorized representative’s electronic signature certifies the applicant agrees to comply with lobbying restrictions. If item 2 is applicable, complete the
SF-LLL, Disclosure of Lobbying Activities form.
Complete only if the organization makes payments to lobbying entities with the intent to influence an officer, employee, or member of any federal agency or Congress in connection with a covered federal action.
Refer to Appendix H for approved formatting for the following documents:
Follow the example in Appendix I to provide basic information about the application.
Follow the guidance in Appendix J to describe briefly the focus of the proposed training material development plan and expected outcome.
Describe the applicant’s business, training experience, interaction with the target audience, successes in completing program obligations, staff’s occupational safety and health knowledge and experience, and planned activities for accomplishing project goals. Use the following outline for the proposal:
Proposal Identification
Applicant/organization name
Grant category (Training and Educational Materials Development)
Training topic
Targeted industry
Proposal Narrative
Organization and Partners Background
Provide an overview of the organization, its purpose, function, usual business activities, and the past five years of experience with governmental (federal, state, or local) grant programs. Discuss the organization’s experience with occupational safety and health, conducting training, and interacting with adults. Include a list of organizational activities that are specific to the selected training topic or industry. Address experience developing materials and training programs, providing training, and other services related to the selected training topic. If the organization has experience developing or conducting the proposed type of training, attach a list of the training conducted or training materials developed over the past five years. Describe the program and include the program titles, type(s) of training materials developed, and if applicable, the numbers of workers and/or employers trained, the trainee contact hours, and whether the materials or training developed were part of a previous Harwood grant. Describe the organization’s experience in conducting and using level 1 training session reaction evaluations and level 2 trainee learning assessments.
Staff Experience
The applicant must use knowledgeable staff to support this grant program. Describe the key personnel and professional staff who will be working on project activities. Describe their experience in developing training materials for adult learners, occupational safety and health qualifications, experience with the training audience, and other experience relevant to the work activities proposed in the application. Include the following attachments:
Organizational chart (may be an attachment)
Identify by name and position the staff working on the grant
Resumes, curricula vitae (CVs), position description/minimum hiring qualifications
Show occupational safety and health knowledge and experience;
Key personnel (authorized representative, project director, and others who spend more than 50% of their time on grant activities)
Professional staff (material developers, trainers, etc.)
Problem, Purpose, and Funding Needs Statement
Provide a clear and concise statement about the goals for the project, issues addressed by the training, and organizational need for federal assistance. The statement may address unmet training needs of an identified industry and population including issues preventing them from obtaining training.
Work Plan Proposal
The work plan allows the applicant to list the grant activities required to complete the project requirements and goals during the 12-month performance period. The work plan proposal is comprised of two components, a matrix table that identifies the grant activities by quarter, and a descriptive narrative about the planned activities. The work plan must address the following:
Training materials to be developed;
Targeted audience, including workers and employers;
Evaluations of the new materials;
Proposal for pilot testing of materials;
Recruitment of trainees
Training session(s)
Training locations and method of delivery
Trainees and training contact hours for each proposed training
Trainer/trainee access to the final materials; and
Anticipated benefits and impact the new materials will have on workplace safety and health.
The work plan must be reasonable and achievable within the 12-month grant performance period. Grantees are accountable for completing the activities listed in the work plan and meeting the proposed quarterly training projections. The work plan goals are the basis for measuring actual quarterly performance reported to the Assistant Secretary of Labor. Grantees must be mindful of performance issues and consult with OSHA as early as possible.
A work plan activity table divided by program quarter for the 12-month performance period must include the activities and tasks projected for each performance quarter. The project’s quarters are:
Quarter 1: September 30, 2020 – December 31, 2020
Quarter 2: January 1, 2021 – March 31, 2021
Quarter 3: April 1, 2021 – June 30, 2021
Quarter 4: July 1, 2021 – September 30, 2021
Develop the work plan activity table to identify the expected results and who, what, when, where, or how the activity or task supports accomplishing the work plan goals. Include all required grant-related activities in your work plan. These include attending OSHA-required meetings and monitoring visits, submitting training materials for OSHA review, submitting quarterly reports, projecting training sessions, projecting trainee numbers and training contact hours, and other grant related activities.
Work plan detailed narrative describes the activities, tasks, and expected results of the project’s performance goals. Program requirements are:
Training and Educational Materials
Applicants must develop new occupational safety and health training and educational materials. They may not duplicate existing materials without a justification. Training materials must address the recognition, abatement, and prevention of occupational safety and health hazards by covering federal OSHA requirements. State OSHA program requirements may not be included in the training materials.
The materials may include a brief overview of OSHA Whistleblower Protection Programs regarding employee rights and employer responsibilities. The overview must be limited to no more than 10 percent of the contact hours, but should not exceed 30 minutes.
OSHA posts grant-developed training materials on the OSHA public website located at www.osha.gov/dte/grant_materials/index.html. These materials cover various topics in multiple languages. Training materials developed under this grant will increase this valuable resource. Training materials include promotional flyers, advertisements, training objectives, presentation/training materials, instructor guides/presenter notes, videos, student manuals/handouts, student exercises, sign-in sheets, pre- and post-tests assessments (or other methods for testing student safety and health knowledge and skills), and evaluations for training material content, instructor, and training environment. Grantees must adhere to all copyright laws and provide a written certification that materials are free from copyright infringements.
Classroom quality Training and Educational Materials must follow the Instructional Systems Design (ISD) that focuses on quality measures for training and educational products. The five major ISD phases are analysis, design, development, implementation, and evaluation (ADDIE Model). Go to www.nwlink.com/~donclark/hrd/sat.html to learn more about the ADDIE model.
Applicants must provide a well-developed concept about the training and educational materials they propose to develop, and describe how the materials will be translated into a non-English language, if applicable. Include an estimated timeline to develop, evaluate, validate, and produce the materials. Explain how the proposed training and educational materials will fill an unmet training and/or training materials need, and describe how the materials will be applicable for other organizations and trainers. Grantees must validate their materials with at least one training session to evaluate content feedback and the need for content revision.
Grantees are encouraged to review the guidance document “Best Practices for the Development, Delivery, and Evaluation of Harwood Training Grants” at www.osha.gov/dte/sharwood/best-practices.html. An updated publication, “Resource for Development and Delivery of Training to Workers,” is available at www.osha.gov/Publications/osha3824.pdf. These resources address needs assessments, proven adult learning techniques, effective models for worker training, and training evaluation documentation.
Acknowledgment of DOL funding is required on all materials developed or revised under the grant. This includes promotional/program flyers and advertisement, training presentations, videos, handouts, student and trainer manuals, evaluations and testing instruments, and student sign-in sheets. Every material developed shall contain the following disclaimer:
This material was produced under grant number SH-____-SH_ from the Occupational Safety and Health Administration, U.S. Department of Labor. It does not necessarily reflect the views or policies of the U.S. Department of Labor, nor does mention of trade names, commercial products, or organizations imply endorsement by the U.S. Government.
OSHA must approve the English version of the grant materials before the grantee may use the materials to conduct a pilot training or translate them into another language. Allow at least three weeks for OSHA to review materials for technical accuracy and suitability. If the grantee revises the materials after receiving OSHA approval, the grantee must submit the updated materials to OSHA for re-approval.
OSHA reserves the right to review the translated materials prior to their use. OSHA may request the grantee to certify accuracy of the translation by identifying the translator and providing the translator’s qualifications. Organizations proposing to develop Spanish-language training materials must use appropriate terminology from the OSHA dictionaries located at www.osha.gov/dcsp/compliance_assistance/spanish_dictionaries.html.
Grantees must post all final training materials on their website in a free downloadable format for three years after the grant is closed. They must provide OSHA with the URL address/direct link to the materials and one (1) bound paper copy and two (2) electronic copies of the final materials no later than the last day of the grant performance period.
OSHA’s Internet posting requirements apply to all materials developed with grant funds. Grantees must provide one (1) bound paper copy and two (2) electronic copies of the final training materials to OSHA no later than the last day of the grant performance period, September 30, 2021. Materials must be compliant with Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973, as amended. This Act requires electronic and information technology (EIT) documents to be accessible for people with disabilities. Section 508 guidance checklists are at www.hhs.gov/web/section-508/making-files-accessible/index.html.
2. Training Plan and Projections
Grantees must pilot their training materials in a classroom environment. Provide a plan for recruiting workers and employers from a targeted audience defined in this funding opportunity. Classroom training will validate the suitability of the training materials for the targeted audience. Individuals trained at conferences or as part of a needs assessment are ineligible trainees, and are not reportable as workers trained or as training contact hours.
The training must focus on a chosen occupational safety and health topic, and must actively involve workers during the training. Provide a description of the method you will use to reach multiple employers and their workers. Explain how you will achieve a participatory learning environment.
A training session must last a minimum of 30 minutes, but may not exceed 7½ trainee contact hours per day. Contact hours refer to time spent covering course content. Trainee contact hours do not include breaks, lunchtime, or instructor-led minutes used for administrative activities such as trainee sign-in, general training site information, training presentation evaluation, or presentation of certificates of completion. If the training occurs over multiple days, the trainee must attend the entire training before the grantee may count them as trained, or to include their contact hours in the quarterly report. Training that begins in one quarter, but ends in the next quarter is reported only in the quarter the training is completed.
training class size must be no fewer than 10 and no more than 30 trainees to facilitate participatory learning that actively involves the trainees. The grantee must ensure the class size is sufficient to evaluate the effectiveness of the training materials.
Training evaluation and assessments are important in validating training materials and improving the training presentation. In accepting grant funding under this program, the grantee agrees to fully cooperate with and provide any data needed for the federally-sponsored evaluation(s) of the training. Training materials and the pilot training must include two levels of training evaluations:
Level 1 – Training Session Evaluations measure how trainees react to the training experience including trainees’ perceptions of the training environment, instructor(s), and quality and usefulness of the training. Level 1 evaluations must be in writing and completed by the trainee. If language or literacy is an issue, the evaluation may include an instructor-documented verbal satisfaction survey.
Level 2 – Trainee Learning Assessment measures the skills, knowledge, and safety attitude the trainee acquires and retains. The instructor must document the pre- and post-training assessment results of each trainee to evaluate the increase in the trainee’s knowledge of the topic. The pre- and post-assessment must measure the training objectives and match in content, format, and approach. This will accurately document changes in trainees’ knowledge and skills because they participated in the training.
Evaluations and assessments from the pilot training must be retained for OSHA monitoring purposes.
Training projections define the proposed training sessions by type of training, course duration, projected number of trainees, and training contact hours. Include a table similar to the following:
Table 1: Training projections by training type and audience
-
Type of Training
Length of training (hours)
Projected Number of Trainees
Total Contact hours
Worker
2
10
20
Employer
4
5
20
Total
15
40
Trainee numbers and training contact hours are estimates based on proposed pilot training. Describe the methodology used to develop the estimates. Projections must be a single number estimate (not a range) as shown in the table below:
Table 2: Training numbers for trainees and training contact hours
-
Quarter
Performance Period
Projected Pilot Trainees
Projected Pilot Contact Hours
Quarter 1
October 1 to December 31
0
0
Quarter 2
January 1 to March 31
0
0
Quarter 3
April 1 to June 30
5
20
Quarter 4
July 1 to September 30
10
20
Totals
15
40
Institutions of higher education must observe Constitution Day and Citizenship Day on September 17 in accordance with 36 USC 106, Consolidated Appropriations Act. The U.S. Department of Education requires every school and college receiving federal money to teach about the U.S. Constitution on the anniversary date of the adoption of the Constitution in 1787. Visit archive.opm.gov/constitution_initiative/ for relevant information. This grant does not fund these activities.
Briefly describe the organization’s financial management process including any separation of fiscal duties and internal funds controls.
The funds requested on the SF-424, Application for Federal Assistance, box 18, take precedence over funds shown on all other documents. Funds requested must be rounded to the nearest dollar. It is important the supporting budget information matches the requested funding stated on the SF-424. Supporting budget documents include the SF-424A, Budget Information – Non-Construction Programs, the project funding stated on the application summary document, and the total funding allocated in the detailed budget and budget narrative.
The applicant’s budget and budget narrative must demonstrate that the funds requested are necessary and sufficient to cover the cost of project activities identified in the proposal. The federal share of the budget shall not exceed the maximum award established in this FOA. No additional federal funds will become available during the performance period.
Proposed costs must be necessary, reasonable, and follow federal guidelines. Allowable costs support developing training and educational materials, recruiting activities, and conducting pilot training on the new materials related to the identification and abatement of occupational safety and health hazards in the workplace. All costs must comply with federal cost principles found in the Uniform Guidance in 2 CFR 200 and 2 CFR 2900. Appendices F and K identify allowable costs for this program.
A detailed project budget support narrative must describe and justify the projected costs stating the methodology for each cost allocation. This includes providing a budget and cost allocation details for all partners. Explaining how the partner’s costs are included in the proposed grant budget. Clearly describe the costs related to the program and administrative activities for the 12-month performance period as shown on the SF-424A, Budget Information. Cost categories must match the SF-424A categories, and be identified as either administrative or program, as defined in Appendix F. The budget must include all grant funding (federal award and non-federal funds, if applicable).
The personnel and benefits cost categories of the detailed budget and narrative must include the names, positions, and percent of time the staff works on grant activities. For the other cost categories, provide detailed lists such as travel locations, supplies, services, and other costs necessary for the project. Show how the costs are calculated. For service contracts, state the purpose of the contract, anticipated duties, and the method for calculating the costs. Contracts must meet the requirements stated in Appendix F.
Administrative costs are costs that support the management and administration of the project. These include salaries and benefits for the authorizing representative, financial certifying representative, administrative assistants, and others who manage the grant and/or complete the reporting requirements, travel costs to attend OSHA-required meetings, and cost of supplies and materials used for administrative tasks. Indirect costs are applicable only as an administrative cost under this grant.
The focus of this program is occupational safety and health training. OSHA has established a maximum allowance for administrative costs under this funding opportunity to be no more than 25 percent of the total funding amount (federal award and applicant’s non-federal funds).
Program costs are direct costs and services necessary to develop and conduct the training and educational program. These include salaries and benefits for the project director, developers, trainers, travel costs to conduct training, and costs to purchase supplies and materials needed for the training development and presentation. Grantees may not use grant funds to compensate trainees or their employers during the grant period, including refreshments, gift cards, stipends, or other enticements.
Applicants must have the capacity to develop training materials, manage websites, and create videos without requesting funding for costly equipment or software purchases. Applicants must provide a justification for proposed purchases explaining why the expenses are necessary for training development. This grant program does not support purchases to establish or update offices or training spaces including desks, tables, chairs, file cabinets, room dividers, technical equipment, machinery, or models. Information about allowable administrative and program costs is included in Appendix K.
Applicants must identify all voluntary resource contributions used to support the project. Describe the source(s) of funds and amount(s). Explain how these funds will be used to support the goals and objectives of this grant program.
The voluntary contributions may not include federal funds received from another agency nor may grant funds be used to pay consultants who are federal employees, or federally funded state employees such as OSHA 21(d) consultants or 23(g) compliance officers.
Indirect or 10 percent de minimis costs allocated to the budget require appropriate supporting documentation. Applicants must submit a copy of their approved negotiated Indirect Cost Rate Agreement (ICRA) with their application. The effective dates in the ICRA must cover the entire grant performance period.
Applicants without an approved ICRA, and who have never had an ICRA, may add a 10 percent de minimis rate to their budget based on their Modified Total Direct Costs (MTDC) as described in 2 CFR 200.68 and 2 CFR 200.414. If allocating a 10 percent de minimis rate to their budget, applicants must provide their method for identifying and calculating the MTDC. All indirect or 10 percent de minimis costs are administrative costs for this grant.
This program requires evidence of an organization’s non-profit status. An institution of higher education supported by a state or local government is exempt. Attach a legible and recent copy of one of the following documents:
Internal Revenue Service letter recognizing the applicant as tax exempt under the Internal Revenue Code, 26 U.S.C. § 501(c)(3);
State taxing body or Secretary of State letter certifying that the organization is a nonprofit organization operating within the state and that no part of its net earnings benefits any private shareholder or individual;
Certified copy of the applicant’s certificate of incorporation or similar document that clearly establishes the nonprofit status of the applicant;
Parent (state or national) organization’s proof of non-profit status listed above, and a statement from the parent organization that the applicant is a local nonprofit affiliate; or
Comparable documentation to that listed above supporting the non-profit status for Indian tribes and other tribal organizations.
Grantees must participate in OSHA meetings and monitoring/observation visits, maintain training documentation, and submit quarterly progress reports. Applicants must include these activities in their work plan and show related costs in their budget proposal. OSHA uses the activities listed in the work plan to measure the grantee’s progress toward the work plan goals. These assessments allow OSHA to evaluate the grantee’s performance and to provide guidance to the grantee as needed. OSHA Instruction TED 03-00-002, “Administering OSHA Discretionary Grant Programs” establishes the requirements. Go to www.osha.gov/dte/sharwood/grant_requirements.html to view the document.
A grantee orientation meeting is mandatory and occurs early in the performance period at a location determined by OSHA. All applicants must budget for two staff members (one program and one financial) to attend this meeting. While an orientation meeting may occur at each OSHA regional office, applicants should budget the time and travel-related costs as an administrative cost based on travel to Chicago, IL.
Grantee reporting requirements include quarterly submission of financial and program progress reports to OSHA. Quarterly reports include a comparison of the planned activities to actual accomplishments, and may include proposed corrective actions, if needed. Quarterly reports are due no later than 30 days after the end of the quarter. The grant closeout report is due no later than 90 days after the end of the grant period. Personnel time and other costs related to OSHA meetings, reporting, and visits requirements are administrative costs.
Table 3: Grantee reporting due dates
-
Report
Reporting Period
Due Date
Quarter 1
10/01/2020 – 12/31/2020
01/30/2021
Quarter 2
01/01/2021 – 03/31/2021
04/30/2021
Quarter 3
04/01/2021 – 06/30/2021
07/30/2021
Quarter 4
07/01/2021 – 09/30/2021
10/30/2021
Closeout/Final
09/30/2021 – 12/29/2021
12/29/2021
SF-425 Federal Financial Report (FFR) is due 30 days after the end of each quarter showing grant expenses for that quarter. The final report is due no later than 90 days after the end of the grant performance period. No expenditures may be obligated to the grant during the closeout period.
The OSHA 171, Grantee Quarterly Progress Report, and progress narrative are due to the regional program staff within 30 days after the end of each quarter. The OSHA 171 is a quantitative report showing the date and location of the training sessions, the number of workers and employers trained, and training contact hours. A separate OSHA 171 is required for each type/tier of training conducted during the quarter.
Accompanying the OSHA 171 is a written self-analysis of the grantee’s progress toward meeting quarterly work plan goals. The grantee identifies successes, challenges, and gaps in meeting work plan goals. When possible, the assessments and evaluations shall provide quantitative and qualitative results.
The analysis of level 1 training evaluations and level 2 trainee assessments must describe the instructor(s)’ training effectiveness, changes in the trainees’ knowledge/skill level, safety attitude, workplace practices, and any long-term changes in the trainees’ safety attitudes and in their workplaces. If the grantee recognizes a gap in achieving their work plan activities, the grantee must identify a plan to resolve the issues that prevented them from reaching their work plan goals.
The “Instructions for Preparing Grantee Quarterly Progress Reports” printed on the back of the OSHA 171 describe the reporting format. The narrative report must address the following:
Quarterly activities completed and compared to the work plan;
Training materials developed;
Recruitment activities;
Pilot training conducted, including type of training;
Training evaluation /assessments completed with results (levels 1 and 2);
Successes and challenges identified;
Corrective plans implemented to correct performance deficiencies; and
Other activities accomplished.
The closeout report is a narrative stating the final analysis of the entire grant performance period, and is due no later than 90 days after the grant ends. This cumulative report summarizes the grant activities by highlighting successes and problems. The report explains how the grant and grant activities enabled the grantee to accomplish the work plan goals. The report must include a summary of the level 1 evaluations and level 2 assessments results. For grants ending on September 30, 2021, the grant closeout report is due no later than December 29, 2021.
Self-certifications must accompany the closeout report. Self-certifications must be on the organization’s letterhead and signed by the authorized representative. The grantee certifies that:
Ineligible audiences did not participate in grant-funded programs or receive grant-funded materials; and
Materials developed with grant funds are free from copyright infringements.
OSHA reserves the right to implement special program requirements and may request additional documentation related to grant activities during the grant cycle. Grantees must immediately respond to OSHA or DOL requests for performance and/or training impact evaluations relating to this grant program. Other special requests may relate, but are not limited, to site visits, review of program, administrative, performance data, and interviews with grant personnel and participants.
The grant application package includes forms and attachments itemized in the Application Checklist located in Appendix C. Use the checklist to verify a complete application package prior to submitting the application at Grants.gov. Attachments submitted as a part of the Grants.gov grant application must be either Microsoft Office or Adobe Acrobat (PDF) documents. Missing and incomplete documents may affect the viability of the application.
Attach required documents only. Do not include sample documents of training materials or training programs. The application summary, program abstract, technical proposal, resumes for key personnel, position descriptions for key vacancies, and budget support documentation are required documents. Other attachments may include a list of prior government grants and signed letters of commitment to the project. If desired, attach the organization chart(s) for the applicant and the partners separately from the technical proposal. However, do not separate other components of the technical proposal including the work plan or work plan matrix.
The Susan Harwood Training Grant Program is not subject to Executive Order 12372 Intergovernmental Review of Federal Programs.
OSHA will screen applications only after Grants.gov determines the viability of the submission. OSHA will use the checklist in Appendix C to determine whether the application meets the requirements of the FOA. Applications who do not comply with one or more of the requirements are non-responsive and disqualified.
A technical panel of OSHA staff will rate each responsive application against a defined criterion similar to the one included in Appendix L. After reviewing the panel ratings, comments, and recommendations, the Assistant Secretary will consider Agency priorities, training value, geographic presence, related cost, and other factors before selecting the applications most advantageous to the government. The Assistant Secretary’s award decisions are final.
Award announcements will occur before September 30, 2020. The Assistant Secretary, or representative, will notify successful applicants. Directorate of Training and Education (DTE) will mail consolation letters to the unsuccessful applicants. The award notice sent to a successful applicant does not constitute approval of the submitted grant application. The acceptance of a proposal and award of federal funds to sponsor any program does not constitute a waiver to comply with grant requirements or procedures. OSHA may elect to award a grant with or without negotiations with the applicant. A grant awarded without negotiations constitutes a binding offer by the authorized representative, shown on the SF-424, Section 21 (the Grants.gov E-Authentication electronic signature) and the application summary document.
OSHA may enter into negotiations with the applicant regarding compliance with program components, staffing, budgeting, funding levels, and/or administrative systems. If negotiations do not result in an acceptable submittal, the Assistant Secretary reserves the right to terminate the negotiation and decline to fund the proposal. Awardees must submit negotiated revisions to their application to the appropriate Regional Office by October 31, 2020.
Award decisions are final and cannot be appealed. Unsuccessful applicants may request comments on their application until March 31, 2021. Requests must be on the organization’s letterhead and signed by the authorized representative as shown in Section 21 of the SF-424, Application for Federal Assistance, and/or identified as the authorized representative on the application summary document. Send requests by email to HarwoodGrants@dol.gov, or by regular mail to:
Susan Harwood Training Grants Program Coordinator
U.S. Department of Labor, OSHA
Directorate of Training and Education
2020 South Arlington Heights Road
Arlington Heights, IL 60005-4102
Include information with the written request:
Funding Opportunity Announcement number (SHTG-FY-20-02);
Grants.gov Tracking Number (GRANT____________);
Organization name;
Training topic;
Authorized representative’s name and complete mailing address, zip + 4; and
A contact phone number or e-mail address.
V. Post Award Administration
All grantees, including faith-based organizations, are subject to applicable federal laws and regulations (including provisions of appropriations law) and the applicable OMB Uniform Guidance. Grantees are required to cooperate with all federal, state, and local requirements. The grant awards under this FOA are subject to the following administrative standards and provisions, as applicable to the particular grantee.
29 CFR 2, Subpart D, equal treatment regulations;
29 CFR Parts 31, 32, 35, and 36, as applicable;
29 CFR 93, restrictions on lobbying;
2 CFR 200, Uniform Administrative Requirements, Cost Principles, and Audit Requirements for Federal Awards (Uniform Guidance), which covers grant requirements for nonprofit organizations, including universities and hospitals (www.gpo.gov/fdsys/pkg/FR-2013-12-26/pdf/2013-30465.pdf);
2 CFR 2900, Department of Labor exceptions to the OMB Uniform Guidance (www.gpo.gov/fdsys/pkg/FR-2014-12-19/pdf/2014-28697.pdf);
General Terms and Conditions of Award (www.osha.gov/dte/sharwood/grant_requirements.html);
Federal Funding Accountability and Transparency Act of 2006 or Transparency Act – Public Law 109-282, as amended by section 6202(a) of Public Law 110-252 (31 U.S.C. 6101) (edocket.access.gpo.gov/2010/pdf/2010-22705.pdf);
2 CFR 25, Financial Assistance Use of Universal Identifier (edocket.access.gpo.gov/2010/pdf/2010-22706.pdf);
2 CFR 170, Reporting Subaward and Executive Compensation Information (www.ecfr.gov/cgi-bin/text-idx?tpl=/ecfrbrowse/Title02/2cfr170_main_02.tpl); and
41 U.S.C. 702 – Drug-Free Workplace Requirement for Federal Grant Recipients Act of 1988, and 2 CFR 182 (www.gpo.gov/fdsys/granule/USCODE-2009-title41/USCODE-2009-title41-chap10-sec702).
Drug-free workplace: The Drug-Free Workplace Act of 1988, 41 U.S.C. 702 et seq., and 2 CFR 182 require that all organizations receiving grants from any federal agency maintain a drug-free workplace. The recipient must notify the awarding office about any employee convicted of a criminal drug statute violation. Failure to comply with these requirements may result in suspension or debarment.
Transparency: DOL is committed to conducting a transparent grant award process and publicizing information about grant awards. The act of submitting a grant application constitutes the applicant’s agreement to indemnify and hold harmless the United States, the U.S. Department of Labor, its officers, employees, and agents against any liability, loss, or damages arising from this application. By such submission of this grant application, the applicant further acknowledges having the authority to execute this release of liability.
The Freedom of Information Act: Grant applications will be protected by DOL from public disclosure in accordance with federal law, including the Trade Secrets Act (18 U.S.C. § 1905), FOIA, and the Privacy Act of 1974 (5 U.S.C. § 552a). If DOL receives a FOIA request for an application, OSHA will respond according to DOL FOIA regulations 29 CFR § 70, and will use the exemptions and procedures in 29 CFR § 70.26 for responding to requests for commercial/business information.
Evaluations of the overall performance of the Harwood grants and/or training impact on participants may be required. As a condition of an award, grantees are required to cooperate with any evaluation of the program DOL may undertake. This cooperation includes, but is not limited to; site visits, collection of program, administrative, performance data, and interviews with grant personnel and participants.
DOL prohibits the use of the DOL seal or OSHA logo by the grantee. This includes using the seal or logos on grant-produced materials.
DOL reserves a royalty-free, non-exclusive, and irrevocable right to reproduce, publish, or otherwise use for federal purposes any work produced under a grant, and to authorize others to do so (2 CFR 200.315). Awardee must agree to provide DOL with a paid-up, non-exclusive, and irrevocable license to reproduce, publish, or otherwise use for federal purposes all products developed, or for which ownership was purchased, under an award including, but not limited to, curricula, training models, technical assistance products, and any related materials, and to authorize others to do so. Such uses include, but are not limited to, the right to modify and distribute such products worldwide by any means, electronic or otherwise.
Grantees must provide to OSHA usable copies of all training and educational materials developed under this grant for inclusion in a public access location on the OSHA webpage. Grantees must provide to OSHA one (1) bound hard copy of all final materials produced by grantees. Additionally, they must provide two (2) Section 508 compliant digital (CD Rom/DVD/flash drive) copies of the materials formatted for publication on the OSHA website. Label the digital materials with the grantee’s name and grant number. The required guidelines for submitting the final materials to OSHA are in Appendix M, Grant-Funded Material Submittal Procedures.
Grantees making public reference to a federal grant award including issuing statements, press releases, proposal requests, bid solicitations, and other documents must describe the project/program funded under the grant and clearly state the following in their public documents in accordance to the Stevens Amendment:
Dollar amount of federal financial assistance for the project or program;
Dollar amount of the total cost of the project or program funded by non-governmental sources;
Percent of the total cost of the program or project funded with federal money; and
Percent of the total cost of the program or project funded with non-governmental sources.
The grantee may satisfy this requirement by supplying the missing information and then including the following in the above-referenced publications:
The [Organization’s Name], at the time of initial publication of this document (MM/YYYY), is funded by a grant of $___ federal funds, which constitutes ___percent of the program budget. __ percent, or $___ of the program budget, is financed through non-governmental sources.
AUTHORITY: Section 21(c) of the Occupational Safety and Health (OSH) Act of 1970, (29 U.S.C. 670), Public Laws 111-117 and 112-10.
OMB Approval No.: 1225-0086
Expiration Date: 07/31/2022
OFFICE OF MANAGEMENT AND BUDGET INFORMATION COLLECTION REQUIREMENTS:
This FOA requests information from applicants. This collection of information is approved under OMB Control No. 1225-0086 (Expires 07/31/2022).
In accordance with the Paperwork Reduction Act of 1995, no person is required to respond to a collection of information unless such collection displays a valid OMB control number. The estimated public reporting burden for the grant application is an average of 56 hours per response, for reviewing instructions, searching existing data sources, gathering, and maintaining the data needed, and completing and reviewing the collection of information. Send comments regarding the burden estimated or any other aspect of this collection of information, including suggestions for reducing this burden, to the U.S. Department of Labor-OASAM, Office of the Chief Information Officer, Attn: Departmental Information Compliance Management Program, Room N1301, 200 Constitution Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20210; or by email: DOL_PRA_PUBLIC@dol.gov. Send a copy of your comments electronically to the Susan Harwood Grants Coordinator at HarwoodGrants@dol.gov, or by mail to Susan Harwood Grants Coordinator, 2020 S. Arlington Heights Road, Arlington Heights, Illinois 60005.
The purpose for collecting this information is to award a grant. Unless otherwise specifically noted in this announcement, information submitted in the respondent’s application is confidential.
Billing Code: 4510-26-P
Appendix A – FY 2020 Training and Educational Materials Development Topics
Applicants must propose to develop training materials on one of the following topics:
Agricultural safety and health – training materials covering hazards and preventive measures for farm and dairy workers, such as lockout/tagout, struck-by/caught between, falls, grain handling, grain bin entry, entrapment, combustible dust, and fires (may not include rescue training).
Bloodborne pathogens – training materials covering safeguards to protect workers against the health hazards from exposure to blood and other potentially infectious materials, and to reduce their risk from exposure.
Confined space – training materials covering confined space entry and hazards in construction, maritime, or general industry.
COVID-19 – training materials covering worker protection as it pertains to COVID-19 including personal protective equipment (PPE).
Drug misuse and hazards in the workplace – training materials covering the recognition of and hazards associated with drug misuse (abuse) in the workplace. This would include resources for employers and workers. Medical treatment and administration of neutralizing agents are beyond the scope of this topic.
Excavation/trenching – training materials covering proper excavation and trenching procedures and prevention of cave-in, collapse, entrapment, and related hazards.
Fire safety – training addresses fire hazards in the workplace, means of egress, and preparation for a fire emergency.
Healthcare – training materials for workers who provide health services to individuals. Safety and health hazards may include safe patient handling, workplace violence, and exposure to chemicals, gases, infectious diseases, bloodborne pathogens, and proper use of personal protective equipment.
Ladders and stairway safety – training materials covering the proper construction, use, placement, and care in using ladders and stairways.
Lockout/tagout – training materials covering procedures to protect workers from unexpected energizing or startup of machinery and equipment, including release of hazardous energy during servicing and maintenance.
Machine guarding/amputation prevention – training materials covering the operation of stationary equipment, press brakes, saws, shears, slicer, etc., guarding points of operations, and related hazards.
Appendix A – FY 2020 Training and Educational Materials Development Topics (cont.)
Maritime – training materials covering dock safety hazards such as dock edge protection, working over water, lifting equipment, cargo handling, mooring operations, gangways, fall protection, lifesaving equipment, traffic safety; marine terminal and longshoring industry hazards covering topics in 29 CFR 1917 and 29 CFR 1918; or shipyard safety such as electrical hazards, arc flash, ergonomics, personal protective equipment (PPE), flotation devices; or emergency procedures.
Natural disaster response and cleanup – training materials covering worker exposure and protection during disaster response and cleanup.
Noise/hearing conservation – training materials covering identification, control, and protection of workers exposed to hazardous noise in construction, maritime, or general industry.
Oil and gas production – training materials covering hazards related to hydraulic fracturing, confined space, falls, explosions, fires, struck-by/caught-in/caught-between, and other hazardous exposures.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) – training materials covering the identification of hazards requiring PPE including selection and proper use of PPE to protect workers from exposure and injury in the workplace.
Powered industrial trucks – training materials covering safety and health hazards related to use, inspection, and maintenance of powered industrial trucks (e.g., forklifts, powered platforms, aerial lifts, and vehicle-mounted work platforms).
Residential construction hazards – training materials covering general safety and health hazards such as falls, electrical, hand/power tools, struck-by/caught-in/caught-between, drywall dust/respiratory protection, PPE, hazard communication, ladders, or scaffolds.
Respiratory protection – training materials covering the identification and use of proper protection to prevent worker injury, infection, and exposure to air contaminants such as harmful dusts, fog, fumes, mists, gases, smoke, vapors, or sprays.
Safety and health training for women – training materials covering occupational safety and health hazards for women in the workplace.
Safety and health training for youth – training materials covering workplace hazards for youth and workers new to the industry.
Scaffolding – training materials covering the proper construction and use of scaffolds including the erecting and dismantling of scaffolds, fall protection, guardrails and cross bracing.
Appendix A – FY 2020 Training and Educational Materials Development Topics (cont.)
Silica – training materials covering the identification, evaluation, and control of silica exposure in construction, general, or maritime industries.
Other special emphasis or emerging industry topic – training materials covering an occupational safety and health topic identified by the applicant (applicant must include a persuasive argument to support the need for training materials for their chosen topic).
Appendix B – Targeted Audiences
A. Eligible Trainees
This grant supports the development of training and educational materials for eligible workers and employers currently covered under the OSH Act of 1970, SEC. 4, codified at 29 U.S.C. 653, who work for small businesses with limited access to safety and health training or work in a high-hazard industry. Other eligible trainees include unemployed workers planning to return to the workforce in a position covered by the OSH Act within the next three months. OSHA covers most private sector employers and workers.
OSH Act of 1970, SEC. 4. Applicability of This Act
(a) This Act shall apply with respect to employment performed in a workplace in a State, the District of Columbia, the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, the Virgin Islands, American Samoa, Guam, the Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands, Wake Island, Outer Continental Shelf Lands defined in the Outer Continental Shelf Lands Act, Johnston Island, and the Canal Zone. The Secretary of the Interior shall, by regulation, provide for judicial enforcement of this Act by the courts established for areas in which there are no United States district courts having jurisdiction.
(b) (1) Nothing in this Act shall apply to working conditions of employees with respect to which other Federal agencies, and State agencies acting under section 274 of the Atomic Energy Act of 1954, as amended (42 U.S.C. 2021), exercise statutory authority to prescribe or enforce standards or regulations affecting occupational safety or health.
Ineligible trainees are public sector employees including federal, state, and local government employees, even though they may have occupational safety and health protection if they work in a state with an OSHA-approved State Plan. Information about OSHA-approved State Plans can be found at www.osha.gov/dcsp/osp/index.html.
B. Targeted Audience(s)
Occupational safety and health training and educational materials must be in a language the prospective participants can understand, and serve employers and workers who are in one or more of the following audiences:
Workers and employers in industries with high fatality rates;
Workers and employers in high-hazard industries;
Temporary workers, minority, or other hard-to-reach workers;
Illiterate, low literacy, or limited-English proficiency workers;
Young workers (ages 16 to 24); or
Workers and employers in small or new businesses.
C. Qualified Opportunity Zone
Applicants who demonstrate, in their abstract, that at least one census tract within their physical service area is designated by the Secretary of Treasury as a qualified Opportunity Zone will
Appendix B – Targeted Audiences (cont.)
receive 2 points toward their overall application score. Applicants will not receive additional points for multiple Opportunity Zones within the proposed physical service area.
For more information on Opportunity Zones, go to www.irs.gov/newsroom/opportunity-zones-frequently-asked-questions.
Please be aware the IRS list provides the full 11-digit census tract numbers. Use the example below to identify your census tract number(s):
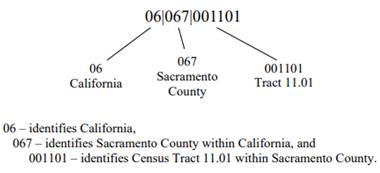
Appendix C – Application Checklist
Applicants must list the same requested federal grant amount on the SF-424, SF-424A, application summary, and budget support documents. If inconsistencies exist between these documents, the budget amount specified on the SF-424 is the official funding amount requested. If selected for an award, grantees must correct any documents that do not match the official award amount.
Application Checklist |
||
Forms to be completed on www.Grants.gov |
||
|
SF-424, Application for Federal Assistance |
|
|
SF-424A, Budget Information – Non-Construction Programs |
|
|
SF-424B, Assurances – Non Construction Programs |
|
|
Project/Performance Site Location(s) |
|
|
Grants.gov Lobbying Form |
|
|
SF-LLL, Disclosure of Lobbying Activities (if applicable) |
|
Documents that must be attached to the application package in Grants.gov |
||
|
Application summary (not to exceed 2 pages) |
|
|
Program abstract (not to exceed 1/2 page) |
|
|
Technical proposal (not to exceed 20 pages) |
|
|
Organizational chart of the grant program |
|
|
Experience of key personnel |
|
|
|
Resumes/curriculum vitae |
|
|
Position description/minimum hiring criteria for vacant positions |
|
Evidence of nonprofit status (state/local institutions of higher education exempted) |
|
|
Detailed budget support documents |
|
|
|
Form showing cost details by cost category |
|
|
Narrative description of the detailed costs for each cost category |
|
|
Explanation of non-federal resource contribution (if applicable) |
|
Indirect cost supporting document (if applicable) |
|
|
|
Approved Indirect Cost Rate Agreement or 10 percent de minimis calculation and certification |
|
Other attachments |
|
|
|
Other letters of support (optional) |
|
|
Other appropriate documents |
Appendix D – Grants.gov Application Submission and Receipt Procedures
This section provides the application submission and receipt instructions for U.S. Department of Labor, Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) program applications. Please read the following instructions carefully and completely. Reference: www.grants.gov/web/grants/grantors/grantor-standard-language.html
1. Electronic Delivery
OSHA is participating in the Grants.gov initiative to provide the grant community with a single site to find and apply for grant funding opportunities. OSHA requires applicants to submit their applications online through Grants.gov.
2. How to Register to Apply through Grants.gov
a. Instructions: Read the instructions below about registering to apply for OSHA funds. Applicants should read the registration instructions carefully and prepare the information requested before beginning the registration process. Reviewing and assembling the required information before beginning the registration process will alleviate last-minute searches for required information.
Organizations must have a Data Universal Numbering System (DUNS) Number, active System for Award Management (SAM) registration, and Grants.gov account to apply for grants. If individual applicants are eligible to apply for this funding opportunity, then you may begin with step 3, Create a Grants.gov Account, listed below.
Creating a Grants.gov account can be completed online in minutes, but DUNS and SAM registrations may take several weeks. Therefore, an organization's registration should be done in sufficient time to ensure it does not impact the entity's ability to meet required application submission deadlines.
Complete organization instructions can be found on Grants.gov here: www.grants.gov/web/grants/applicants/organization-registration.html.
1) Obtain
a DUNS Number: All entities applying for funding, including
renewal funding, must have a DUNS Number from Dun & Bradstreet
(D&B). Applicants must enter the DUNS Number in the data entry
field labeled "Organizational DUNS" on the SF-424 form.
For more detailed instructions for obtaining a DUNS Number, refer to:
www.grants.gov/web/grants/applicants/organization-registration/step-1-obtain-duns-number.html.
2) Register with SAM:
All organizations applying online through Grants.gov must register
with the System for Award Management (SAM). Failure to register with
SAM will prevent your organization from applying through Grants.gov.
SAM registration is free and must be renewed annually. For more
detailed instructions for registering with SAM, refer to:
www.grants.gov/web/grants/applicants/organization-registration/step-2-register-with-sam.html.
Appendix D – Grants.gov Application Submission and Receipt Procedures (Cont.)
3) Create a Grants.gov Account: The next step is to register an account with Grants.gov. Follow the on-screen instructions or refer to the detailed instructions here: www.grants.gov/web/grants/applicants/registration.html.
4) Add a Profile to a Grants.gov Account: A profile in Grants.gov corresponds to a single applicant organization the user represents (i.e., an applicant) or an individual applicant. If you work for or consult with multiple organizations and have a profile for each, you may log in to one Grants.gov account to access all of your grant applications. To add an organizational profile to your Grants.gov account, enter the DUNS Number for the organization in the DUNS field while adding a profile. For more detailed instructions about creating a profile on Grants.gov, refer to: www.grants.gov/web/grants/applicants/registration/add-profile.html.
5)
EBiz POC Authorized Profile Roles: After you register with
Grants.gov and create an Organization Applicant Profile, the
organization applicant's request for Grants.gov roles and access is
sent to the EBiz POC. The EBiz POC will then log in to Grants.gov
and authorize the appropriate roles, which may include the Applicant
Representative (AR) role, thereby giving you permission to complete
and submit applications on behalf of the organization. You will be
able to submit your application online any time after you have been
assigned the AOR role. For more detailed instructions about creating
a profile on Grants.gov, refer to:
www.grants.gov/web/grants/applicants/registration/authorize-roles.html.
6) Track
Role Status: To track your role request, refer
to:
www.grants.gov/web/grants/applicants/registration/track-role-status.html.
b. Electronic Signature: When applications are submitted through Grants.gov, the name of the organization applicant with the AOR role who submitted the application is inserted into the signature line of the application, serving as the electronic signature. The EBiz POC must authorize people who are able to make legally binding commitments on behalf of the organization as a user with the AOR role; this step is often missed and it is crucial for valid and timely submissions.
3. How to Submit an Application to OSHA via Grants.gov
Grants.gov applicants can apply online using Workspace. Workspace is a shared, online environment where members of a grant team may simultaneously access and edit different webforms within an application. For each funding opportunity announcement (FOA), you can create individual instances of a workspace.
Below is an overview of applying on Grants.gov. For access to complete instructions on how to apply for opportunities, refer to: www.grants.gov/web/grants/applicants/workspace-overview.html.
Appendix D – Grants.gov Application Submission and Receipt Procedures (Cont.)
1) Create a Workspace: Creating a workspace allows you to complete it online and route it through your organization for review before submitting.
2) Complete a Workspace: Add participants to the workspace to work on the application together, complete all the required forms online or by downloading PDF versions, and check for errors before submission. The Workspace progress bar will display the state of your application process as you apply. As you apply using Workspace, you may click the blue question mark icon near the upper-right corner of each page to access context-sensitive help.
a. Adobe Reader: If you decide not to apply by filling out webforms, you can download individual PDF forms in Workspace. The individual PDF forms can be downloaded and saved to your local device storage, network drive(s), or external drives, then accessed through Adobe Reader.
NOTE: Visit the Adobe Software Compatibility page on Grants.gov to download the appropriate version of the software at: www.grants.gov/web/grants/applicants/adobe-software-compatibility.html.
b. Mandatory Fields in Forms: In the forms, you will note fields marked with an asterisk and a different background color. These fields are mandatory fields that must be completed to submit your application successfully.
c. Complete SF-424 Fields First: The forms are designed to fill in common required fields across other forms, such as the applicant name, address, and DUNS Number. Once it is completed, the information will transfer to the other forms.
3) Submit a Workspace: An application may be submitted through workspace by clicking the Sign and Submit button on the Manage Workspace page, under the Forms tab. Grants.gov recommends submitting your application package at least 24-48 hours prior to the close date to provide you with time to correct any potential technical issues that may disrupt the application submission.
4) Track a Workspace Submission: After successfully submitting a workspace application, a Grants.gov Tracking Number (GRANTXXXXXXXX) is automatically assigned to the application. The number will be listed on the Confirmation page that is generated after submission. Using the tracking number, access the Track My Application page under the Applicants tab or the Details tab in the submitted workspace.
For additional training resources, including video tutorials, refer to: www.grants.gov/web/grants/applicants/applicant-training.html.
Applicant Support: Grants.gov provides applicants 24/7 support via the toll-free number
1-800-518-4726 and email at support@grants.gov. For questions related to this grant opportunity, contact the number listed in the application package.
Appendix D – Grants.gov Application Submission and Receipt Procedures (Cont.)
If you are experiencing difficulties with your submission, it is best to call the Grants.gov Support Center and get a ticket number. The Support Center ticket number will assist OSHA with tracking your issue and understanding background information on the issue.
4. Timely Receipt Requirements and Proof of Timely Submission
a. Online Submission. All applications must be received by 11:59 p.m. eastern time on the due date established for each program. Proof of timely submission is automatically recorded by Grants.gov. An electronic date/time stamp is generated within the system when the application is successfully received by Grants.gov. The applicant with the AOR role who submitted the application will receive an acknowledgement of receipt and a tracking number (GRANTXXXXXXXX) from Grants.gov with the successful transmission of their application. This applicant with the AOR role will also receive the official date/time stamp and Grants.gov Tracking number in an email serving as proof of their timely submission.
When OSHA successfully retrieves the application from Grants.gov, and acknowledges the download of submissions, Grants.gov will provide an electronic acknowledgment of receipt of the application to the email address of the applicant with the AOR role who submitted the application. Again, proof of timely submission shall be the official date and time that Grants.gov receives your application. Applications received by Grants.gov after the established due date for the program will be considered late and will not be considered for funding by OSHA.
Applicants using slow internet, such as dial-up connections, should be aware that transmission can take some time before Grants.gov receives your application. Again, Grants.gov will provide either an error or a successfully received transmission in the form of an email sent to the applicant with the AOR role attempting to submit the application. The Grants.gov Support Center reports that some applicants end the transmission because they think that nothing is occurring during the transmission process. Please be patient and give the system time to process the application.
Appendix E – Non-Viable Applications
OSHA will not review non-viable applications. Applications must meet all of the viability components listed.
Viable applications are:
Submitted through Grants.gov;
Submitted before the application deadline;
Validated by Grants.gov;
Submitted under the correct FOA;
Complete with all the required forms and documents (Appendix C);
Submitted by eligible nonprofit organizations;
Submitted with a readable and valid proof of current nonprofit status (state/local institutions of higher education are exempt);
Proposing training on a topic that is one of the OSHA-identified topics listed in this FOA; and
Meeting the program requirements as outlined in this FOA.
Appendix F – Administrative and Program Costs Definition
The SF-424A – Budget Information, detailed project budget support, and detailed project budget narrative must break down grant costs for federal and non-federal grant funds by the cost categories shown on the SF-424A and assigned to the budget as either a program or an administrative cost.
Program costs are direct costs incurred to develop and conduct training and other grant program activities. Direct program costs are easily identifiable and relate to training development and training presentation activities.
Program personnel salaries and benefits include costs related to:
Developing and presenting training for workers and employers
Recruiting trainees
Tracking and monitoring training activities and participant information
Basic worker information
Employer information
Statistical information relevant to program evaluations and assessments
Reasonable travel costs to carry out training activities:
Costs for trainer(s) to go to a training location
Cost for grant personnel to monitor trainers
Costs of goods and services required for direct program functions:
Advertising and outreach services specific to recruiting the target audience for training
Training supplies, including local materials reproduction
Rental or purchase of approved training supplies (limited to the costs related to grant activities, and may not include office or classroom furniture, storage, equipment)
Rental or maintenance of training space (limited to the costs related to grant activities)
Payments to partners, vendors, or contractors for services supporting program activities
Some direct costs may support both program and administration, e.g., grant personnel may provide program services and spend time doing administrative functions. Separate and allocate these shared costs based on the role and task. Document the method used to allocate these costs, e.g., based on actual time worked on each function, actual supplies used, or other equitable cost allocation method.
Administrative costs may not exceed 25 percent of the total funding. Any deviation from this restriction requires a written justification and OSHA approval. Administrative costs include direct and indirect costs. Administrative direct costs are easily identifiable costs associated with grant-related activities that support the administration of the grant.
Appendix F – Administrative and Program Costs Definition (Cont.)
General administrative functions are:
Administrative personnel salary and fringe benefit costs related to:
Report preparation
Review resolution
Development of systems and procedures for administrative functions
Budget, accounting, and audits
Financial and cash management
Purchasing and procurement
Payroll functions
Personnel management
Travel costs for official business to carry out administrative or management activities of the grant, including travel associated with required attendance at the OSHA Orientation Meeting and other OSHA meetings.
Costs of goods and services required for administrative functions of the program:
Advertising and outreach to the general public
Office supplies
Postage
Rent for office space (justification required, and limited to the costs related to grant activities)
Renting/leasing and maintenance of office equipment (copiers, printers, etc. if justified and deemed necessary, and must be limited to the costs related to grant activities)
Utilities (telephones, internet service, etc. necessary to support the grant program)
Costs to manage administrative functions; i.e., reasonable costs for personnel management, accounting and payroll, or procurement/purchasing
Partners’ administrative costs allocated to the applicable costs category. Partners budgeting for indirect costs must provide an approved Indirect Cost Rate Agreement (ICRA).
Indirect costs, as specified in the Uniform Guidance 2 CFR 200, are costs incurred for a common or joint purpose, and benefit more than one program, project, or unit. Indirect costs are not easily identifiable or assignable. For this grant, indirect costs are budgeted as an administrative cost.
Indirect costs represent the unidentifiable expenses of doing business for a grant, contract, project function, or activity, but are necessary for the general operation of the organization.
An ICRA states the proportion of organization indirect costs each program should bear.
The approved ICRA must show effective dates that cover the entire grant performance period.
Appendix F – Administrative and Program Costs Definition (Cont.)
The negotiated rate approved by the organization’s cognizant federal agency is applicable to all federal grant programs.
The allowed indirect costs are based on the approved ICRA rate (percentage) times the approved base.
If the organization has never had an ICRA, they may apply a 10 percent de minimis allowance as an indirect cost, but must certify that the organization has never had an ICRA and must provide the method used to calculate the modified base.
Contracts/Sub-Awards
Contracts must meet the requirements of 2 CFR 200 and the grant award. Prior to awarding a contract, use a full and open competition method for procurement to the maximum extent possible. This FOA prohibits grantees from entering into a sub-award agreement with a third party to execute grant activities. OSHA encourages applicants to offer contracting opportunities to historically Black colleges and universities, Hispanic serving institutions, and tribal colleges and universities, as stated in the policies outlined in Executive Orders 13256, 12928, 13230, and 13021 as amended.
Appendix G – Example of Budget Forms
Example SF-424A
(Completed at Grants.gov)
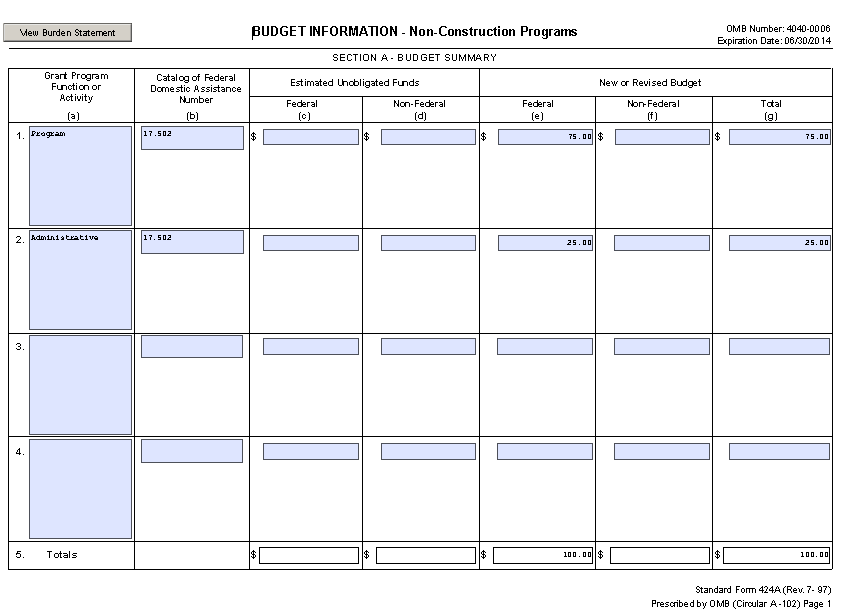
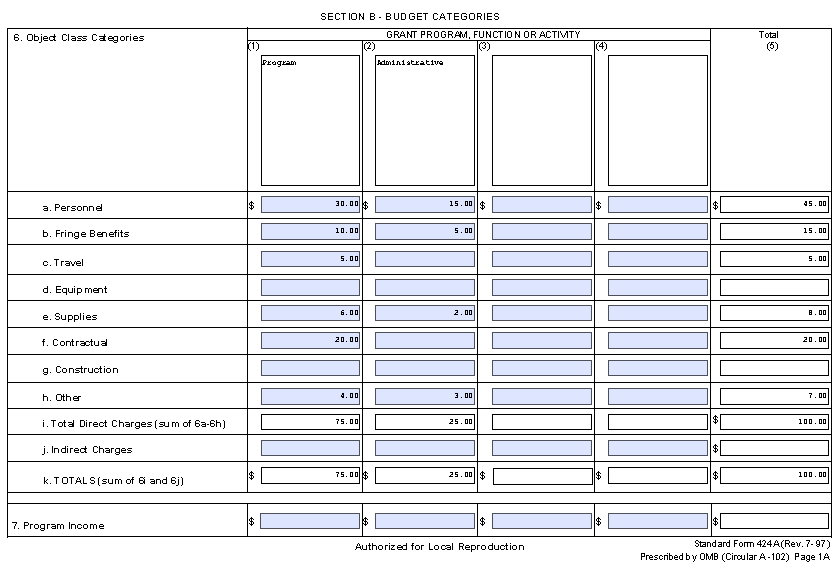
Appendix G – Example of Budget Forms (Cont.)
Example Detailed Budget
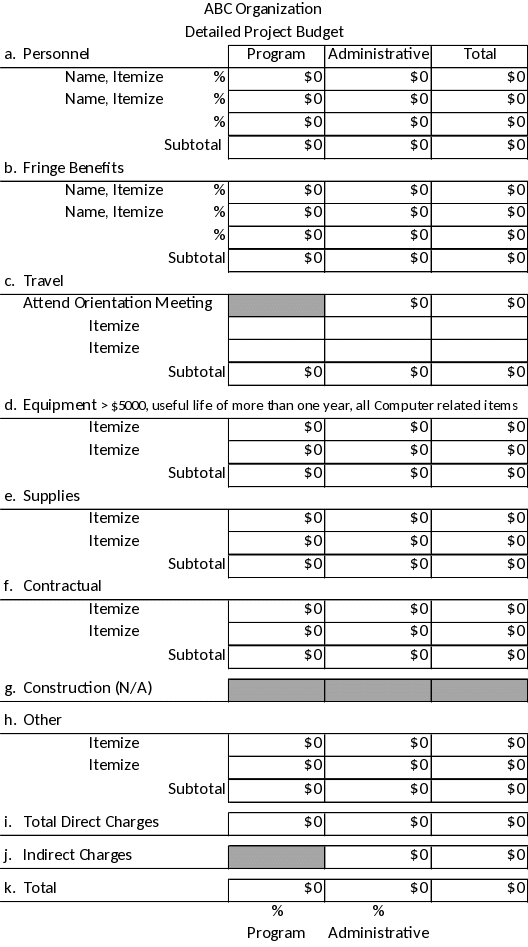
Totals for each category on the detailed program budget must match the category lines on the SF-424A.
Personnel and travel costs to attend the Grantee Orientation Meeting must be allocated to the administrative costs column. All indirect charges must be allocated to the administrative costs column.
Total direct and indirect administrative costs may not exceed 25 percent of the total grant funding.
Attach a budget narrative to this detailed program budget that justifies the itemized costs for each cost category, and the method used for estimating the costs.
Appendix H – Application Formatting Requirements
The program abstract and technical proposal must be double-spaced on plain white 8½” x 11” paper with one-inch margins and portrait layout. Fonts must be 12-point Times New Roman, Verdana, Arial, Tahoma, Helvetica, or Calibri. Graphs and tables in the technical proposal may be single-spaced.
All attachments must be saved as one of the following: Microsoft Word, Microsoft Excel, or Adobe.pdf. Documents must be accessible and may not be locked, password protected, or water marked. For consistency, name the attachments using the applicant name and document type, e.g. ABCOrg AppSum.docx. Do not submit sample training materials. Ensure all documents, including Excel spreadsheets, are legible and formatted for printing on 8½” x 11” paper. Compressed files will not be accepted.
File attachment names may not exceed 30 characters. The DOL Grants system limits the special characters in the file names. Using other characters may prevent OSHA from viewing the attachments. Allowable characters in the attachment file names are:
letters and numbers – A-Z, a-z, 0-9
underscore ( _ ) and hyphen (-)
parenthesis (()), curly brackets ({}), and square brackets ([])
tilde (~)
exclamation point (!), comma (,), and period (.)
dollar sign ($), percent sign (%), plus sign (+), and equal sign (=)
spaces
If an application document exceeds the cited page number limitation for double-spaced pages in the technical proposal, program abstract, or application summary, OSHA reviewers will disregard the excess pages. If a document is single-spaced or one-and-one-half-spaced (in whole or in part), OSHA will convert the document to double spacing, and OSHA reviewers will disregard pages exceeding the document’s length limit.
Appendix I – Application Summary Document Sample Outline
Organization name and physical address
Authorized representative (AR)
(May include secondary AR, e.g. Pre-award AR and Post-award AR)
Name and title (same as on SF-424, section 21)
Physical address (for courier delivery)
Telephone and fax number
Email address
Project director
Name and title
Address
Telephone and fax number
Email address
Financial certifying representative
Name and title
Address
Telephone and fax number
Email address
Grant type: Training and Educational Materials Development
Grant topic (must be from appendix A)
Targeted audience/industry
Languages
Funds requested (do not include cents)
Federal funds $
Other funds $
Total funds $
Projected number to be trained
Projected contact hours
Type of organization (labor union, community/faith based, employer association, local or state supported institution of higher education, native tribal, specify other non-profit)
Affiliations (unions or other non-profits), OSHA alliances (federal or state), and/or Partners (associated with this proposal)
Targeted cities/counties/states and associated congressional districts
Qualified Opportunity Zone for at least one census tract for population where proposed training will occur, if applicable
Appendix J – Program Abstract Narrative Example
A program abstract narrative should be brief (limit to ½ page) and include the following information:
Applicant Name
Grant Category: Training and Educational Materials Development
Program abstract narrative:
Targeted topic for new materials
Materials focused on audience/industry
Types of training materials being developed
Languages
Pilot training
Estimated total number of trainees for the pilot training
Estimated contact hours for pilot training per trainee
Other activities planned during the program year
Following is an abbreviated example of a program abstract narrative:
ABC non-profit proposes to develop new fall prevention training materials for employers and workers in the residential roofing industry. The targeted audience includes youth, hard-to-reach, and limited English proficiency workers in this high-hazard industry. Training topics included are using ladders, scaffolds, and preventing falls from roofs. Training materials will be tested during a pilot training for XX workers and employers. Training will be available in English and Spanish.
Appendix K – Allowable/Unallowable Use of Grant Funds
Proposed costs must be necessary, reasonable, and in accordance with federal guidelines. Determinations of allowable costs are in accordance with the Cost Principles found in the Uniform Guidance 2 CFR 200 and in 2 CFR 2900. OSHA may disallow costs that are unallowable in accordance with the applicable federal cost principles or other conditions defined by the grant program and this FOA.
Allowable uses of Grant Funds
Grant awards include OSHA federal funding as requested on the SF-424, and the applicant’s non-federal money, if any. Federal funds may not include funding from other federal programs. Grantees must carry out grant activities in accordance with all applicable legal and program requirements. Allowable grant funds support the following:
Developing training and educational materials for the project;
Conducting outreach and recruiting activities to increase the number of workers and/or employers participating in the program; and
Conducting free training, and other activities that inform workers and/or employers about workplace occupational safety and health hazards and hazard abatement.
Prohibited use of Grant Funds
While the activities described below may be part of an organization’s regular programs, the terms of this grant program prohibit the use of grant funds, whether from OSHA federal funds or recipient matching resources for the following:
Conducting activities that are incongruent with the goals and objectives of the OSH Act;
Conducting activities that benefit state and local government employees unless they have occupational safety and health responsibilities (e.g. occupational safety and health trainers, program managers, committee members, or employees responsible for abating unsafe and unhealthy working conditions for their organization);
Providing program activities that involve self-employed workers or workplaces that are precluded from enforcement action by OSHA under section 4(b)(1) of the Act, codified at 29 U.S.C. 653(b)(1);
Training on topics that do not cover the recognition and prevention of unsafe or unhealthy working conditions (e.g. workers’ compensation, first aid);
Attending, presenting, or conducting training at conferences;
Publishing materials prejudicial to labor, management, or OSHA;
Assisting workers in arbitration cases or other actions against employers, or assisting workers and/or employers in the prosecution of claims against federal, state or local governments; and
Duplicating services offered by OSHA, a state under an OSHA-approved State Plan, or consultation programs provided by state designated agencies under section 21(d) of the OSH Act, codified at 29 U.S.C. 670(d)(1).
Appendix K – Allowable/Unallowable Use of Grant Funds (Cont.)
Prohibited use of Grant Funds (cont.)
Conducting OSHA Outreach Training Program’s 10- or 30-hour training (https://www.osha.gov/dte/outreach/index.html);
Conducting or attending OSHA Training Institute or OSHA Training Institute Education Center courses;
Providing staff development or using grant funds to train the organization’s employees or contractors unless expressly approved by OSHA;
Conducting training through any pre-existing, proprietary, industry, or certification program;
Identifying or using training for a certification program or requirement for a certification program;
Describing training as OSHA certified training;
Proposing training required by other federal and/or state agencies;
Duplicating services of other federal and/or state agencies;
Paying salary, travel, and other expenses for an OSHA State Plan, OSHA Consultation, or federal employee;
Reimbursing trainees or employers for the cost of lost-time wages while attending grant-funded training;
Providing compensation, stipends, or incentives to trainees, including train-the-trainer trainees, for any grant-related activities prior to, during, or after attending grant-funded training;
Generating membership in the grantee and/or partner’s organization (e.g., requiring participants to be members to attend training, informing non-members about membership benefits, including membership information, appeals for members printed in materials produced with grant funds, conducting membership drives);
Providing food and beverages at meetings or training events; and
Reimbursing pre-award costs (e.g., grant writing costs).
Prohibited religious Activities
The treatment of DOL programs with religious organizations is contained in 29 CFR Part 2, Subpart D. All organizations, including religious ones, must carry out grant-supported activities in accordance with all applicable legal and program requirements. DOL prohibits the use of grant funds for explicitly religious activities including activities that involve overt religious content, such as worship, religious instruction, or proselytization.
Appendix L – Training and Educational Materials Development Criteria
Sample Evaluation Components |
Points |
|
44 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
76
|
|
53 |
|
7 |
Total |
180 |
Appendix M – Grant Funded Materials Submittal Process
Grant materials developed with grant funds are subject to OSHA review and approval. OSHA must approve the materials prior to the grantee using the materials to conduct training. Prior to the end of the performance period, September 30, 2021, the grantee must submit to OSHA two (2) electronic copies and one (1) hard copy of the materials developed with grant funds. OSHA will provide public access to grant-produced materials on the Susan Harwood website. Electronic files must meet the requirements of Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act. Following are submittal procedures for grant-funded training materials.
1. Material Requirements
The word “draft” must not appear on any materials (printed or electronic).
A final English version of materials must accompany the materials created for translation into a non-English language.
Training materials must be appropriate for all audiences.
Remove references to training of specific groups, members of a group, or individuals
Remove personal information (instructor names, addresses, phone numbers, e-mail addresses, etc.)
Blank tests and answer keys must be provided.
Grant-funded materials developed by a grantee must contain the following disclaimer:
This material was produced under grant number SH________-SH_ from the Occupational Safety and Health Administration, U.S. Department of Labor. It does not necessarily reflect the views or policies of the U.S. Department of Labor, nor does mention of trade names, commercial products, or organizations imply endorsement by the U.S. Government.
A list of all training materials developed during the grant period must include the following:
Description of materials;
Type of materials;
Title or subject of materials;
Copyright approvals, if needed; and
Material uses, i.e., instructional, recruiting, evaluating, audiovisual.
2. Software Requirements
Produce grant-funded training materials in a format that is widely accessible to the public. Microsoft Office meets this requirement. Do not submit Adobe Acrobat (.pdf) files without
Appendix M – Grant Funded Materials Submittal Process (Cont.)
OSHA approval. Currently there is no preferred program for providing media files.
Word Files: Submit manuals and other printed materials in an unlocked editable Word documents.
PowerPoint Files: Submit presentations that are unlocked and editable. (Do not provide files saved in the “Show” format.)
File must be Section 508 compliant
Photographs and other images must be compressed in JPEG format and include an alternate text description
Presentation with linked or embedded audio or video files
Submit two (2) copies of the presentation
One copy with the links and embedded files
One copy without the links and embedded files
Describe what link or embedded file was used at this location in the materials, and where the user can find the link or embedded file
Presenter talking points must be added to each slide
Media Files (For online courses)
Files must be Section 508 compliant
Images such as photographs must have descriptive captions
Audio files must have transcripts
Video files must be captioned and have transcripts
3. Section 508 Compliance
Training materials must comply with Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973. Fixing accessibility issues by using the Accessibility Checker built into the Microsoft Office software allows access to the materials by all users. Accessibility issues involve images, document navigation, hyperlinks, data tables, color, blank spaces, titles, tabs, and other non-readable placeholders. Make Microsoft Office documents Section 508 compliant by using the document’s accessibility checker. Fix errors, warnings, and tips found by the checker.
Correct common errors:
Add alternate text to pictures, images, and hyperlinks
Add slide titles
Rename duplicate slide titles
Delete extra spaces
Appendix M – Grant Funded Materials Submittal Process (Cont.)
4. Materials Submission
Submit all grant-funded training materials in printed and electronic format (one (1) printed and two (2) electronic). Before sending the materials to OSHA, ensure all files open and that all grant-funded materials are included. Do not submit files that are encrypted, password protected, or in “read only” format. Provide:
A list of materials submitted by the grantee;
A list of other materials used by the grantee;
Materials developed by the grantee, printed, bound, and shelf-ready (i.e., 3-ring binder);
Photographs of other materials developed by the grantee that are not practical for mailing (banners, etc.);
Materials submitted as an electronic file may not exceed 15MB, and must be certified as Section 508 compliant;
Save images and pictures as .jpg files
Compress pictures and images to email size (96 ppi)
Delete cropped areas of pictures
Divide the materials into several smaller files that do not exceed the file size limit
CDs, DVDs, or USB flash drives that are clearly labeled with the name of the grantee’s organization and the grant number (e.g., SH-12345-SH9); and
Electronic file names on CD, DVD, or USB flash drives are clearly identified by type of material (examples: Instructor Manual, Student Manual, Pre-Test, Post-Test, Test Answers, Assessments and Evaluation Forms).
References
Acronyms
AR/AOR Authorized Representative
CFR Code of Federal Regulations
DOL U.S. Department of Labor
DTE Directorate of Training and Education
FFR Federal Financial Report SF-425
FOA Funding Opportunity Announcement
FY Fiscal Year
MTDC Modified Total Direct Costs
ICRA Indirect Cost Rate Agreement
OSHA Occupational Safety and Health Administration
OSH Occupational Safety and Health
OMB Office of Management and Budget
SAM System for Award Management
SF Standard Form
U.S.C. United States Code
Websites
2 CFR 200, Uniform Administrative Requirements, Cost Principles, and Audit Requirements for Federal Awards (Uniform Guidance) –
www.ecfr.gov/cgi-bin/text-idx?tpl=/ecfrbrowse/Title02/2cfr200_main_02.tpl
2 CFR 2900, Department of Labor exceptions to the OMB Uniform Guidance – www.gpo.gov/fdsys/pkg/FR-2014-12-19/pdf/2014-28697.pdf
DUNS Number – fedgov.dnb.com/webform
Grants.gov – www.Grants.gov/
Opportunity Zones – www.irs.gov/newsroom/opportunity-zones-frequently-asked-questions
OSHA - www.osha.gov
Rehabilitation Act of 1973, Section 508 – www.hhs.gov/web/section-508/making-files-accessible/index.html
Susan Harwood Training Grant Program – www.osha.gov/dte/sharwood/index.html
System Award Management (SAM) – www.sam.gov/portal/SAM/
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| Author | Robertson, Donna - OSHA |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 2021-01-14 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy