0245 - Ceap - Ssa - 2014
0245 - CEAP - SSA - 2014.docx
Conservation Effects Assessment Project
OMB: 0535-0245
1Supporting Statement A
CONSERVATION EFFECTS ASSESSMENT PROJECT
OMB No. 0535-0245
This supporting statement addresses the renewal of data collection efforts for the National Resources Inventory Conservation Effects Assessment Project (NRI CEAP) cropland assessment for a period of three years. The current NRI CEAP information collection package expires on October 31, 2014. The first year of this renewal (2014) will be conducted at a regional level in the St. Francis River Basin (Arkansas and Missouri). Approximately 1,700 farmers will be contacted for this region. In 2015 and 2016 the NRI CEAP program will be expanded to a US level. The target sample size will be approximately 22,000 farm operators for each of these years.
Data collected under this docket is under a cooperative agreement between the National Agricultural Statistics Service (NASS) and the Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS) in cooperation with the Iowa State University Center for Survey and Statistical Methods (ISU-CSSM). Under this agreement NRCS will provide total funding for the NRI CEAP survey program, including: the cost of planning, development, testing, data collection, editing, summarization, etc.
The National Resources Inventory (NRI) is a scientifically-based, longitudinal panel survey designed to assess conditions and trends of soil, water, and related resources of the Nation’s non- Federal lands. The NRI is conducted for the USDA by NRCS in cooperation with ISU-CSSM and provides information to address agricultural and environmental issues at national, regional, and State levels. Data gathered in the NRI are linked to NRCS soil and climate databases. These linked data, along with NRI historical data, form the basis for unique modeling applications and analytical capabilities.
A. JUSTIFICATION
1. Explain the circumstances that make the collection of information necessary. Identify any legal or administrative requirements that necessitate the collection. Attach a copy of the appropriate section of each statute and regulation mandating or authorizing the collection of information.
The primary function of NASS is to prepare and issue official State and national estimates of crop and livestock production, disposition, and prices. Auxiliary services such as statistical consultation, data collection, and summary tabulation are performed for other Federal and State agencies on a reimbursable basis. The goal of this NASS information collection is to obtain land management information that will assist NRCS in assessing environmental benefits associated with implementation of various conservation programs such as the Environmental Quality Incentives Program (EQIP), the Conservation Reserve Program (CRP), the Wetland Reserve Program (WRP), and other conservation programs. Tracking the environmental benefits of these programs allows policy makers and program managers to evaluate and modify existing programs and design new programs to more effectively meet the goals of Congress.
The NRI CEAP was initiated by USDA in 2003 as a multi-agency effort to quantify the environmental effects of conservation practices on agricultural lands. The assessment was initiated in support of the 2002 Farm Bill, which substantially increased funding for conservation programs on agricultural lands. NRCS was designated the lead agency for the NRI CEAP. NRCS needs updated scientifically credible data on residue and tillage management, nutrient management, and conservation practices in order to quantify and assess impacts of current farming practices and to document changes.
Sample points will be drawn from the NRCS NRI data base, using a stratified sample with a non-response adjustment. The NRI sampling frame will be used for this project because it captures agricultural resources such as soil type(s), topography, and climate; critical factors in estimating benefits of conservation practices. Also important are the historical and linked data that exist for each NRI sample site. The assessment of benefits is not possible without augmenting the existing data with additional information on land management, the adoption of conservation practices, and conservation program participation.
NASS will collaborate with NRCS in the acquisition of this additional information by conducting a survey for a sub-sample of NRI sample units. The survey will utilize personal interviews with farm operators to administer a questionnaire that is designed to obtain field-specific data associated with the selected NRI sample units. These units are fields that encompass the NRI points and will be defined by enumerators at the time of the interviews. Specific questions are asked about physical characteristics of the field, farming activities, and conservation practices associated with the field. Information regarding participation in conservation programs will be obtained from the local NRCS field office.
Benefit measures will include soil quality enhancement, erosion reduction, reduction in nutrient and sediment losses from farm fields, soil carbon sequestration, and reductions of in-stream nutrient and sediment concentrations. Benefits will be estimated by applying transport models and other physical process models at sample sites associated with the NRI sampling frame; this methodology is explained in part B.1.
General authority for these data collection activities is granted under U.S. Code Title 7, Section 2204(a) which specifies that "The Secretary of Agriculture shall procure and preserve all information concerning agriculture which he can obtain ... by the collection of statistics ... and shall distribute them among agriculturists."
2. Indicate how, by whom, and for what purpose the information is to be used. Except for a new collection, indicate the actual use the agency has made of the information received from the current collection.
Data collected in the NRI CEAP farm operator survey will be used in conjunction with previously collected NRI data on soils types, climate, and cropping history as input to field-level physical process models.
NRCS and Texas AgriLife have developed a system of databases and models that can be used to assess the environmental benefits of conservation programs. The primary models that will be used for the NRI CEAP cropland assessment are the Erosion-Productivity Impact Calculator (EPIC) and Agricultural Policy Environmental Extender Model (APEX). EPIC is a continuous simulation model developed to assess the movement of materials from farm fields, such as nitrogen, phosphorous, sediment, salt, and pesticides. The APEX model was developed to extend the EPIC model beyond the individual field to the whole farm and watershed levels. The performance of the EPIC and APEX models have been well documented and widely used in policy analysis. For details, refer to http://epicapex.brc.tamus.edu/applications.
EPIC operates on a daily time step, integrating daily weather data; soil characteristics; farming operations such as planting, tillage, and nutrient applications; and a plant growth model to simulate the growth and harvest of a crop. All farming operations that take place on the field throughout the year are taken into account. On a daily basis, EPIC tracks the movement of water; the cycling of nitrogen, phosphorus, and carbon; and soil erosion. The drainage area considered by EPIC is generally a homogeneous field-sized area of up to about 250 acres. Model outputs represent pollutant and water movement to the "bottom of the root zone" and "edge of the field." The wide variety of input options for data collected on soils, weather, and cropping practices, allows simulation of most crops on virtually any soil and climate combination.
APEX has components for routing water, sediment, nutrients, and pesticides across landscapes, into stream channels, and further downstream to the watershed outlet. Water quality, in terms of nitrogen, phosphorous, and pesticide residues, may be estimated for subareas within the watershed and at the watershed outlet.
As EPIC is a daily time step model, daily inputs are needed on every activity conducted in the production of a crop. The input data collected from surveys of farm operators are necessary to realistically simulate material losses from farm fields. For more information on the EPIC and APEX models, see http://epicapex.brc.tamus.edu.
Additional documentation and associated publications regarding NRI CEAP
modeling methodology can be found at: http://www.nrcs.usda.gov/technical/nri/ceap/cropland.html.
Impacts of Conservation Adoption on Cultivated Acres of Cropland in the Chesapeake Bay Region, 2003-06 to 2011
http://www.nrcs.usda.gov/wps/portal/nrcs/detail/national/technical/nra/ceap/?cid=stelprdb1240074
Additional NRI CEAP cropland reports can be found at
http://www.nrcs.usda.gov/wps/portal/nrcs/main/national/technical/nra/ceap/
3. Describe whether, and to what extent, the collection of information involves the use of automated, electronic, mechanical, or other technological collection techniques or other forms of information technology, e.g., permitting electronic submission of responses, and the basis for the decision for adopting this means of collection. Also describe any consideration of using information technology to reduce burden.
Electronic data collection will be used to help identify the operator of the selected farm fields in which the NRI points lie, and to determine if the selected field is in scope.
NRI sample points will be matched with the USDA Farm Service Agency (FSA) Common Land Use (CLU) geospatial database to determine the name of the farm operator. If the farm field has been registered with FSA, the name of the current operator will be available. This will reduce the amount of time spent in gathering
operator information by field enumerators and will reduce respondent burden.
In order to determine if the selected point is in scope, field enumerators will make use of an iPad application prior to the start of each interview. The iPad application includes an aerial image of the field containing the NRI sample point and a series of screening questions. Once the enumerator has determined that the correct farm operator has been identified for the point and the field is in the land use of interest, the farm operator will draw off the borders of the selected field on the iPad aerial image. The enumerator will get a message to either “Proceed with interview” or “Do not proceed with interview”, based on the screening information. In areas of the country where the iPad cannot connect to a viable signal, the NASDA enumerators will be able to conduct the screening portion of the questionnaire on paper.
Currently, only the screening phase is conducted with an iPad and the rest of the questionnaire is done on paper. The survey must be conducted by a Field Enumerator since the reference point is tied to a NRI sample point. The enumerator will have to show the farmer the aerial photograph of the target point and make sure that the data collected correlates with that point. The enumerator will also collect farm/field level land management data that is unavailable through remote sensing but by visual observation alone; this information cannot be collected online.
4. Describe efforts to identify duplication. Show specifically why any similar information already available cannot be used or modified for use for the purposes described in Item 2 above.
NASS cooperates with State departments of agriculture, land grant universities, and other State and Federal agencies to conduct surveys. Wherever possible, surveys meet both State and Federal needs, thus eliminating duplication and minimizing reporting burden on the agricultural industry.
The data collected during farm operator interviews for the NRI CEAP are being collected primarily for NRCS. Some data will be obtained from the NRCS county offices, eliminating the need to collect these data elements from producers. However, field-level data on all activities conducted in the production of the crop must be obtained from farm operators; they are not available from any other source.
5. If the collection of information impacts small businesses or other small entities (Item 5 of OMB Form 83-I), describe any methods used to minimize burden.
This information collection will not have a significant economic impact on small entities.
6. Describe the consequence to Federal program or policy activities if the collection is not conducted or is conducted less frequently, as well as any technical or legal obstacles to reducing burden.
Congress and the Office of Management and Budget have indicated that the environmental impacts of conservation programs designated in the U.S. Farm Bill should be measured consistently, quantitatively, and credibly. This information is needed in order to make informed decisions about future conservation programs. Annual collections are necessary to collect sufficient information in order for the Erosion – Productivity Impact Calculator (EPIC) modeling process to accurately assess environmental benefits.
7. Explain any special circumstances that would cause an information collection to be conducted in a manner inconsistent with the general information guidelines in 5 CFR 1320.5.
There are no special circumstances associated with this information collection.
8. Provide a copy and identify the date and page number of publication in the Federal Register of the agency's notice, required by 5 CFR 1320.8 (d), soliciting comments on the information collection prior to submission to OMB. Summarize public comments received in response to that notice and describe actions taken by the agency in response to these comments.
The Notice soliciting comments was published in the Federal Register on March 17, 2014, on pages 14664 - 14665. No public comments were received.
Describe efforts to consult with persons outside the agency to obtain their views on the availability of data, frequency of collection, the clarity of instructions and record-keeping, disclosure, or reporting format (if any), and on the data elements to be recorded, disclosed, or reported.
NRI CEAP incorporates peer review and comments from recognized experts in the conservation community, and scientists and modelers within and outside of government. Findings are presented at professional meetings and workshops.
An external peer review of the NRI CEAP was conducted in 2006 by the Soil and Water Conservation Society (SWCS). A blue-ribbon panel composed of academics and leaders of nongovernmental organizations and State agencies was charged with conducting the review, for the purpose of making NRI CEAP more useful and credible and to assure that NRI CEAP’s products have utility for policymakers, program managers, and the conservation community.
Results of the review may be found in the report “Final Report from the Blue Ribbon Panel Conducting an External Review of the U.S. Department of Agriculture Conservation Effects Assessment Project.”, available online at: www.swcs.org/en/publications/ceap_review_recommendations/index.cfm.
In addition to this peer review process, oversight of the project is provided by two groups with interagency representation:
• The NRI CEAP Executive Steering Committee, consisting of leaders from Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS); National Agricultural Statistics Service (NASS); Farm Service Agency (FSA); Agricultural Research Service (ARS); Economic Research Service (ERS); Cooperative State Research, Education, and Extension Service (CSREES); Environmental Protection Agency (EPA); and United States Geological Survey (USGS); and,
• The NRI CEAP Steering Committee and Interagency Advisory Group, consisting of mid-level managers from the participating agencies.
The combination of peer review and oversight is designed to provide policy and technical guidance to those directly implementing NRI CEAP and to assure the scientific credibility and public acceptance of national and watershed assessments of the environmental benefits of conservation practices
A listing of federal agencies, universities, and nongovernmental organizations that are collaborating with NRI CEAP may be found at:
www.nrcs.usda.gov/technical/nri/ceap/about.html.
Specific to this project, NASS conducted a cognitive, pre-test of the survey instrument in early 2011 and used producer input to improve the data collection process. NASS tested several different layouts of the questionnaire to see if we could improve the flow of the survey; to improve response rates and reduce respondent burden. Our findings showed that the layout of the questionnaire and the order of the questions used in the previous approval were still the best approach to collecting this type of data. However, the testing did show that enumerator training needed to be expanded. NASS discovered some variances in farming and conservation practices that were specific to different regions being tested. Consultation on the questionnaire was provided by modelers from Texas AgriLife and by pest management experts within NRCS. Statisticians at ISU-CSSM conducted the sample design for NRI CEAP. FSA records are being utilized to obtain initial operator information, which increases efficiency and lowers burden on respondents. The recommendations that were made by Ms. Moody and the members of the Stewardship Programs were all incorporated into the questionnaires.
The only other significant change made to the questionnaire involved the lessons learned from the NRI CEAP survey conducted in 2006. NASS attempted to integrate the NRI CEAP survey with the Agricultural Resource Management Survey (ARMS III, OMB # 0535-0218) in order to reduce respondent burden and potentially reduce data collection costs. This proved to be too difficult to do and did not produce the savings we had hoped for. The two surveys will be conducted independently in the future.
9. Explain any decision to provide any payment or gift to respondents.
There are no payments or gifts to respondents.
10. Describe any assurance of confidentiality provided to respondents and the basis for the assurance in statute, regulation, or agency policy.
Questionnaires include a statement that individual reports are kept confidential. U.S. Code Title 18, Section 1905 and U.S. Code Title 7, Section 2276 provide for the confidentiality of reported information. All employees of NASS and all enumerators hired and supervised under a cooperative agreement with the National Association of State Departments of Agriculture (NASDA) must read the regulations and sign a statement of compliance
Additionally, NASS and NASS contractors comply with OMB Implementation Guidance, “Implementation Guidance for Title V of the E-Government Act, Confidential Information Protection and Statistical Efficiency Act of 2002 (CIPSEA), (Public Law 107-347). CIPSEA supports NASS’ pledge of confidentiality to all respondents and facilitates the agency’s efforts to reduce burden by supporting statistical activities of collaborative agencies through designation of NASS agents; subject to the limitations and penalties described in CIPSEA. The following CIPSEA Pledge statement will appear on all future NASS questionnaires.
The information you provide will be used for statistical purposes only. In accordance with the Confidential Information Protection provisions of Title V, Subtitle A, Public Law 107–347 and other applicable Federal laws, your responses will be kept confidential and will not be disclosed in identifiable form to anyone other than employees or agents. By law, every employee and agent has taken an oath and is subject to a jail term, a fine, or both if he or she willfully discloses ANY identifiable information about you or your operation.
11. Provide additional justification for any questions of a sensitive nature.
There are no questions of a sensitive nature.
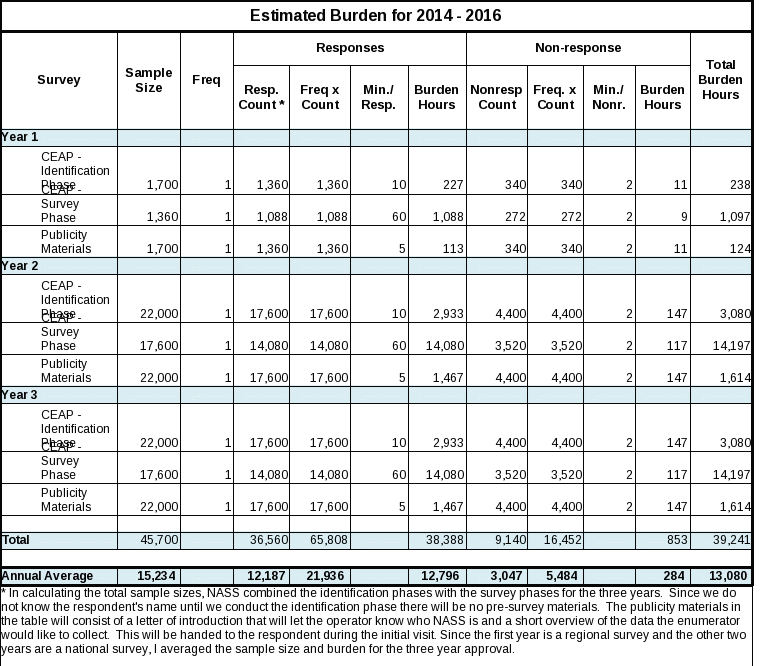
12. Provide estimates of the hour burden of the collection of information. The statement should indicate the number of respondents, frequency of response, annual hour burden, and an explanation of how the burden was estimated. If this request for approval covers more than one form, provide separate hour burden estimates for each form and aggregate the hour burdens in Item 13 of OMB Form 83-I. Provide estimates of annualized cost to respondents for the hour burdens for collections of information, identifying and using appropriate wage rate categories.
Response burden hours are shown in the table below. The projected response rate was based on a targeted response rate of 80%.
Cost to the public of completing the questionnaire is assumed to be comparable to the hourly rate of those requesting the data. The annual, estimated reporting time of 13,080 hours is multiplied by $25 per hour for a total cost to the public of $327,000.
NASS regularly checks the Bureau of Labor Statistics’ Occupational Employment Statistics. Mean wage rates for bookkeepers, farm managers, and farm supervisors are averaged to obtain the wage for the burden cost. The May, 2013 mean wage for bookkeepers is $17.91. The mean wage for farm managers is $35.20. The mean wage for farm supervisors is $22.09. The mean wage of the three is $25.07.
13. Provide an estimate of the total annual cost burden to respondents or record-keepers resulting from the collection of information.
There are no capital/start-up or ongoing operation/maintenance costs associated with this information collection.
14. Provide estimates of annualized cost to the Federal government; provide a description of the method used to estimate cost which should include quantification of hours, operational expenses, and any other expense that would not have been incurred without this collection of information.
The annual estimated cost to Federal government for the CEAP survey is $7,100,000.
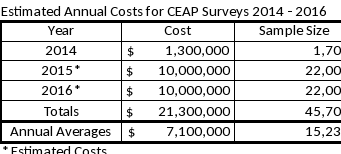
The cost estimates are calculated based on actual costs from surveys conducted in 2011 - 2013 with adjustments for changes in sample sizes, questionnaire interview time, and procedures. Actual costs for items such as Federal and NASDA salaries, data processing, printing, postage, promotion, travel, training, etc. were used to calculate an average cost per unit, per hour, or per sample. Per unit costs were adjusted for inflation and certain fixed costs.
15. Explain the reasons for any program changes or adjustments reported in Items 13 or 14 of the OMB Form 83-I (reasons for changes in burden).
The annual average of 13,080 hours of burden is an increase from the previous 2,251 hours due to a larger sample sizes for the 2015 and 2016 NRI CEAP. The sample increase is a result of the NRI CEAP moving from a regionally based sample to a national sample.
16. For collections of information whose results will be published, outline plans for tabulation and publication. Address any complex analytical techniques that will be used. Provide the time schedule for the entire project, including beginning and ending dates of the collection of information, completion of report, publication dates, and other actions.
There will not be any publications directly from these surveys. Data will be combined with related databases and entered into transport and other physical models. This will be combined with performance reporting data from NRCS to obtain an estimate of the environmental benefit of conservation practices.
Sample selection May
Questionnaire design May - Jul
Materials to field offices Jul
Enumerator Training Aug
Data Collection Aug - Feb
Data entry and edit Sep - Feb
Analysis Oct - Mar
Edited data to NRCS Apr
NRCS Report Fall
Above Tasks repeated Annual
17. If seeking approval to not display the expiration date for OMB approval of the information collection, explain the reasons that display would be inappropriate.
No approval is requested for non-display of the expiration date.
18. Explain each exception to the certification statement identified in Item 19, “Certification for Paperwork Reduction Act Submissions” of OMB Form 83-I.
There are no exceptions to the certification statement.
June, 2014
Revised September, 2014
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| File Title | Supporting Statement |
| Author | brouka |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 2021-01-25 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy